Organic Reactions with Mechanism (Part-1) | Organic Chemistry PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Organic Named Reactions |

|
| Acyloin Condensation |

|
| Mechanisms |

|
| Pinacol Coupling Reactions |

|
| The McMurry Reaction |

|
| The Aldol Reaction |

|
Organic Named Reactions
A name reaction is a chemical reaction named after its discoverers or developers. Among the tens of thousands of organic reactions that are known, hundreds of such reactions are well-known enough to be named after people.
The Organic Reactions discussed in this part are:
- Acyloin Condensation
- Pinacol Coupling Reactions
- The McMurry Reaction
- The Aldol Reaction
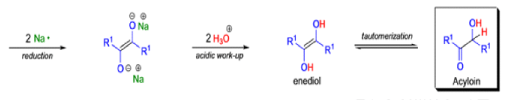
Acyloin Condensation
Acyloin condensation is a reductive coupling of two carboxylic esters using metallic sodium to yield an α-hydroxyketone, also known as an acyloin.
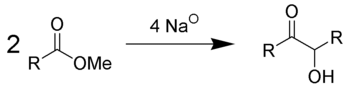
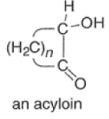
- The acyloin condensation affords acyloins (αhydroxy ketones) by treating aliphatic monoesters or w-diesters with dispersions of sodium or a sodium-potassium alloy in refluxing toluene or xylene.
- The resulting disodium acyloin derivatives are acidified to liberate the corresponding acyloins, which may include valuable synthetic intermediates.
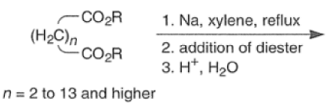
Aliphatic monoesters give symmetrical compounds, while diesters lead to cyclic acyloins. - The intramolecular acyloin condensation is one of the best ways of closing rings of 10 members or higher. For the preparation of aromatic acyloins (R=Ar), the benzoin condensation between two aromatic aldehydes is applied.
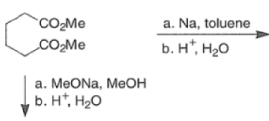
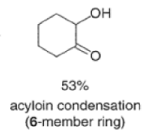
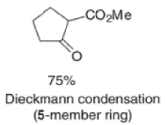
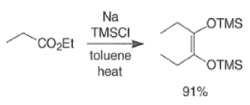
- These side reactions can be minimized by adding trimethylsilyl chloride to the reaction mixture as an alkoxide scavenger.
- This traps the enediolate dianion is a bis- silyl enol ether and traps the sodium or potassium alkoxides, which are catalysts for the Dieckmann ring closure, as neutral silyl ether.
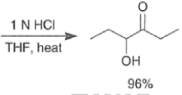
- The resultant bis-siloxy cycloalkenes are either isolated or converted in situ to a-hydroxy ketones by alcoholysis or by acid hydrolysis.
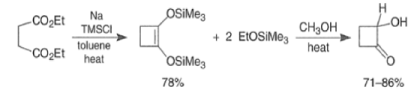
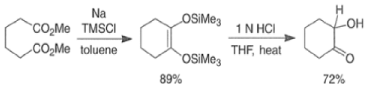
- The acyloin coupling reaction is suitable for the synthesis of medium and large (2-12 membered) carbocyclic systems using the high-dilution technique.
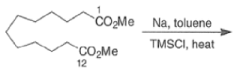
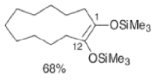
- Intermolecular dimerization of mono-esters via acyloin condensation is a viable tool for the preparation of acyclic, symmetrically substituted α-hydroxy ketone. However, attempted coupling of two different mono-esters usually produces mixtures of products.
- For the intramolecular and intermolecular acyloin ester condensation reaction, the initial step is reductive coupling, electron transfer from Na or K to the diester leads to a di(radica1 anion) species (two ketyl radical anions), which then combine.
- Elimination of alkoxide produces the 1, 2-diketone, which is further reduced to an enediolate by the transfer of two electrons.
- Protonation of the dianion with dilute aqueous acid leads to the enediol, which tautomerizes to the a-hydroxy ketone.
Mechanisms
Mechanism for intramolecular acyloin ester condensation reaction:
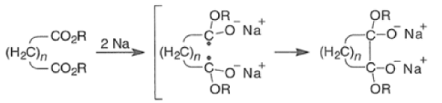
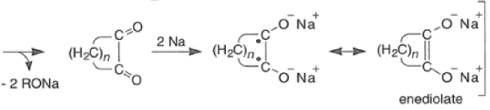
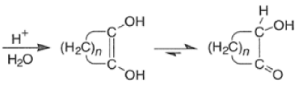
Mechanism for intermolecular acyloin ester condensation reaction:
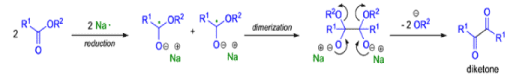
Pinacol Coupling Reactions
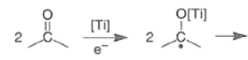
The inter-and intramolecular coupling of two carbonyl groups of aldehydes or ketones in the presence of a low-valent titanium species produces a C-C bond with two adjacent stereocenters, a 1,2-diol (a pinacol).
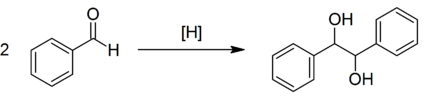
- These may be further elaborated into ketones by the pinacol rearrangement or be deoxygenated to alkenes (McMurry reaction).
- Low-valent titanium metal species [Ti(II), Ti(I), Ti(O)] is generated by reduction of TiCl, with magnesium amalgam or by reduction of TiCl, with either Li, K, Zn-Cu couple, or LiAlH4.
- It involves an initial one-electron transfer from titanium metal to the aldehyde or ketone carbonyl group to produce radical anions (ketyl species), which then dimerize to a Ti-pinacolate. Hydrolysis of the pinacolate generates the vicinal diol.
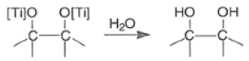
- The following reaction scheme illustrates the intermolecular pinacol coupling of cyclopentanone and conversion of the pinacol to the spirodecanone.”
- When employing low-valent Ti-species, it is important to carry out the coupling at low temperature to avoid deoxygenation of the initially formed 1,2-diol to the corresponding alkene.
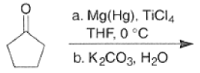
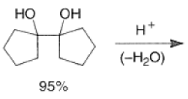
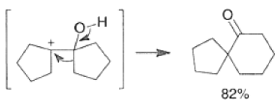
- The titanium-mediated intramolecular pinacol coupling is suitable for the construction of both small-ring and macrocyclic 1,2-diols. Interestingly, the yields of cyclic diols obtained are nearly independent of the ring size.
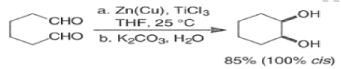
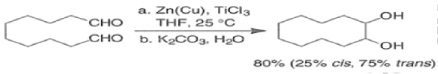
The McMurry Reaction
The McMurry reaction is an organic reaction in which two ketone or aldehyde groups are coupled to form an alkene using a titanium chloride compound such as titanium (III) chloride and a reducing agent. The reaction is named after its co-discoverer, John E. McMurry.
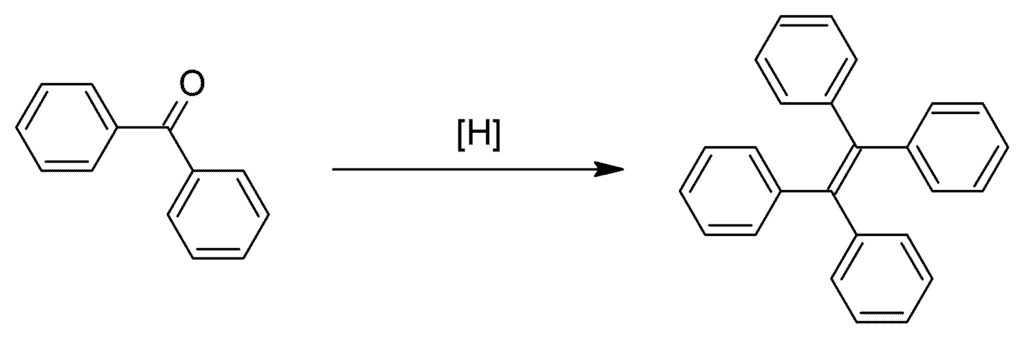 McMurry Reaction of Benzophenone
McMurry Reaction of Benzophenone
The general features of this coupling reaction are:
- It is used most often for the homocoupling of aldehydes and ketones to afford alkenes. However, mixed-coupling is feasible if one component is used in excess or one of the coupling partners is a diaryl ketone.
- The low-valent titanium reducing agent can be prepared in many ways but the most common is the reduction of TiCl3 with a zinc-copper couple (Zn-Cu) in DME.
- If the reaction is conducted at a low temperature, the pinacol intermediate may be isolated.
- At high temperatures, the alkenes are formed directly.
- Sterically hindered and/or strained olefins, which cannot be prepared by other means, are formed in high yield.
- Even sterically hindered tetrasubstituted alkenes can be prepared.
- Macrocyclization under high dilution conditions is successful for the synthesis of medium and large rings and the yields are independent of the ring size unlike in other macrocyclizations (e.g., acyloin condensation).
- Intramolecular reactions are the fastest for the formation of five- and six-membered rings and the formation of eight- or higher-membered rings is considerably slower.
- The reaction conditions do not tolerate the presence of easily reducible functional groups (e.g., epoxides, αhalo ketones, unprotected 1,2-diols; allylic and benzylic alcohols, quinones, halohydrins, aromatic and aliphatic nitro compounds, oximes, and sulfoxides), but most other functional groups are compatible.
- Aldehydes react much faster than ketones so the coupling of two aldehydes in the presence of a ketone can be performed chemoselectively.
- The alkene product is formed with poor stereoselectivity, although there is a slight preference for the formation of (E)-alkenes in intermolecular reactions; and
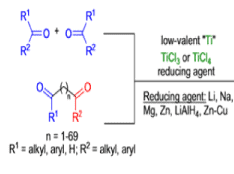
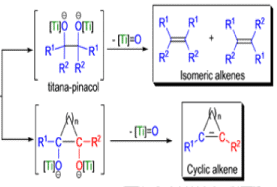
The mechanism of the McMurry coupling is not entirely clear, but it is composed of two distinct steps: 1) pinacol formation and 2) deoxygenation to the alkene.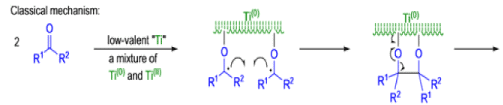
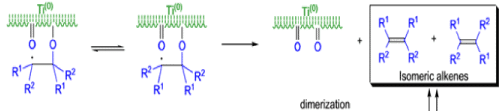
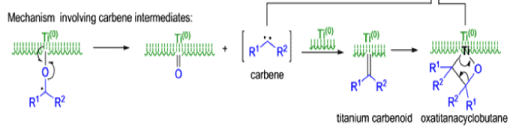
Finely divided Ti(0) metal particles produced by reduction of TiC13, with potassium or Synthesis of Alkene lithium metal or with a zinc-copper couple reductive1 couple aldehydes and ketones at elevated temperature to produce alkenes.

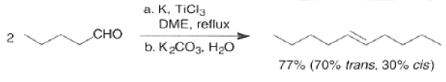
The Aldol Reaction
The aldol reaction is one of the most useful methods for the construction of C—C bonds. The products of aldol reactions are either β-hydroxy carbonyl compounds or, after dehydration, α, β-unsaturated carbonyl compounds.
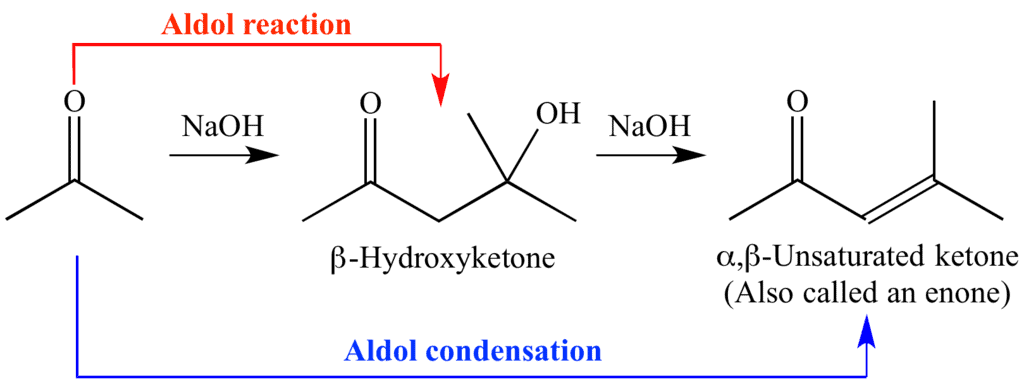
- The aldol reaction is useful not only for making C-C bonds but also for providing two functional groups, the C=O and a β-OH, which can be further elaborated.
- In the strictest sense, the aldol reaction involves the condensation of an enolate derived from an aldehyde or a ketone with another aldehyde or ketone to give α, β-hydroxyaldehyde or α, β-hydroxyketone, respectively.
- In a broader sense, the aldol reaction encompasses reactions of enolates-usually derived from ketones, esters, or amides-with an aldehyde or a ketone
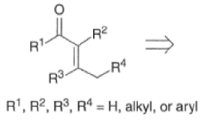
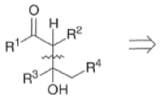
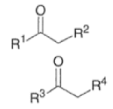
- The aldol reaction is catalyzed by base or by acid. Both base- and acid-catalyzed condensation reactions are reversible in the 1,2-addition step.
- The equilibrium constant for the additional step is usually unfavorable for ketones
Base-catalyzed Aldol Reaction
The base-catalyzed aldol reaction for aldehydes is slightly exothermic while the reaction for ketones is somewhat endothermic
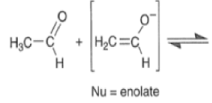
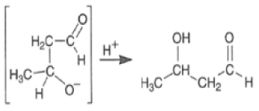
Acid-catalyzed Aldol Reaction
The enol content of simple ketones is quite low under standard acid-catalyzed conditions (for acetone Keq = 10–7; cyclohexanone Keq = 10–6).
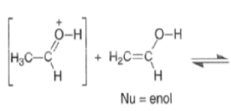
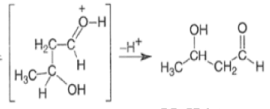
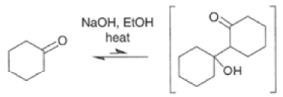
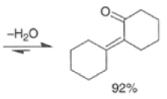
Aldol Condensation
The β-hydroxy aldehydes and β-hydroxy ketones formed in aldol reactions are readily dehydrated to yield conjugated systems. This is called Aldol Condensation.
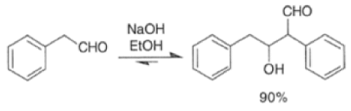
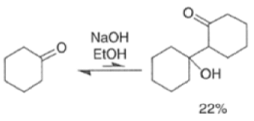
These elimination reactions can be affected by either acid or base while heating during the condensation.
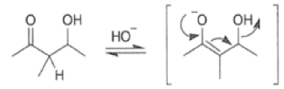
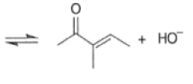
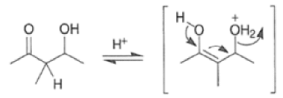
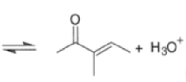
Removal of H2O from the reaction mixture drives the equilibrium toward product formation. Even though the initial aldol step itself may be unfavorable (as it usually is for ketones), the subsequent dehydration step allows most aldol reactions to be carried out in good yield.
|
44 videos|102 docs|52 tests
|
FAQs on Organic Reactions with Mechanism (Part-1) - Organic Chemistry
| 1. What is the mechanism of the Aldol Reaction? |  |
| 2. How does the Acyloin Condensation reaction proceed? |  |
| 3. What is the significance of Pinacol Coupling Reactions in organic chemistry? |  |
| 4. Can you explain the mechanism of the McMurry Reaction? |  |
| 5. How do Organic Named Reactions with mechanisms contribute to the field of organic chemistry? |  |
















