Amino Acid Structure | Biology and Biochemistry for MCAT PDF Download
What is the General Molecular Structure of an Amino Acid?
Amino acids are organic compounds that combine to form proteins. The general formula of an amino acid is R-CH(NH2)-COOH.
Amino acids are known to contain amine and carboxyl functional groups. They also contain a side chain that is made up of an R-group (where ‘R’ can denote any alkyl or aryl group). These R-groups are what differentiate amino acids and are responsible for their unique properties.
Structure of Amino Acid
The general structure of an amino acid is illustrated below.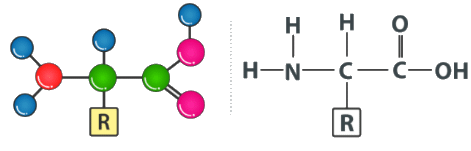
From the illustration, it can be noted that the key elements that make up amino acids are hydrogen, carbon, nitrogen, and oxygen. However, it is not uncommon for other elements to be found in the side chain of an amino acid. It can also be noted that there are over 500 naturally occurring amino acids known to us. Of these, only 20 amino acids are known to appear in genetic code.
In the human body, these biomolecules are involved in many biological and chemical functions and are important ingredients for human growth and development. Amino acids usually have a melting and boiling point that is very high. They usually exist in the form of white, crystalline, stable compounds. A few amino acids are known to be sweet, tasteless, and bitter in flavour. Most amino acids are water soluble. However, it can also be noted that most amino acids are insoluble in organic solvents.
Some Common Amino Acids and Their Structures
The structures of some common amino acids, such as glycine, serine, leucine, cysteine, and valine have been illustrated below.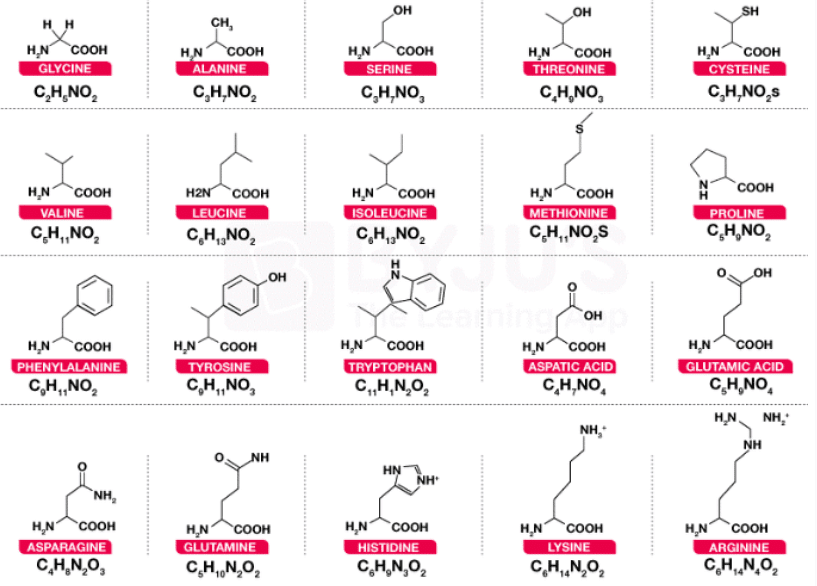
Glycine
- Glycine is an amino acid that contains, in its side chain, only a single hydrogen atom. It is known to be the simplest amino acid with the chemical formula NH2-CH2-COOH (because carbamic acid is known to be unstable).
- Glycine is known to be a protein-genic amino acid. Glycine, due to its compact shape, is integral to the formation of alpha-helices in the secondary protein structure. For the same explanation, in collagen triple-helices, it is the most abundant amino acid. It is important to note that glycine is an inhibitory neurotransmitter.
- Because of uninhibited muscle contraction, interference with its release inside the spinal cord, such as in clostridium tetani infections for example, can trigger spastic paralysis.
Serine
- Serine is an alpha-amino acid which is often used in protein biosynthesis. It comprises an alpha-amino group which, under biological conditions, is in the protonated -NH3+ form. It also contains a carboxyl group which, under biological conditions, is in the deprotonated -COO– form.
- Serine is also known to contain a side chain consisting of a hydroxymethyl group and can, therefore, be classified as a polar amino acid. Under normal physiological conditions, it can be synthesised in the human body, rendering it a nonessential amino acid.
Leucine
- Leucine is an important amino acid which is used in protein biosynthesis. Leucine is an alpha-amino acid, which implies that it contains an alpha-amino group (which, under biological conditions, is in the protonated -NH3+ form), an alpha-carboxylic acid group (which, under biological conditions, is in the deprotonated -COO– form), and a side chain isobutyl group, making it a non-polar aliphatic amino acid.
- In human beings, it is an essential amino acid, implying that it can not be synthesised by the body. It must, therefore, be derived from the diet. The foods that produce protein, such as dairy products, meats, beans, soy products, and other legumes are human dietary sources of this amino acid.
Cysteine
- Cysteine is a proteinogenic amino acid which is generally categorized as a semi-essential amino acid. Since it functions as a nucleophile, the thiol side chain in this amino acid also participates in several enzymatic reactions. The disulfide derivative cystine, which is known to play an essential structural role in a large number of proteins, is known to be susceptible to oxidation by thiol.
- Cysteine has the general same structure as serine, but with one of its oxygen atoms substituted by sulphur. Selenocysteine can be obtained by replacing the same oxygen atom with selenium instead of sulfur.
- Cysteine, along with its oxidised dimeric form, cystine, like other common amino acids, can be found in most high-protein foods. While it is listed as a non-essential amino acid, cysteine can be essential in some rare cases the elderly, for children, and people with certain metabolic disorders or those who have syndromes of malabsorption.
- Under normal physiological conditions, cysteine is normally synthesised by the human body as long as an adequate quantity of methionine is available in it.
Valine
- Valine is an important amino acid which is used in protein biosynthesis. Valine is an alpha-amino acid, which implies that it contains an alpha-amino group (which, under biological conditions, is in the protonated -NH3+ form), an alpha-carboxylic acid group (which, under biological conditions, is in the deprotonated -COO– form), and a side chain containing the isopropyl group. It can, therefore, be referred to as a non-polar aliphatic amino acid.
Most Basic Amino Acid
- There are three amino acids that have basic side chains at neutral pH. These are arginine (Arg), lysine (Lys), and histidine (His). Their side chains contain nitrogen and resemble ammonia, which is a base.
- Lysine has two amine groups, which makes it overall basic. It is the lone pair of nitrogen, in amines, which gives them basicity.
|
129 videos|60 docs|24 tests
|
FAQs on Amino Acid Structure - Biology and Biochemistry for MCAT
| 1. What is the general molecular structure of an amino acid? |  |
| 2. How many different amino acids are there? |  |
| 3. How are amino acids linked together to form proteins? |  |
| 4. What is the significance of the side chain in an amino acid? |  |
| 5. Why are amino acids important for human health? |  |
















