Akhirah | Religion, Philosophy & Ethics for GCSE/IGCSE - Year 11 PDF Download
Life After Death (Akhirah)
- All Muslims hold a belief in Akhirah, which forms an integral part of both the six Articles of Faith and the five Roots of Usul ad-Din.
- Muslims believe that Allah possesses the knowledge and authority to decide the time of each person’s death.
- Death does not signify the end of existence.
- Through Allah’s power and mercy, an afterlife is made possible for all.
- A person’s destination in the afterlife depends on the choices they make during their earthly life, making this life a preparation for what comes next.
- Life on Earth serves as a test, with individuals judged based on their actions.
- Humans are endowed with free will, enabling them to choose their beliefs and how they interact with others.
- Muslims believe that individuals are responsible for their deeds, and after death, angels will question them about their faith in the grave.
- The angels Munkar and Nakir will interrogate each soul, assessing their faith.
- Akhirah is a central theme in the Qur’an, with roughly one-fourth of its content addressing this subject.
‘O tranquil soul, come back to your Lord, pleased and pleasing to Him. Join My devoted servants and enter My paradise’ (Qur’an, 89:27-30).

Day of Judgement
- The Angel Israfil will signal the Day of Judgement by sounding a trumpet.
- For those who pass away before this day, Muslims believe the angel of death, Azrail, will retrieve their souls to await the final trumpet in a state known as barzakh.
- Numerous signs will herald the world’s end for Muslims, with the most significant being the arrival of the Mahdi and the return of Isa (Jesus).
- Other indicators include frequent earthquakes, widespread violence, rejection of Islamic principles, and increases in deceit, intoxication, immorality, immodesty, and illicit behavior.
- On the Day of Judgement, the deceased will rise from their graves, and everyone will stand before Allah to be judged based on their earthly conduct.
- Each person will receive a book detailing their deeds. If their good actions outweigh the bad, they will receive the book in their right hand and enter heaven. If it is given in their left hand, they will be among the condemned.
Human Responsibility & Accountability
- While many Muslims believe in Al-Qadr (divine predestination), they also hold that humans have the freedom to make choices in their lives.
- The Qur’an contains numerous warnings about the Day of Judgement, prompting Muslims to reflect: Am I prepared for death? What steps have I taken for that day?
- Thus, individuals bear responsibility for their actions and are accountable for any wrongs they commit.
- On the Day of Judgement, the Book of Deeds, which records ‘every small and great thing’ (Qur’an 54:52), will be reviewed.
- After judgment, individuals will face eternal reward or punishment based on their actions.
- Muslims believe that Akhirah:
- Demonstrates Allah’s justice, compensating for earthly hardships with rewards in paradise.
- Ensures that wrongdoers face consequences for their actions.
- Offers hope for the future, easing the burden of life’s challenges.
- Encourages Muslims to adhere to Allah’s commandments, such as observing the Five Pillars and avoiding harm to others.
- Provides meaning to humanity’s brief existence on earth and clarifies the purpose of life.
Resurrection in Islam
- On the Day of Judgement, the world will transform into a new realm (Akhirah), where all who have lived will be resurrected and judged.
- Muslims believe that, prior to entering heaven or hell, a soul resides in barzakh while the body decomposes in the grave.
- In the grave, the soul faces questioning by Munkar and Nakir, who ask: Who is your Lord? What is your faith? Who is your prophet?
- The soul’s experience in barzakh will be pleasant or unpleasant based on their answers, foreshadowing their afterlife.
- This state persists until Allah ends the world, reuniting souls with their resurrected bodies on the Day of Resurrection.
- The Qur’an teaches that resurrection involves both body and soul, not necessarily as the same physical form but as a physical and spiritual existence.
- Allah will determine each resurrected person’s final destination on the Day of Judgement.
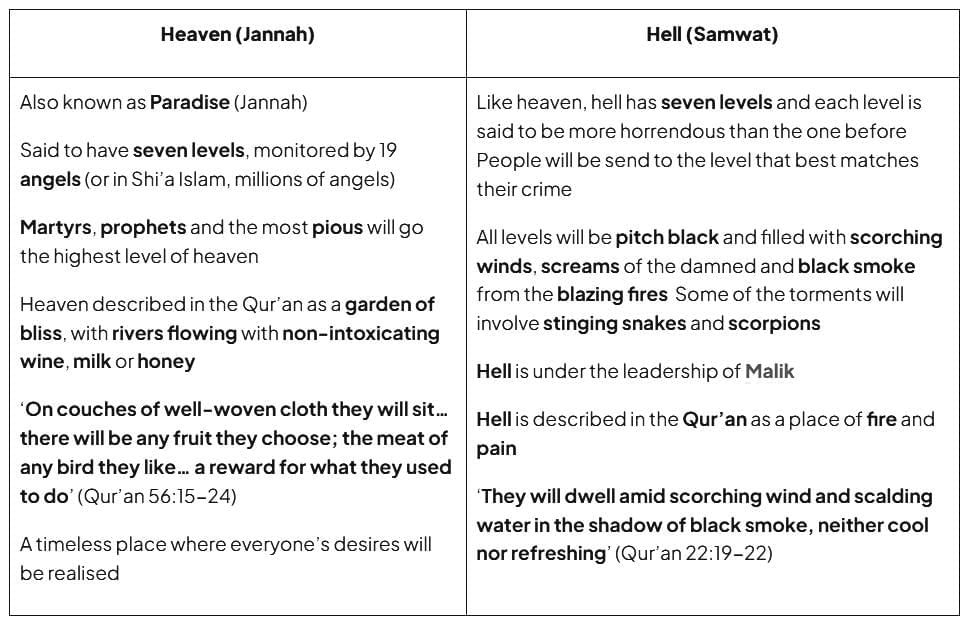
Heaven and Hell in Islam
- Muslims believe that after the Day of Judgement, individuals will spend eternity in either heaven or hell.
- Following judgment, righteous and faithful Muslims will cross the narrow As-Sirat bridge to reach heaven.
- The wicked, condemned by Allah, will fail to cross the bridge and fall into hell.
- Righteous Muslims will enter heaven, while non-Muslims and unrighteous Muslims will be sent to hell.
- Allah evaluates both actions and intentions (niyyah) when judging individuals.
- While interpretations of heaven and hell vary among Muslims, the Qur’an provides vivid descriptions of both.
The document Akhirah | Religion, Philosophy & Ethics for GCSE/IGCSE - Year 11 is a part of the Year 11 Course Religion, Philosophy & Ethics for GCSE/IGCSE.
All you need of Year 11 at this link: Year 11
|
172 docs|3 tests
|
FAQs on Akhirah - Religion, Philosophy & Ethics for GCSE/IGCSE - Year 11
| 1. What is the concept of Akhirah in Islam? |  |
Ans. Akhirah, or the Afterlife, is a fundamental belief in Islam that refers to life after death. It signifies the eternal existence that follows this life, where individuals are held accountable for their actions on Earth. Muslims believe that Akhirah encompasses the Day of Judgment, where everyone will be resurrected and judged by Allah based on their deeds, leading them to either Paradise (Heaven) or Hell.
| 2. How does resurrection work in Islamic belief? |  |
Ans. In Islamic belief, resurrection occurs on the Day of Judgment when all humans will be brought back to life from their graves. This event is known as Yawm al-Qiyamah. Each person's deeds will be weighed, and they will be judged accordingly. The Quran describes this resurrection as a powerful event where all are summoned before Allah, and their eternal fate is determined based on their faith and actions during their lifetime.
| 3. What are the descriptions of Heaven and Hell in Islam? |  |
Ans. Heaven (Jannah) in Islam is depicted as a place of eternal bliss, filled with gardens, rivers, and comforts that surpass human imagination. It is reserved for those who have lived righteously and fulfilled their obligations to Allah. Hell (Jahannam), on the other hand, is described as a place of punishment and suffering for those who rejected faith and committed grave sins. It is characterized by fire, darkness, and torment, serving as a warning for the consequences of one’s actions.
| 4. What role do good deeds play in the journey to Akhirah? |  |
Ans. Good deeds play a crucial role in an individual's journey to Akhirah. In Islam, it is believed that the quality and quantity of one's actions in this life directly influence their standing on the Day of Judgment. Performing acts of worship, helping others, and fulfilling moral obligations are seen as essential for gaining Allah's mercy and favor, ultimately leading to a favorable judgment and entrance into Paradise.
| 5. How do the concepts of Heaven and Hell reflect on a Muslim's daily life? |  |
Ans. The concepts of Heaven and Hell significantly influence a Muslim's daily life by instilling a sense of accountability and moral responsibility. Belief in Akhirah encourages individuals to lead a life in accordance with Islamic teachings, strive for righteousness, and avoid sinful behavior. This belief promotes ethical conduct, compassion, and community service, as Muslims seek to attain Allah's pleasure and secure a place in Jannah while avoiding Jahannam.
Related Searches















