Grade 10 Exam > Grade 10 Notes > Chemistry for Grade 10 > Amount of Substance & Gas Volume
Amount of Substance & Gas Volume | Chemistry for Grade 10 PDF Download
Calculating Gas Volumes
Higher Tier OnlyAvogadro's Law
- Avogadro’s Law states that at the same conditions of temperature and pressure, equal amounts of gases occupy the same volume of space
- At room temperature and pressure, the volume occupied by one mole of any gas was found to be 24 dm3 or 24,000 cm3
- This is known as the molar gas volume at RTP
- RTP stands for “room temperature and pressure” and the conditions are 20ºC and 1 atmosphere (atm)
- From the molar gas volume the following formula triangle can be derived:
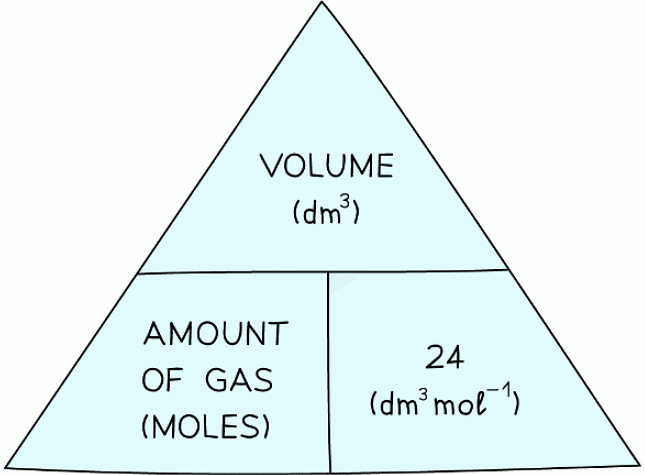 Formula triangle showing the relationship between moles of gas, volume in dm3 and the molar volume
Formula triangle showing the relationship between moles of gas, volume in dm3 and the molar volume - If the volume is given in cm3 instead of dm3, then divide by 24,000 instead of 24:
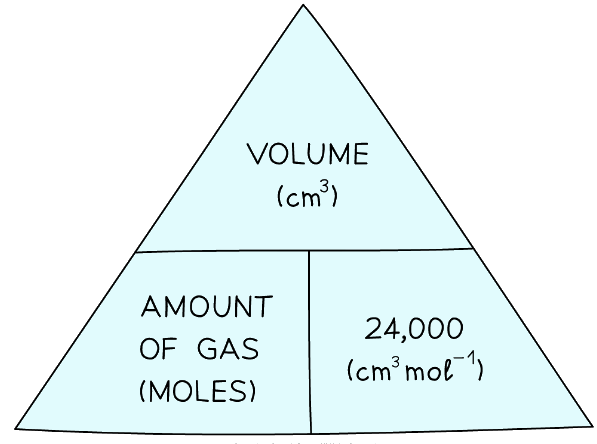 Formula triangle showing the relationship between moles of gas, volume in cm3 and the molar volume
Formula triangle showing the relationship between moles of gas, volume in cm3 and the molar volume
- The formula can be used to calculate the number of moles of gases from a given volume or vice versa
- Simply cover the one you want and the triangle tells you what to do
To find the volume
Volume = Moles x Molar Volume
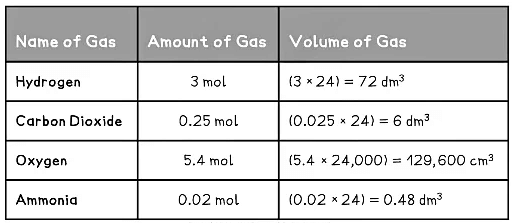
Examples of Converting Moles into Volumes Table
To find the moles
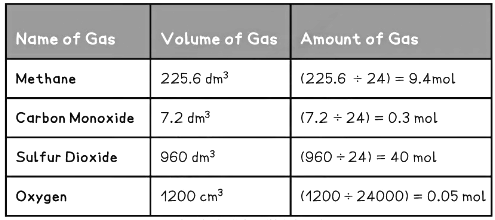
Moles = Volume ÷ Molar Volume
Examples of Converting Volumes into Moles Table
Calculations Involving Reacting Gases
- You may be asked to calculate the volume of a gas from a given amount stated in grams instead of moles
- To answer these type of questions you must first convert grams to moles and then calculate the volume.
Solved Examples
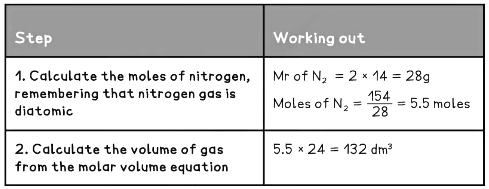
Example 1: What is the volume of 154 g of nitrogen gas at RTP?
- A second style of gas calculation involves calculating the volumes of gaseous reactants and products from a balanced equation and a given volume of a gaseous reactant or product
- These problems are straightforward as you are applying Avogadro's Law, so the moles ( and coefficients) in equations are in the same ratio as the gas volumes
Example 2: The complete combustion of propane gives carbon dioxide and water vapour as the products
C3H8 (g) + 5O2 (g) → 3CO2 (g) + 4H2O (g)
Determine the volume of oxygen needed to react with 150 cm3 of propane and the total volume of the gaseous products
- The balanced equation shows that 5 moles of oxygen are needed to completely react with 1 mole of propane
- Therefore the volume of oxygen needed would be = 5 moles x 150 cm3 = 750 cm3
- The total number of moles of gaseous products is = 3 + 4 = 7 moles
- The total volume of gaseous products would be = 7 moles x 150 cm3 = 1050 cm3
Exam Tip
Make sure you use the correct units as asked by the question when working through reacting gas volume questions.
The document Amount of Substance & Gas Volume | Chemistry for Grade 10 is a part of the Grade 10 Course Chemistry for Grade 10.
All you need of Grade 10 at this link: Grade 10
|
82 videos|200 docs|26 tests
|
Related Searches