Air Pollution - People, Development and Environment Notes
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction to Air Pollution |

|
| Air Pollution and its Impacts |

|
| Types of Air Pollutants |

|
| Government Initiatives to Control Air Pollution |

|
| Methods to Control Air Pollution |

|
Introduction to Air Pollution
Air pollution refers to the presence of harmful substances in the atmosphere, which pose risks to human health, the environment, and the planet's climate.

- These substances, known as pollutants, can be in the form of gases, particulate matter, or biological molecules.
- When pollutants exceed their natural concentration levels, they lead to various adverse effects, including respiratory diseases, environmental degradation, and global warming.
Air Pollution and its Impacts
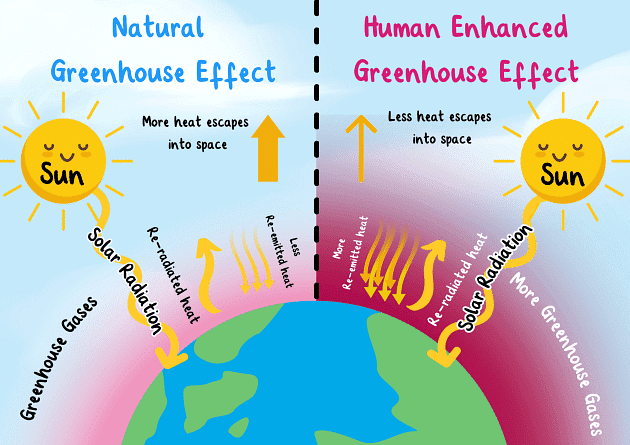
Greenhouse Gases (GHGs) and Air Pollution
Greenhouse gases like carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), and nitrous oxide (N2O) contribute to global warming, which affects climatic patterns, increasing temperatures, and severe weather events.
Composition of Earth's Atmosphere
- Nitrogen (78.08%) - Not a GHG
- Oxygen (20.95%) - Not a GHG
- Water vapor (0-4%) - Yes, a GHG
- Argon (0.93%) - Not a GHG
- Carbon Dioxide (0.039%) - Yes, a GHG
- Neon (0.0018%) - Not a GHG
- Helium (0.0005%) - Not a GHG
- Methane (0.00017%) - Yes, a GHG
- Hydrogen (0.00005%) - Not a GHG
- Nitrous Oxide (0.00003%) - Yes, a GHG
- Ozone (0.000004%) - Yes, a GHG
World Health Organization Definition of Air Pollution
Air pollution is the presence of harmful materials in the air that exceed threshold concentration levels, affecting living beings. It includes primary and secondary pollutants.
Types of Air Pollutants
1. Primary Pollutants: Directly enter the atmosphere from sources.
- Suspended particulate matter (SPM)
- Oxides of carbon
- Hydrocarbons (Methane)
- Sulfur oxides (SOx)
- Nitrogen oxides (NOx)
- Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs)
- Lead
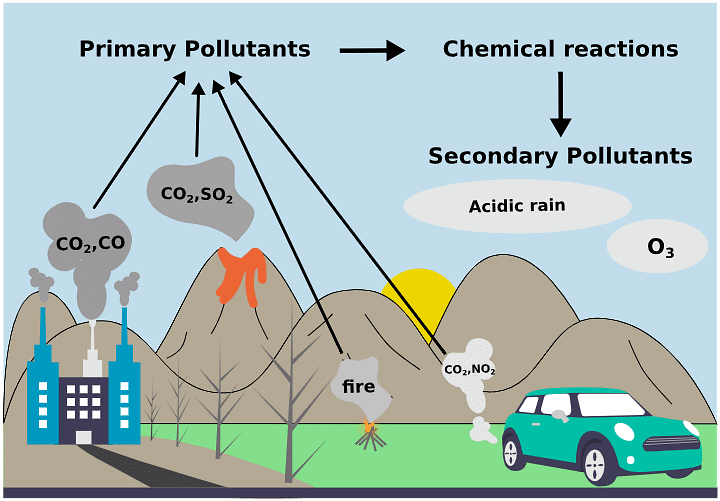
2. Secondary Pollutants: Formed through chemical reactions between primary pollutants and atmospheric constituents.
- Sulfur trioxide (forms sulfuric acid with water)
- Smog (combination of smoke and fog)
- Sulfurous or London smog: Caused by sulfur dioxide, prevalent in winter mornings.
- Photochemical or Los Angeles smog: Formed from nitrogen oxides and sunlight, prevalent on warm sunny days.
- Ground-level ozone: Formed from reactions between VOCs and NOx.
- Acid rain: Caused by sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxides reacting with water and oxygen.
Impact of Global Warming
- Warmer Arctic regions
- Shifts in climatic patterns
- Increased rainfall and flash floods
- Soil moisture loss and decreased agricultural productivity
- Melting glaciers and higher sea levels
- More intense storms and extreme weather events
- Increased rainfall in low regions
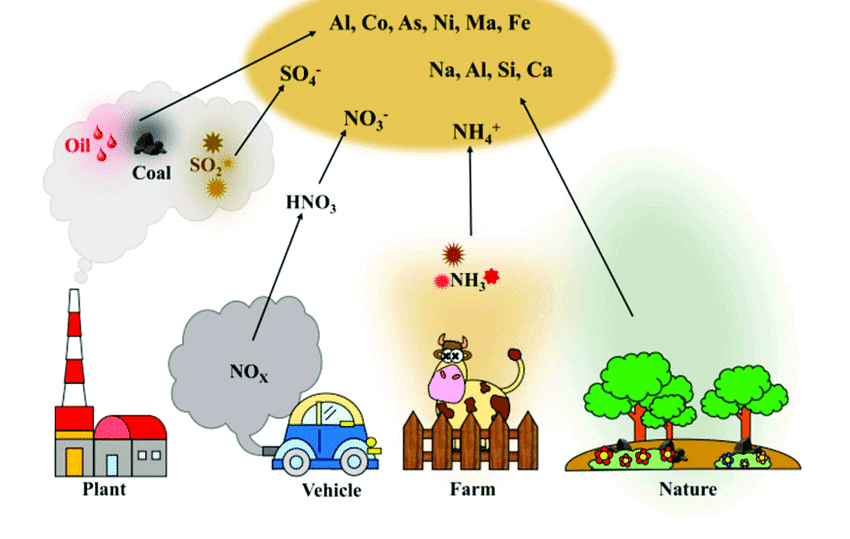
Major Air Pollution-Related Chemical Substances

- Ozone (Ground level): Lung issues, asthma, bronchitis
- Lead: Affects central nervous system, RBC development
- Sulfur dioxide: Respiratory problems, reduces gas exchange in lungs
- Nitrogen oxides: Heart, lung issues, bronchitis, asthma, carcinogenic
- Carbon monoxide: Reduces oxygen-carrying capacity of blood
- Hydrogen sulfide: Nausea, eye, throat irritation
- Hydrogen cyanide: Headache, nerve dysfunction
- Ammonia: Water body acidification
- Phosgene: Pulmonary edema
- Volatile organic compounds: Smog formation
- Arsenic: Damages red blood cells, kidneys, causes jaundice
- SPM: Respiratory issues, asthma, chronic bronchitis
Government Initiatives to Control Air Pollution
National Air Quality Monitoring Programme (NAMP)
- Monitors ambient air quality
- National Air Quality Index (NAQI) categories: Good, Satisfactory, Moderately polluted, Poor, Very Poor, Severe
National Ambient Air Quality Standards
- Standards for 12 pollutants including PM10, PM2.5, NO2, SO2, CO, Ozone, Ammonia, Lead, Arsenic, Nickel, Benzene, Benzopyrene
- Measures include use of cleaner fuels, emission norms, and conversion to CNG.
System of Air Quality and Weather Forecasting (SAFAR)
- Provides real-time air quality information and forecasts
4. Bharat Stage Norms
- Emission standards for vehicles to reduce pollution.
- BS-VI norms to be implemented by 2020, reducing particulate matter and sulfur content in fuel.
Methods to Control Air Pollution
Gaseous Pollutants
 Gaseous Pollutants
Gaseous Pollutants
Combustion:
- Description: Combustion involves burning organic pollutants, converting them into less harmful substances such as carbon dioxide and water vapor.
- Process: This method is commonly used in thermal oxidizers where high temperatures are maintained to ensure complete combustion of pollutants.
- Applications: It is widely used in industries where organic vapors are emitted, such as in chemical manufacturing and petrochemical plants.
Absorption:
- Description: Absorption is a process where gaseous pollutants are removed by passing them through absorbent liquids.
- Process: The gas stream is brought into contact with a liquid that can dissolve the pollutant. Common absorbents include water and chemical solutions like sodium hydroxide.
- Applications: Used in scrubbing systems for removing sulfur dioxide, ammonia, and other soluble gases from industrial emissions.
Adsorption:
- Description: In adsorption, pollutants stick to the surface of solid absorbents.
- Process: Pollutants adhere to the surface of materials like activated carbon, which has a high surface area and porosity.
- Applications: Effective for controlling volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and other gas-phase pollutants in industries such as pharmaceuticals and food processing.
Particulate Pollutants
 Particulate Pollutants
Particulate Pollutants
Fabric Filters:
- Description: Fabric filters trap particles in a porous fabric material.
- Process: As the polluted air passes through the fabric, particles are captured on the fibers. The clean air then exits, leaving the particles behind.
- Applications: Commonly used in baghouses in industries like cement, steel, and power generation.
Mechanical Devices:
- Description: Mechanical devices use gravity or momentum to separate particles from the air stream.
- Types:
- Cyclones: Use centrifugal force to remove larger particles.
- Settling Chambers: Allow particles to settle out of the air stream due to gravity.
- Applications: Often used in pre-cleaning stages in industries with high dust loads such as mining and milling.
Electrostatic Precipitators:
- Description: Electrostatic precipitators use electric charges to collect particles from emissions.
- Process: Polluted air is passed through a chamber where particles are electrically charged. These charged particles are then attracted to and collected on oppositely charged plates.
- Applications: Widely used in power plants and industrial facilities that burn fossil fuels.
Other Measures
Use of Cleaner Fuels and Biogas: Cleaner fuels, such as natural gas and biogas, produce fewer pollutants compared to coal and oil.
Transitioning to cleaner fuels in transportation, heating, and power generation reduces air pollution significantly.Pooling of Transport or Public Transport: Reducing the number of vehicles on the road by promoting carpooling and public transportation.
Implementing policies and infrastructure to support public transportation and carpooling, such as dedicated bus lanes and carpool incentives.Regular Vehicle Maintenance: Ensuring that vehicles are well-maintained to operate efficiently and emit fewer pollutants.
Installation of Pollution Control Devices in Industries: Equipping industrial facilities with devices that reduce emissions.
Air pollution poses significant risks to health and the environment. Effective control measures, government initiatives, and awareness are crucial in mitigating its impacts
|
25 videos|40 docs|10 tests
|
FAQs on Air Pollution - People, Development and Environment Notes
| 1. What are the common types of air pollutants? |  |
| 2. How does air pollution impact human health? |  |
| 3. What are some government initiatives to control air pollution? |  |
| 4. What are some effective methods to control air pollution? |  |
| 5. How does air pollution impact the environment? |  |















