Analysis of a Transistor Amplifier Circuit Using H-Parameters | Analog and Digital Electronics - Electrical Engineering (EE) PDF Download
ANALYSIS OF A TRANSISTOR AMPLIFIER USING H-PARAMETERS:
To form a transistor amplifier it is only necessary to connect an external load and signal source as indicated in fig. 1 and to bias the transistor properly.
Consider the two-port network of CE amplifier. RS is the source resistance and ZL is the load impedance. The h-parameters are assumed to be constant over the operating range. The ac equivalent circuit is shown in fig. 2. (Phasor notations are used assuming sinusoidal voltage input). The quantities of interest are the current gain, input impedance, voltage gain, and output impedance.
Current gain:
For the transistor amplifier stage, Ai is defined as the ratio of output to input currents.
1.3.2 Input impedance:
The impedance looking into the amplifier input terminals ( 1,1' ) is the input impedance Zi
Voltage gain:
The ratio of output voltage to input voltage gives the gain of the transistors.
Output Admittance:
It is defined as
Av is the voltage gain for an ideal voltage source (Rv = 0).
Consider input source to be a current source IS in parallel with a resistance RS as shown in fig. 3.
In this case, overall current gain AIS is defined as
h-parameters:
To analyze multistage amplifier the h-parameters of the transistor used are obtained from manufacturer data sheet. The manufacturer data sheet usually provides h-parameter in CE configuration. These parameters may be converted into CC and CB values. For example fig. 4 hrc in terms of CE parameter can be obtained as follows.
Fig. 4
For CE transistor configuaration
Vbe = hie Ib + hre Vce
Ic = hfe Ib + hoe Vce
The circuit can be redrawn like CC transistor configuration as shown in fig. 5.
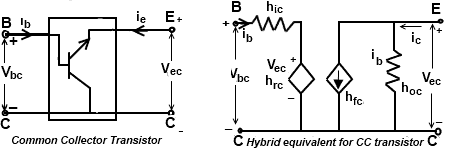
Vbc = hie Ib + hrc Vec
Ic = hfe Ib + hoe Vec
Hybrid model for transistor in three different configurations
Typical h-parameter values for a transistor:
Analysis of a Transistor amplifier circuit using h-parameters
A transistor amplifier can be constructed by connecting an external load and signal source and biasing the transistor properly.
The two port network of Fig. 1.4 represents a transistor in any one of its configuration. It is assumed that h-parameters remain constant over the operating range.The input is sinusoidal and I1,V1,I2 and V2 are phase quantities.
Fig. 1.5 Transistor replaced by its Hybrid Model
Current Gain or Current Amplification (Ai)
For transistor amplifier, the current gain Ai is defined as the ratio of output current to input current,i.e,
Ai =IL /I1 = -I2 / I1
From the circuit of Fig 1.5
I2= hf I1 + hoV2
Substituting V2 = ILZL = -I2ZL
I2= hf I1- I2ZL ho
I2 + I2ZL ho = hf I1
I2( 1+ ZL ho) = hf I1
Ai = -I2 / I1 = - hf / ( 1+ ZL ho)
Therefore,
Ai = - hf / ( 1+ ZL ho)
Input Impedance (Zi)
In the circuit of Fig 1.5, RS is the signal source resistance .The impedance seen when looking into the amplifier terminals (1,1’) is the amplifier input impedance Zi,
Zi = V1/I1
From the input circuit of Fig V1 = hi I1 + hrV2
Zi = ( hi I1 + hrV2) / I1
= hi + hr V2 / I1
Substituting
V2 = -I2 ZL = A1I1ZL
Zi = hi + hr A1I1ZL / I1
= hi + hr A1ZL
Substituting for Ai
Zi = hi - hf hr ZL / (1+ hoZL)
= hi - hf hr ZL / ZL(1/ZL+ ho)
Taking the Load admittance as YL =1/ ZL
Zi = hi - hf hr / (YL + ho)
Voltage Gain or Voltage Gain Amplification Factor(Av)
The ratio of output voltage V2 to input voltage V1 give the voltage gain of the transistor i.e,
Av = V2 / V1
Substituting
V2 = -I2 ZL = A1I1ZL
Av = A1I1ZL / V1 = AiZL / Zi
Output Admittance (Yo)
Yo is obtained by setting VS to zero, ZL to infinity and by driving the output terminals from a generator V2. If the current is I2 then Yo= I2/V2 with VS=0 and RL= ∞.
From the circuit of fig 1.5
I2= hf I1 + hoV2
Dividing by V2,
I2 / V2 = hf I1/V2 + ho
With V2= 0, by KVL in input circuit,
RSI1 + hi I1 + hrV2 = 0
(RS + hi) I1 + hrV2 = 0
Hence, I2 / V2 = -hr / (RS + hi)
= hf (-hr/( RS + hi)+ho
Yo= ho- hf hr/( RS + hi)
The output admittance is a function of source resistance. If the source impedance is resistive then Yo is real.
Voltage Amplification Factor(Avs) is taking into account the resistance (Rs) of the source.
Fig. 5.6 Thevenin’s Equivalent Input Circuit
This overall voltage gain Avs is given by
Avs = V2 / VS = V2V1 / V1VS = Av V1/ VS
From the equivalent input circuit using Thevenin’s equivalent for the source shown in Fig. 5.6,
V1 = VS Zi / (Zi + RS)
V1 / VS = Zi / ( Zi + RS)
Then, Avs = Av Zi / ( Zi + RS)
Substituting Av = AiZL / Zi
Avs = AiZL / ( Zi + RS)
Avs = AiZL RS / ( Zi + RS) RS
Avs = AisZL / RS
Current Amplification (Ais) taking into account the source Resistance(RS)
Fig. 1.7 Norton’s Equivalent Input Circuit
The modified input circuit using Norton’s equivalent circuit for the calculation of Ais is shown in Fig. 1.7
Overall Current Gain, Ais = -I2 / IS = - I2I1 /I1 IS = Ai I1/IS
From Fig. 1.7 I1= IS RS / (RS + Zi)
I1 / IS = RS / (RS + Zi)
and hence, Ais = Ai RS / (RS + Zi)
Operating Power Gain (AP)
The operating power gain AP of the transistor is defined as
AP = P2 / P1 = -V2 I2 / V1 I1 = AvAi = Ai AiZL/ Zi
AP = Ai2(ZL/ Zi)
Small Signal analysis of a transistor amplifier
Simplified common emitter hybrid model:
In most practical cases it is appropriate to obtain approximate values of A V , A i etc rather than calculating exact values. How the circuit can be modified without greatly reducing the accuracy. Fig. 4 shows the CE amplifier equivalent circuit in terms of h-parameters Since 1 / hoe in parallel with RL is approximately equal to RL if 1 / hoe >> RL then hoe may be neglected. Under these conditions,
Ic = hfe IB .
hre Vc = hre Ic RL = hre hfe Ib RL .
Fig. 4
Since hfe.hre = 0.01(approximately), this voltage may be neglected in comparison with hie Ib drop across hie provided RL is not very large. If load resistance RL is small than hoe and hre can be neglected.
Output impedance seems to be infinite. When Vs = 0, and an external voltage is applied at the output we find Ib = 0, I C = 0. True value depends upon RS and lies between 40 K and 80K.
On the same lines, the calculations for CC and CB can be done.
CE amplifier with an emitter resistor:
The voltage gain of a CE stage depends upon hfe. This transistor parameter depends upon temperature, ageing and the operating point. Moreover, hfe may vary widely from device to device, even for same type of transistor. To stabilize voltage gain AV of each stage, it should be independent of hfe. A simple and effective way is to connect an emitter resistor Re as shown in fig. 5. The resistor provides negative feedback and provide stabilization.
An approximate analysis of the circuit can be made using the simplified model
Subject to above approximation A V is completely stable. The output resistance is infinite for the approximate model
Comparison of Transistor Amplifier Configuration
The characteristics of three configurations are summarized in Table. Here the quantities Ai, Av, Ri, Ro and AP are calculated for a typical transistor whose h-parameters are given in table .The values of RL and Rs are taken as 3KΩ.
Table: Performance schedule of three transistor configurations.
The values of current gain, voltage gain, input impedance and output impedance calculated as a function of load and source impedances.
Characteristics of Common Base Amplifier
- Current gain is less than unity and its magnitude decreases with the increase of load resistance RL,
- Voltage gain AV is high for normal values of RL,
- The input resistance Ri is the lowest of all the three configurations, and
- The output resistance Ro is the highest of all the three configurations.
Applications: The CB amplifier is not commonly used for amplification purpose. It is used for
- Matching a very low impedance source
- As a non inverting amplifier to voltage gain exceeding unity.
- For driving a high impedance load.
- As a constant current source.
Characteristics of Common Collector Amplifier
- For low RL (< 10 kΩ), the current gain Ai is high and almost equal to that of a CE amplifier.
- The voltage gain AV is less than unity.
- The input resistance is the highest of all the three configurations.
- The output resistance is the lowest of all the three configurations.
Applications: The CC amplifier is widely used as a buffer stage between a high impedance source and a low impedance load.
Characteristics of Common Emitter Amplifier
- The current gain Ai is high for RL < 10 kΩ.
- The voltage gain is high for normal values of load resistance RL.
- The input resistance Ri is medium.
- The output resistance Ro is moderately high.
Applications: CE amplifier is widely used for amplification.
|
135 videos|181 docs|71 tests
|
FAQs on Analysis of a Transistor Amplifier Circuit Using H-Parameters - Analog and Digital Electronics - Electrical Engineering (EE)
| 1. What are H-parameters in transistor amplifier circuits? |  |
| 2. How do H-parameters differ from other transistor parameters like hFE or β? |  |
| 3. How are H-parameters calculated in a transistor amplifier circuit? |  |
| 4. Why are H-parameters important in transistor amplifier design? |  |
| 5. Can H-parameters be used to analyze different types of transistor amplifier circuits? |  |

















