RPSC RAS (Rajasthan) Exam > RPSC RAS (Rajasthan) Notes > Course for RPSC RAS Preparation > Ahar-Banas Culture
Ahar-Banas Culture | Course for RPSC RAS Preparation - RPSC RAS (Rajasthan) PDF Download
Ahar-Banas Culture of Rajasthan
A number of Chalcolithic cultures have been discovered in northern, central and western India. These included:
- The Ochre-Coloured Pottery (OCP) culture in the Punjab, Haryana, north-east Rajasthan and upper Ganga-Yamuna doab.
- The Narhan culture and its variants in the northern Vindhyas and the middle and lower Ganga valley.
- The Ahar culture in the Mewar region of Rajasthan.
- The Kayatha and Malwa cultures in the Malwa region of western Madhya Pradesh.
- The Jorwe culture in western Maharashtra
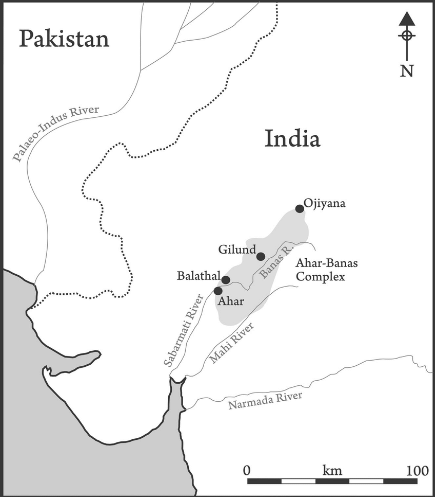
Ahar-Banas Culture
- The Ahar culture, also known as the Banas culture, is a Chalcolithic Culture of southeastern Rajasthan, lasting from 3000 to 1500 BCE, contemporary and adjacent to the Indus Valley Civilization.
- The main distribution of this culture seems to be concentrated in the river valleys of Banas and its tributaries namely Berach and Ahar.
- More than 90 sites of the culture have been identified till date, out of which, Gilund, Ahar, Ojiyana and Balathal are prominent sites. These sites of Ahar culture provide important information about the transformation of life from hunting-gathering to agriculture in the Mewar region.
Features of Ahar-Banas Culture
- Houses:
- People lived in single, double & multi-roomed rectangular, square or circular houses.
- The houses were made of stones, mud bricks, the walls being plastered with mud.
- Pottery:
- Typical Ahar pottery is a Black-and-Red ware (BRW) with linear and dotted designs painted on it in white pigment and has limited range of shapes, which include bowls, bowls-on-stands, elongated vases and globular vases.
- Economy & Subsistence:
- The subsistence of Ahar-Banas people was based on cultivation, animal rearing and hunting. They sustained on a number of crops, including wheat and barley.
- The people of Ahar culture had trade links with the Harappans.
- Technology:
- The technology of Ahar people was mostly based on copper. They exploited the copper ores of the Aravalli Range to make axes and other artefacts.
- However, the Neolithic trend of using polished stone tools continued in this period also and microlithic tools of silicious material were also very common.
Important Sites of Ahar-Banas Culture
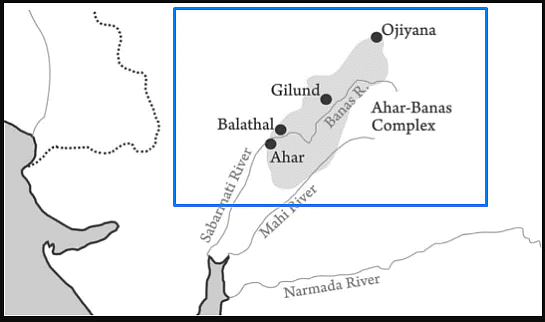
- Gilund
- Ahar
- Ojiyana
- Balathal
- Pachamta (Because, Excavation done in 2015)
The document Ahar-Banas Culture | Course for RPSC RAS Preparation - RPSC RAS (Rajasthan) is a part of the RPSC RAS (Rajasthan) Course Course for RPSC RAS Preparation.
All you need of RPSC RAS (Rajasthan) at this link: RPSC RAS (Rajasthan)
FAQs on Ahar-Banas Culture - Course for RPSC RAS Preparation - RPSC RAS (Rajasthan)
| 1. What is the significance of Ahar-Banas Culture in Punjab? |  |
Ans. The Ahar-Banas Culture refers to an archaeological culture that existed in the region of Punjab, particularly in the Ahar and Banas rivers. This culture is significant as it provides insights into the early human settlements, their lifestyle, agriculture practices, and artistic expressions during the Neolithic period in Punjab.
| 2. What are the main characteristics of the Ahar-Banas Culture? |  |
Ans. The Ahar-Banas Culture is characterized by the presence of distinctive pottery, including red and black pottery with intricate designs. The culture also showcases the use of copper tools, evidence of agriculture practices, and the presence of burial sites indicating a belief in an afterlife. Additionally, the culture exhibits artistic expressions through various artifacts like terracotta figurines and beads.
| 3. How does the Ahar-Banas Culture contribute to our understanding of ancient Punjab? |  |
Ans. The Ahar-Banas Culture provides valuable insights into the ancient history of Punjab. Through the study of artifacts, pottery, and burial sites, archaeologists can understand the social, economic, and religious aspects of the people living during that time. It helps in reconstructing their lifestyle, agricultural practices, and artistic expressions. Additionally, the culture aids in establishing the timeline and sequence of human settlements in Punjab.
| 4. Are there any similarities between the Ahar-Banas Culture and other ancient cultures in the Indian subcontinent? |  |
Ans. Yes, there are similarities between the Ahar-Banas Culture and other ancient cultures in the Indian subcontinent. The presence of red and black pottery, use of copper tools, and agricultural practices are common features found in various contemporary cultures like the Indus Valley Civilization and the Chalcolithic cultures of Rajasthan and Gujarat. These similarities suggest cultural exchanges and interactions between different regions during that period.
| 5. What are the challenges faced by archaeologists in studying the Ahar-Banas Culture? |  |
Ans. Archaeologists studying the Ahar-Banas Culture face several challenges. The excavation sites may have been disturbed over time due to urbanization, agriculture, or natural factors, making it difficult to obtain a complete understanding of the culture. Additionally, the lack of written records from that period requires archaeologists to rely solely on artifacts and physical evidence. Preservation of delicate artifacts and proper documentation are also significant challenges in studying this ancient culture.
Related Searches
















