Annuity | Quantitative Aptitude for CA Foundation PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Definition |

|
| Types of Annuities |

|
| Ordinary Annuity Or Annuity Regular |

|
| Annuity immediate/Due |

|
Definition
An annuity is a series of payments, typically uniform in amount, disbursed at regular intervals. Examples include monthly rent, premiums for life insurance policies, deposits into a recurring bank account, consistent monthly payments received by a retired government servant as a pension, and installment payments for loans related to houses or automobiles.
Some terms related with annuities
- Periodic Payment: The individual payment size within an annuity is referred to as the periodic payment of the annuity.
- Annual Rent: The collective sum of all payments made in one year within an annuity is termed its annual rent.
- Payment Period/Interval: The time span between two consecutive payments of an annuity is known as the payment period (or payment interval) of the annuity.
- Term: The overall duration from the commencement of the first payment period to the conclusion of the last payment period is denoted as the term of the annuity.
- Amount of an Annuity: The comprehensive value of all payments at the maturity time of an annuity is defined as the amount (or future value) of the annuity.
- Present Value of an Annuity: The sum of the present values of all payments within an annuity is termed the present value or capital value of the annuity.
Types of Annuities
- Ordinary Annuity: An annuity in which payments are made at the end of the payment interval is referred to as an Ordinary Annuity or Regular Annuity.
- Annuity Due: An annuity in which payments are made at the beginning of the payment interval is known as an Annuity Due or Annuity Immediate.
- Perpetuity: A perpetuity is an annuity characterized by payments that continue indefinitely.
Note: In the upcoming discussion, it is assumed that the payment interval aligns with the interest period, unless stated otherwise.
Ordinary Annuity Or Annuity Regular
Definition: Annuity payments occur at the conclusion of the payment interval.
Type I
(TO Find Amount)
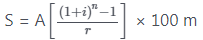
Where S = Amount of an Annuity
A = Value of each instalment
r = rate of interest
m = No. of conversion periods in a year
n = m.t = No. of instalments made in t yrs.
 = Rate of interest of one conversion Period
= Rate of interest of one conversion Period
Calculator Trick
Step -1 Find (1 + i)n by calculator i.e. Type r ÷ 100 m + 1 Then push × button then push = button (n – 1) times.
Step-II Then – 1
Step – III ÷ r × 100m
Step – IV Then × A push = button (We get the required value of Amount)
Example 1: Find the future value of an annuity of ₹ 500 is made annually for 7 years at interest rate of 14% compounded annually. [Given that (1.14)7 = 2.5023]
(a) ₹ 5365.25
(b) ₹ 5265.25
(c) ₹ 5465.25
(d) none
Ans: (a)
Calculator Trick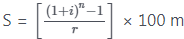 = ₹ 5365.25
= ₹ 5365.25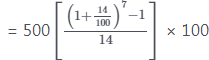 = ₹ 5365.25
= ₹ 5365.25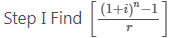
As Type 14 ÷ 100 + 1 × Push = button 6 times.
Step – II Type – 1 ÷ 14 then × 100 (Because it is annually)
Step – III Then × 500 = (we get the result)
Example 2: ₹ 200 is invested at the end of each month in an account paying interest 6% per year compounded monthly. What is the future value of this annuity after 10th payment? Given that (1,005)10=1.0511
(a) ₹ 2544
(b) ₹ 2144
(c) ₹ 2544
(d) None
Ans: (a)
Here A = 200 ; r = 6% compounded monthly
n = 10 = No. of payments.
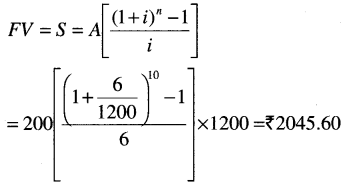
Calculator Trick
Step-1 Type 6 ÷ 1200 + 1 Then push × button then push = button 9 times.
Step-II Type – 1 Then ÷ 6 × 1200
Step-III Then Type × 200 = buttons we get the required amount.
Note: If (1 + i)n value is given in the question then use given value in the question otherwise answer may vary.
Type – II
To find the Value of Each Instalment
Example 3: If a bank pays 6% interest compounded quarterly what equal deposit have to be made at the end of the each quarter for 3 years if you want to have ₹ 1500 at the end of 3 years?
(a) ₹ 117.86
(b) ₹ 115.01
(c) ₹ 150.50
(d) None of these
Ans: (b)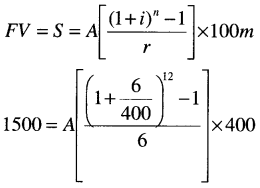
A = ₹ 150.01
Calculator Trick
Step-I Type 6 ÷ 400 + 1 Then push × button then push = buttons 11 times
Step-II Then push – 1 ÷ 6 × 400 buttons
Step-III Then push M + button to save the typed value.
Step-IV Then type 1500 then ÷ button then push “MRC” button 2 times then push = button.
[we get the required result]
Type-III
(To find Present Value for Ordinary Annuity)
PV = Present value = 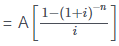
Calculator Trick
Step-I Type (1 + i) value then push= button
Step-II Then push = buttons “n” times
Step-III Push GT button
Step-IV Then type × A (value) then push = button
we get the required result.
Example 4: Find the present value of an annuity which pays 200 at the end of each 3 months for 10 years assuming money to be worth 5% converted quarterly?
(a) ₹ 3473.86
(b) ₹ 3108.60
(c) ₹ 6265.38
(d) None of these
Ans: (c)
Here A = 200 ; m = 4 ; r = 5% 1/4 yrly.
t = 10 years ⇒ n = mt = 4 × 10 = 40 year PV=?
Calculator Trick
Step-I Type 5 + 400 + 1 then push + button
Step-II Then push = buttons 40 times
Step-III Then Push GT button
Step-IV Then typex 200 = buttons [We get the resulting value]
Type-IV
(To find instalment value if PV is given).
Example 5: Mr. A borrows 5,00,000 to buy a house.
If he pays equal instalments for 20 years and 10% interest on outstanding balance what will be the equal annual instalment?
(a) ₹ 58239.84
(b) ₹ 58729.84
(c) ₹ 68729.84
(d) None of these
Ans: (b)
Here PV = ₹ 5,00,000 ; r = 10% yrly.
t = 20 years
n = 20; A = ?
5,00,000 = 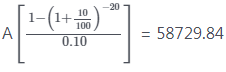
Calculator Trick
Step-I Type 10+ 100 + 1 then push + button
Step-II Push = buttons 20 times
Step-III Then Push GT button
Step-IV Then M+ buttons to save the result.
Step-V Type 5,00,000 then push + button then MRC button 2 time and then = button.
(We get the required result)
Annuity immediate/Due
Definition: An annuity due is an annuity the first payment of which is made at the beginning of the first payment interval
Type – V
(T0 find Amount)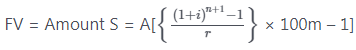
Calculator Trick (work as ordinary annuity)
Step-I Type r ÷ 100 m + 1 then pushx button
Step-II Push = buttons n + 1 – 1 = n times then push -1 button then push button then push r value then push × 100m value buttons.
Step-III Push -1 button then × button and then type A value & then push = button (we get the required result)
|
116 videos|164 docs|98 tests
|
FAQs on Annuity - Quantitative Aptitude for CA Foundation
| 1. What is an ordinary annuity or annuity regular? |  |
| 2. What is an annuity immediate? |  |
| 3. What is an annuity due? |  |
| 4. What is the difference between an ordinary annuity and an annuity due? |  |
| 5. How are annuities typically used? |  |
|
116 videos|164 docs|98 tests
|

|
Explore Courses for CA Foundation exam
|

|

















