Agriculture - 1 Class 4 Worksheet SST
Q1: Fill in the blanks.
(i) Dry farming is done where rainfall is less than ______ and there are no facilities of irrigation.
Ans: 20 inches Dry farming, also called Dryland Farming, is the cultivation of crops without irrigation in regions of limited moisture, typically less than 20 inches (50 centimetres) of precipitation annually.
Dry farming, also called Dryland Farming, is the cultivation of crops without irrigation in regions of limited moisture, typically less than 20 inches (50 centimetres) of precipitation annually.
(ii) Agriculture provide ______ of the employment in the country.
Ans: opportunities
Agriculture provides employment opportunities for rural people on a large scale in underdeveloped and developing countries.
(iii) Land is the major ______ asset of the country.
Ans: fixed
Land is among the most important natural resources.
(iv) Agriculture means cultivation of _________. It also includes horticulture, livestock rearing and fishing.
Ans: crops Agriculture is the practice of cultivating crops and raising animals for various purposes, including food production. Horticulture involves the cultivation of fruits, vegetables, and ornamental plants. Livestock rearing is the raising of animals like cattle, goats, and poultry for their products like meat, milk, and eggs. Fishing involves catching fish and other aquatic organisms for consumption.
Agriculture is the practice of cultivating crops and raising animals for various purposes, including food production. Horticulture involves the cultivation of fruits, vegetables, and ornamental plants. Livestock rearing is the raising of animals like cattle, goats, and poultry for their products like meat, milk, and eggs. Fishing involves catching fish and other aquatic organisms for consumption.
(v) Agriculture provide _____________ for people and ___________ for industries.
Ans: food, raw materials
Agriculture is the primary source of food production, providing a variety of crops and livestock products for human consumption. Additionally, it supplies raw materials like cotton, sugarcane, and oilseeds to industries, which use them to manufacture various products such as textiles, sugar, and cooking oil.
(vi) More than half of Indians are farmers. This makes agriculture the main ___________ in our country.
Ans: occupation
In India, a significant portion of the population is engaged in agriculture, making it the primary occupation for many people. Farmers cultivate crops and rear livestock to support themselves and provide food for the nation.
(vii) India has a favourable climate, fertile soil and good irrigation facilities to grow many _______________.
Ans: crops
India's diverse geography and climate conditions allow for the cultivation of a wide range of crops. Fertile soil, adequate rainfall, and irrigation facilities contribute to the country's agricultural productivity.
(viii) The crops grown are of two types _____________ and ______________.
Ans: food crops and cash crops
Food crops are grown primarily for consumption and include staples like rice, wheat, and pulses. Cash crops are grown for sale in the market and include crops like sugarcane, cotton, and jute.
(ix) The crops which are grown to be eaten are called ________________ crops example rice, wheat.
Ans: food crops
Food crops are cultivated primarily for direct human consumption. Examples include grains like rice and wheat, which are staples in many diets worldwide.
(x) The crops which are grown to be used in industries or for sale in the market are called _____________ crops eg sugarcane, jute.
Ans: cash crops Cash crops are cultivated primarily for their economic value. They are sold in the market or used in industries to produce various products. Sugarcane, for instance, is used to make sugar and ethanol.
Cash crops are cultivated primarily for their economic value. They are sold in the market or used in industries to produce various products. Sugarcane, for instance, is used to make sugar and ethanol.
(xi) Our total agricultural production has increased since _______________.
Ans: recent years
This statement suggests that agricultural production in India has been on the rise in recent years. This increase could be due to factors such as improved farming practices, better technology, and increased use of fertilizers.
(xii) Jaggery is made from _____________________________.
Ans: sugarcane juice Jaggery is a traditional, unrefined sugar product made by boiling sugarcane juice. It is widely used in Indian cuisine as a sweetener.
Jaggery is a traditional, unrefined sugar product made by boiling sugarcane juice. It is widely used in Indian cuisine as a sweetener.
(xiii) _______________ is the main producer of wheat and sugarcane.
Ans: Punjab
Punjab, a state in northern India, is known for its high wheat and sugarcane production. The region's fertile soil and favorable climate make it suitable for these crops.
(xiv) The cultivation of fruits, flowers and vegetables is called ________________
Ans: horticulture
Horticulture is a branch of agriculture that focuses on the cultivation of fruits, vegetables, nuts, seeds, herbs, sprouts, mushrooms, algae, seaweeds, non-food crops such as grass and ornamental trees and plants.
(xv) Wheat is a ________________ crop.
Ans: Rabi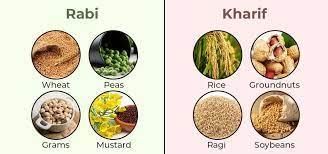 Wheat is a Rabi crop, which means it is sown in the winter season (usually from October to December) and harvested in the spring (usually from April to June). Rabi crops depend on winter rainfall and are an essential part of India's crop cycle.
Wheat is a Rabi crop, which means it is sown in the winter season (usually from October to December) and harvested in the spring (usually from April to June). Rabi crops depend on winter rainfall and are an essential part of India's crop cycle.
Q2: True or False.
(i) The quality of Indian cotton is the best in the world.
Ans: True
India is famous for its finest and beautiful cotton fabrics. Punjab, Haryana, Gujarat, and Rajasthan are the important cotton cultivating regions.
(ii) Sugar cane is the native plant of India.
Ans: True
Sugarcane is a tropical grass native to Asia where it has been grown for over 4,000 years. Sugar cane is the most produced food commodity in India followed by rice and wheat.
(iii) Rabi crop is sown after the rainy season stops.
Ans: False
The rabi crops are sown around mid-November, preferably after the monsoon rains are over, and harvesting begins in April / May.
Q3: Complete the Sentences.
(i) Fibre crops are ______.
Ans: plants that are deliberately grown for the production of fiber for textile.
(ii) Wet farming is done where rainfall is ______.
Ans: more than 200cm. Wet Farming is practiced in the regions of alluvial soils where every year the average rainfall is more than 200cm.
(iii) India has stepped up the production of ______.
Ans: rice.
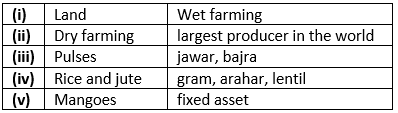
Q4: Match the following.
Ans:
Q5: Answer Briefly.
(i) What are the major crops grown in India?
Ans: A variety of food and non food crops are grown in different parts of the country depending upon the variations in soil, climate and cultivation practices. Major crops grown in India are rice, wheat, millets, pulses, tea, coffee, sugarcane, oil seeds, cotton and jute, etc.
(ii) Name any four reasons which decide the nature of farming?
Ans: Reasons which decide the nature of farming:
- availability of irrigation facility
- use of hyv seeds
- use of manure and fertilizers
- use of protective medicines weedicides and insecticides
(iii) What are the major types of farming?
Ans: Types of farming include subsistence farming, terrace farming, dry farming, mixed farming, nomadic herding, commercial plantation, livestock rearing, etc. Farming involves rearing animals and growing crops for raw materials and food.
|
33 videos|264 docs|50 tests
|
FAQs on Agriculture - 1 Class 4 Worksheet SST
| 1. What is agriculture? |  |
| 2. How does agriculture contribute to the economy? |  |
| 3. What are the different types of farming methods? |  |
| 4. How can sustainable agricultural practices be implemented? |  |
| 5. What are the challenges faced by farmers in modern agriculture? |  |
















