Area of Parallelogram | Mathematics (Maths) Class 7 PDF Download
Area of Parallelogram
The area of a parallelogram is defined as the region or space covered by a parallelogram in a two-dimensional plane. A parallelogram is a special kind of quadrilateral. If a quadrilateral has two pairs of parallel opposite sides, then it is called a parallelogram. Rectangle, square, and rhombus are all examples of a parallelogram. Geometry is all about shapes, 2D or 3D. All of these shapes have a different set of properties with different formulas for area. The prime focus here will be entirely on the following:
- Definition of the area of a parallelogram
- Formula of the area of a parallelogram
- Calculation of a parallelogram's area in vector form
What Is the Area of Parallelogram?
The area of a parallelogram refers to the total number of unit squares that can fit into it and it is measured in square units (like cm2, m2, in2, etc). It is the region enclosed or encompassed by a parallelogram in two-dimensional space. Let us recall the definition of a parallelogram. A parallelogram is a four-sided, 2-dimensional figure with:
- two equal, opposite sides,
- two intersecting and non-equal diagonals, and
- opposite angles that are equal
We come across many geometric shapes other than rectangles and squares in our daily lives. Since few properties of a rectangle and the parallelogram are somewhat similar, the area of the rectangle is similar to the area of a parallelogram.
Area of a Parallelogram Formula
The area of a parallelogram can be calculated by multiplying its base with the altitude. The base and altitude of a parallelogram are perpendicular to each other as shown in the following figure. The formula to calculate the area of a parallelogram can thus be given as,
Area of parallelogram = b × h square units
where,
- b is the length of the base
- h is the height or altitude
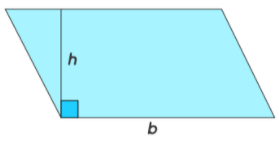 Area of Parallelogram, A•bh
Area of Parallelogram, A•bh
Let us analyze the above formula using an example. A assume PQRS is a parallelogram. Using a grid paper, let us find its area by counting the squares.
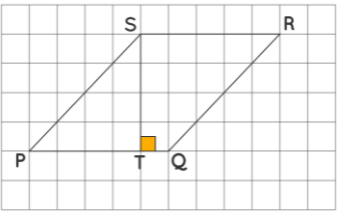 From the above figure:
From the above figure:
Total number of complete squares = 16
Total number of half squares = 8
Area = 16 + (1/2) × 8 = 16 + 4 = 20 unit2
Also, we observe in the figure that ST ⊥ PQ. By counting the squares, we get:
Side, PQ = 5 units
Corresponding height, ST=4 units
Side x height = 5 × 4 = 20 unit2
Thus, the area of the given parallelogram is base times the altitude.
Let's do an activity to understand the area of a parallelogram.
- Step I: Draw a parallelogram (PQRS) with altitude (SE) on a cardboard and cut it.
- Step II: Cut the triangular portion (PSE).
- Step III: Paste the remaining portion (EQRS) on a white chart.
- Step IV: Paste the triangular portion (PSE) on the white chart joining sides RQ and SP.
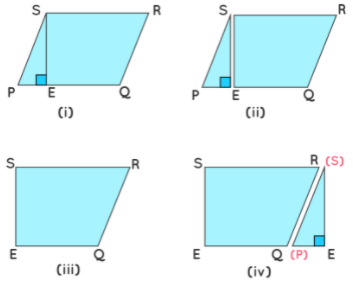
After doing this activity, we observed that the area of a rectangle is equal to the area of a parallelogram. Also, base and height of the parallelogram is equal to the length and breadth of the rectangle respectively.
Area of Parallelogram = Base × Height
How To Calculate Area of a Parallelogram?
The parallelogram area can be calculated with the help of its base and height. Also, the area of a parallelogram can also be evaluated if its two diagonals are known along with any of their intersecting angles are known, or if the length of the parallel sides along with any of the angles between the sides is known.
Parallelogram Area Using Height
Suppose 'a' and 'b' are the set of parallel sides of a parallelogram and 'h' is the height (which is the perpendicular distance between 'a' and 'b'), then the area of a parallelogram is given by:
Area = Base × Height
A = b × h [square units]
Example: If the base of a parallelogram is equal to 5 cm and the height is 4 cm, then find its area.
Solution: Given, length of base = 5 cm and height = 4 cm
As per the formula, Area = 5 × 4 = 20 cm2
Parallelogram Area Using Lengths of Sides
The area of a parallelogram can also be calculated without the height if the length of adjacent sides and angle between them are known to us. We can simply use the area of the triangle formula from the trigonometry concept for this case.
Area = ab sin (θ)
where,
- a and b = length of parallel sides, and,
- θ = angle between the sides of the parallelogram.
Example: The angle between any two sides of a parallelogram is 90 degrees. If the length of the two parallel sides is 4 units and 6 units respectively, then find the area.
Solution:
Let a = 4 units and b = 6 units
θ = 90 degrees
Using area of parallelogram formula,
Area = ab sin (θ)
⇒ A = 4 × 6 sin (90º)
⇒ A = 24 sin 90º
⇒ A = 24 × 1 = 24 sq.units.
Note: If the angle between the sides of a parallelogram is 90 degrees, then the parallelogram becomes a rectangle.
Parallelogram Area Using Diagonals
The area of any given parallelogram can also be calculated using the length of its diagonals. There are two diagonals for a parallelogram, intersecting each other at certain angles. Suppose, this angle is given by x, then the area of the parallelogram is given by:
Area = ½ × d1 × d2 sin (x)
where,
- d1 and d2 = Length of diagonals of the parallelogram, and
- x = Angle between the diagonals.
Area of Parallelogram in Vector Form
The area of the parallelogram can be calculated using different formulas when either the sides or the diagonals are given in the vector form. Consider a parallelogram ABCD as shown in the figure below,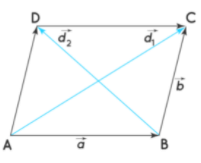 Area of parallelogram in vector formArea of parallelogram in vector form using the adjacent sides is,
Area of parallelogram in vector formArea of parallelogram in vector form using the adjacent sides is, 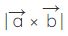
where, 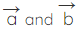 are vectors representing two adjacent sides.
are vectors representing two adjacent sides.
Here,
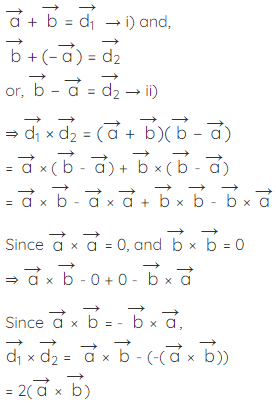
Therefore, area of parallelogram when diagonals are given in vector form = 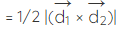
where, 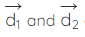 are diagonals.
are diagonals.
Solved Examples
Example 1: The adjacent sides of a parallelogram are 10 in and 6 in. The altitude corresponding to side 10 in is 5 in. Using the area of parallelogram formula, find the area and the length of the altitude corresponding to its adjacent side.
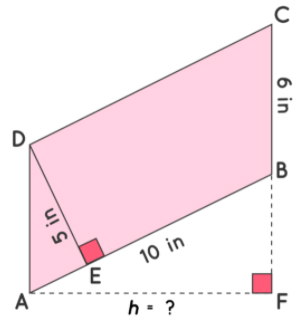
Solution: Let ABCD be a parallelogram where DE⊥AB, AF⊥BC
Using the area of parallelogram formula,
Area of Parallelogram ABCD = (10) × (5) = 50 in2
Length of BC = 6 in
Length of Altitude AF = (50 ÷ 6) = 8.3 in
Example 2: Calculate the area of a solar sheet which is in the shape of a parallelogram, given that, the base measures 20 in, and the altitude measures 8 in.
Solution: Using the area of parallelogram formula,
Area of the solar cell sheet = B × H = (20) × (8) = 160 in2
Example 3: The area of a playground which is in the shape of a parallelogram is 2500 in2, with one side measuring 250 in. Find the corresponding altitude using area of parallelogram formula.
Solution: Area of the playground = 2500 in2
Side of a playground = 250 in
Corresponding altitude = 2500/250 = 10 in
|
76 videos|344 docs|39 tests
|
FAQs on Area of Parallelogram - Mathematics (Maths) Class 7
| 1. What is the formula to find the area of a parallelogram? |  |
| 2. How do you determine the base and height of a parallelogram? |  |
| 3. Can you find the area of a parallelogram if only the length of one side is given? |  |
| 4. Is the area of a parallelogram always equal to the product of its base and height? |  |
| 5. Can the area of a parallelogram be negative? |  |

|
Explore Courses for Class 7 exam
|

|

















