Class 10 Exam > Class 10 Notes > Mathematics for GCSE/IGCSE > Applications of Trigonometry
Applications of Trigonometry | Mathematics for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 PDF Download
Applications of Trigonometry
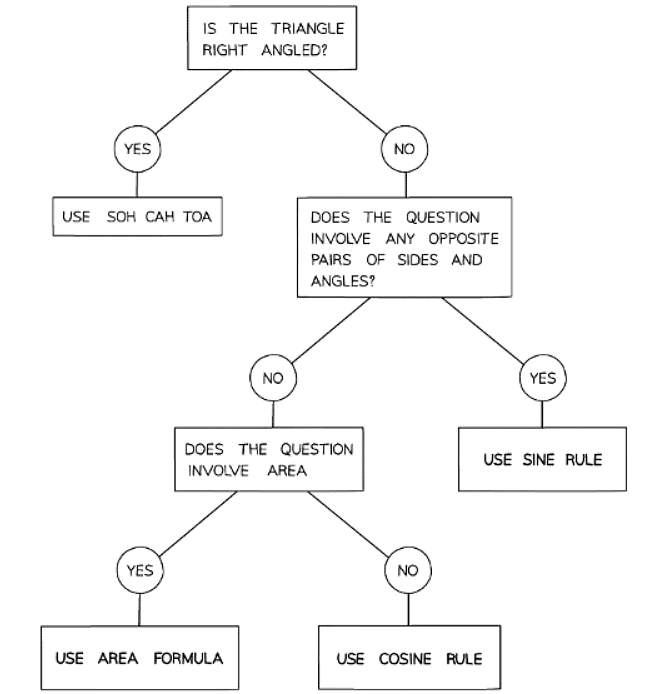
Choosing which rule or formula to use
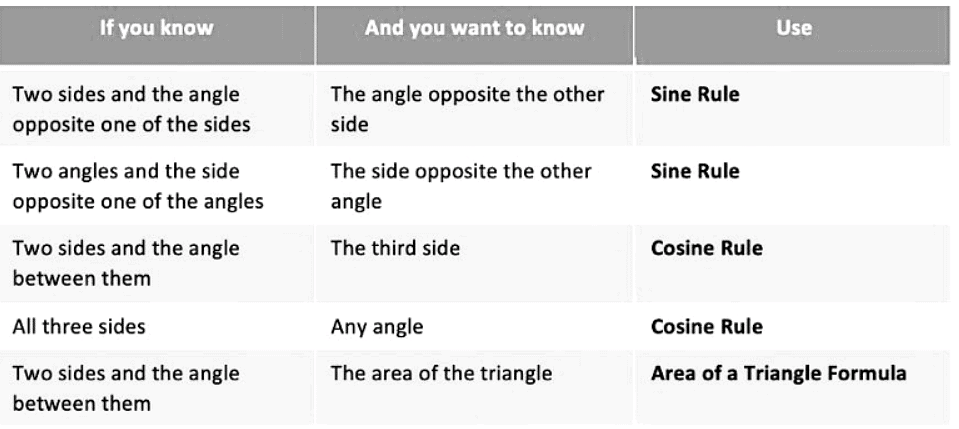
- It is crucial to determine the appropriate Rule or Formula to solve a problem. The following table outlines the options:
- It is essential to make informed decisions regarding Rule or Formula selection when addressing problems.
Using the cosine rules to find angles
- The Cosine Rule can be manipulated to determine:
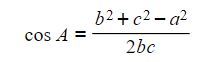
- When using the inverse cosine function (i.e. cos-1) we can use this to find the size of angle A:
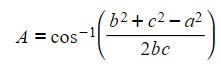
- Make sure you can do this rearrangement, or remember this form of the formula
Using the sine rule to find angles
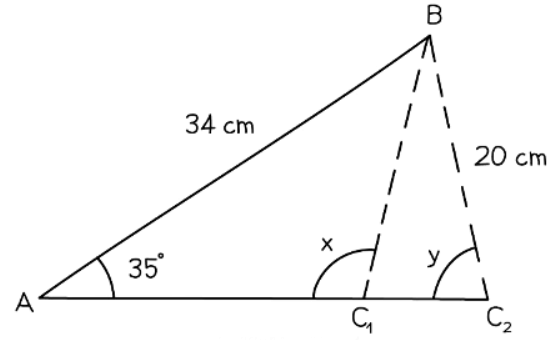
- When only the lengths of sides AB, BC, and the measure of angle BAC are known, there could be two potential triangles.
- One triangle could have side BC1 with an angle 𝑥x measuring 102.8 degrees, while the other triangle could have side BC2 with an angle y measuring 77.2 degrees.
- Utilizing a calculator and the Sine Rule would only yield the possibility corresponding to angle y.
- To find the alternative angle, you might need to subtract your obtained angle from 180 degrees.
Question for Applications of TrigonometryTry yourself: Using which rule or formula can we find the size of angle A?View Solution
The document Applications of Trigonometry | Mathematics for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 is a part of the Class 10 Course Mathematics for GCSE/IGCSE.
All you need of Class 10 at this link: Class 10
|
42 videos|395 docs|19 tests
|
FAQs on Applications of Trigonometry - Mathematics for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10
| 1. How is trigonometry used in real life applications? |  |
Ans. Trigonometry is used in various real-life applications such as architecture, engineering, physics, and navigation. It helps in calculating distances, angles, heights, and other measurements in these fields.
| 2. Can you give an example of how trigonometry is applied in architecture? |  |
Ans. In architecture, trigonometry is used to calculate the height of buildings, the slope of roofs, and the angles of support beams. It helps architects design structures that are stable and aesthetically pleasing.
| 3. How is trigonometry helpful in physics? |  |
Ans. In physics, trigonometry is used to analyze the motion of objects, calculate forces, and predict the behavior of waves. It is essential for understanding concepts such as projectile motion, oscillations, and wave interference.
| 4. What is the significance of trigonometry in engineering? |  |
Ans. Trigonometry is crucial in engineering for designing structures, analyzing forces, and solving problems related to mechanics. Engineers use trigonometric functions to model and predict the behavior of materials and systems.
| 5. How does trigonometry play a role in navigation and GPS systems? |  |
Ans. Trigonometry is essential for determining the position, speed, and direction of vehicles and ships in navigation. GPS systems rely on trigonometric calculations to pinpoint locations accurately and provide navigation instructions to users.
Related Searches















