Grade 10 Exam > Grade 10 Notes > Chemistry for Grade 10 > Addition Reactions of Alkenes
Addition Reactions of Alkenes | Chemistry for Grade 10 PDF Download
Hydrogenation
- The chemistry of the alkenes is determined by the C=C functional group
- Since all members of the alkene homologous series contain the same functional group then they all react similarly
- Alkenes mainly undergo addition reactions in which atoms of a simple molecule add across the C=C double bond
- The carbon-carbon double bond opens up, forming a single bond between the carbons allowing for two more atoms to bond, one on each carbon
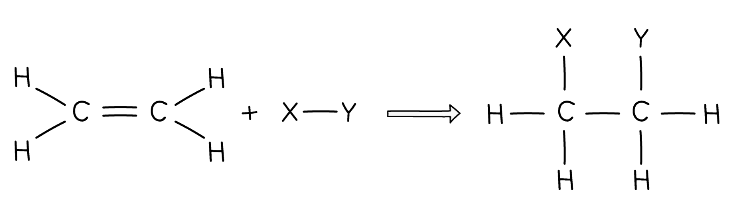 Diagram showing the general equation for the addition reaction of alkenes
Diagram showing the general equation for the addition reaction of alkenes - Hydrogen, water and the halogens can take part in these reactions
Hydrogenation
- Alkenes undergo addition reactions with hydrogen in which an alkane is formed
- These are hydrogenation reactions and occur at 150ºC using a nickel catalyst
- Hydrogenation reactions are used to manufacture margarine from vegetable oils
- Vegetable oils are polyunsaturated molecules which are partially hydrogenated to increase the Mr and turn the oils into solid fats
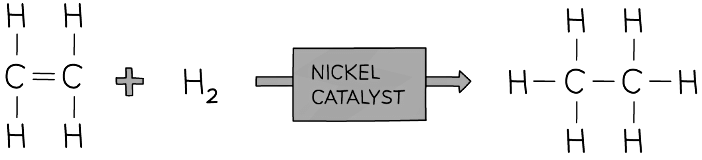 Hydrogen atoms add across the C=C in the hydrogenation of ethene to produce ethane
Hydrogen atoms add across the C=C in the hydrogenation of ethene to produce ethane
Hydration
- Alkenes also undergo addition reactions with steam in which an alcohol is formed. Since water is being added to the molecule it is also called a hydration reaction
- The reaction is very important industrially for the production of alcohols and it occurs using the following conditions:
- Temperature of around 330ºC
- Pressure of 60 – 70 atm
- Concentrated phosphoric acid catalyst
- When the reaction is complete, the reaction chamber holds unreacted ethene, ethanol and water
- The contents are transferred to a condenser where ethene is separated easily as it has a much lower boiling point than ethanol and water:
- Ethanol: 78oC
- Ethene: -103oC
- Water: 100oC
- The ethanol and water are separated afterwards by fractional distillation
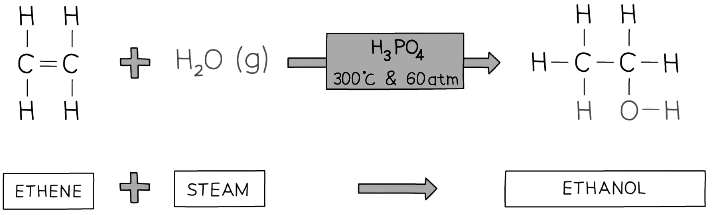 A water molecule adds across the C=C in the hydration of ethene to produce ethanol
A water molecule adds across the C=C in the hydration of ethene to produce ethanol
Halogenation
- The halogens also participate in addition reactions with alkenes
- The same process works for any halogen and any alkene in which the halogen atoms always add to the carbon atoms involved in the C=C double bond
- The reaction occurs readily at room temperature
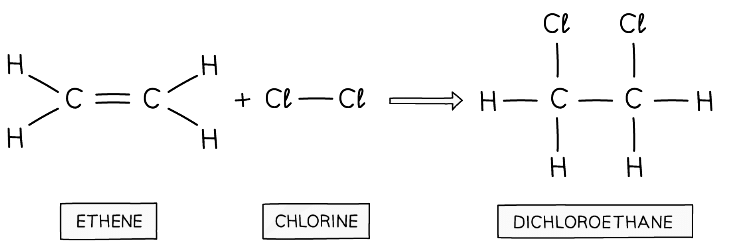 Chlorine atoms add across the C=C in the addition reaction of ethene and chlorine
Chlorine atoms add across the C=C in the addition reaction of ethene and chlorine
Exam Tip
Since members of the same homologous series react similarly, we can deduce the reactions of other compounds of the same series based on observations of how just one member of the series reacts.
The document Addition Reactions of Alkenes | Chemistry for Grade 10 is a part of the Grade 10 Course Chemistry for Grade 10.
All you need of Grade 10 at this link: Grade 10
|
75 videos|131 docs|24 tests
|
Related Searches




















