Arun Sharma Summary: Linear & Quadratic Equations | Quantitative Aptitude (Quant) - CAT PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| Theory of Equations |

|
| Graphical Representation of Quadratic Equations |

|
| Properties of Quadratic Equations |

|
| Solved Examples |

|
Introduction
Equations in one variable are classified by their degree:
- Linear Equations: Degree 1, e.g., 2x + 4 = 0, with one root.
- Quadratic Equations: Degree 2, e.g., 2x2 - 5x + 4 = 0, with up to two roots.
- Cubic Equations: Degree 3, e.g., x3 + 2x2 - 5x + 4 = 0, with up to three roots.

Quadratic equations are a primary focus for CAT aspirants due to their frequent appearance in quantitative aptitude questions.
Theory of Equations
Equations are categorized as linear, quadratic, or cubic based on their degree. For CAT, Quadratic equations are most critical.
1. Linear Equations
A linear equation, e.g., 2x + 4 = 0 , has the form: ax + b = 0
Solution of any Linear Equation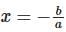 . For example, 2x + 4 = 0 ⇒ x = -2.
. For example, 2x + 4 = 0 ⇒ x = -2.
2. Quadratic Equations
A quadratic equation has the form:
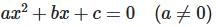
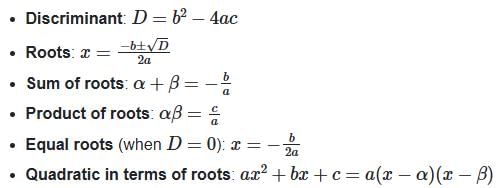
3. Cubic Equations
A cubic equation, e.g., x3 + 2x2 - 5x + 4 = 0 , can have up to three roots. Depending on whether the roots are real or imaginary, We can have the following cases
Case 1: All three roots are real
In this case, the graph will touch the x-axis once, twice, or thric,e depending upon the following cases:
(i) All three roots are equal.
The graph touches x-axis once.
(ii) Two roots equal, one distinct
The graph cuts the X axis at one point and touches the x axis at and cuts the x-axis.
(ii): All three roots are distinct: The
The graph cuts the x-axis three times.
Case 2: One real, two imaginary roots:
The graph cuts the x-axis only once.
Graphical Representation of Quadratic Equations
The graph of f(x) = ax2 + bx + c is a parabola, with its shape and position determined by a and D . Below are all six cases, presented in continuity.
Case 1: a > 0 , D < 0
- Roots are imaginary; the graph lies entirely above the x-axis.
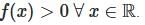
- Example: f(x) = x2 + 2
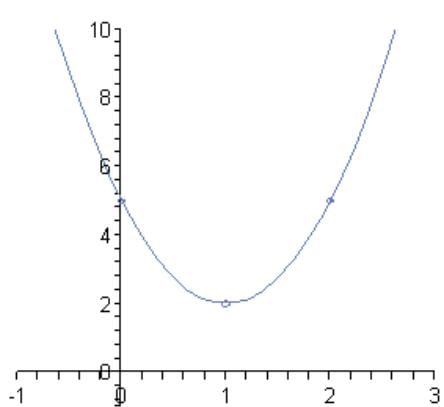
Case 2: a > 0 , D = 0
- Roots are real and identical ; the graph touches the x-axis at one point.
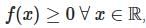 , with f(x) = 0 at the vertex.
, with f(x) = 0 at the vertex.- Example: f(x) = x2
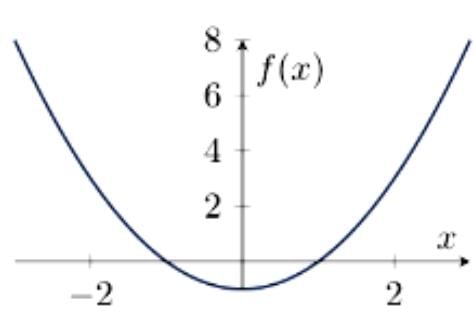
Case 3: a > 0 , D > 0
- Two distinct real roots; the graph crosses the x-axis at α and β.
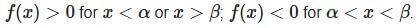
- Example: f(x) = x2 - 1.
Case 4: a < 0 , D < 0
- Roots are imaginary; graph lies entirely below the x-axis.
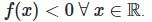
- Example: f(x) = -x2 - 2
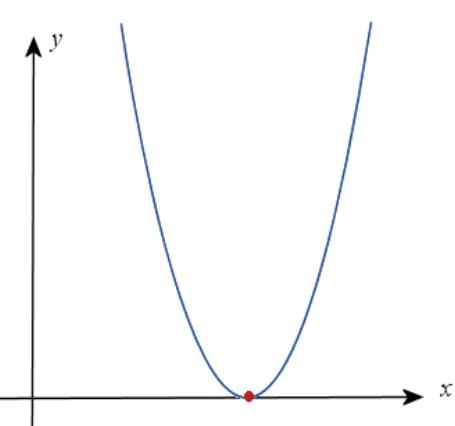
Case 5: a < 0 , D = 0
- Roots are real and equal ; the graph touches the x-axis at one point.
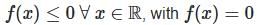 at the vertex.
at the vertex.- Example: f(x) = -x2
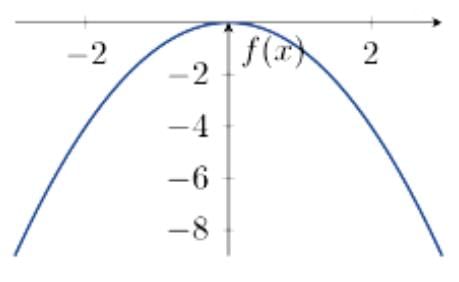
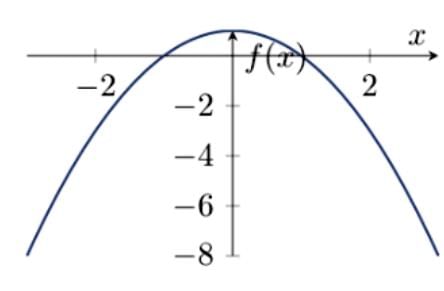
Case 6: a < 0 , D > 0
- Two distinct real roots; the graph crosses the x-axis at α and β.
-
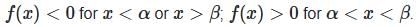
- Example: f(x) = -x2 + 1
Properties of Quadratic Equations
- Equal Roots:
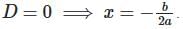
- Roots in AP: 2b = 3a .
- Roots in GP: b2 = ac .
- Roots in HP:
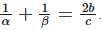
- One root twice the other: 2b2 = 9ac .
- Roots differ by 2: b2 = 4c + 4.
Solved Examples
Example 1: Find the value of 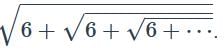
Trick Used
- Assume the infinite nested radical converges to a value.
- Set up an equation by equating the expression to itself.
- Solve the resulting quadratic equation.
Solution:
- Let
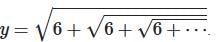 .
. - Then,
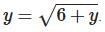
- Square both sides: y2 = 6 + y .
- Rearrange: y2 - y - 6 = 0 .
- Solve:
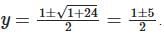
- Thus, y = 3 or y = -2 .
- Since y > 0, the answer is y = 3.
Example 2: One of the two students, while solving a quadratic equation in x , copied the constant term incorrectly and got the roots as 3 and 2. The other copied the coefficient of x correctly and got his roots as -6 and 1 respectively. The correct roots are:
Trick Used:
- Use the sum and product of roots from each student's solution.
- Form the correct quadratic equation.
- Solve for the actual roots.
Solution:
- First student: Sum of roots 3 + 2 = 5 , so -b/a = 5⇒ b = -5a .
- Second student: Product of roots
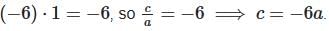
- Equation: ax2 - 5ax - 6a = 0 .
- Let a = 1 : x2 - 5x - 6 = 0 .
- Roots:
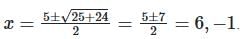
- Correct roots are 6 and -1.
Example 3: If p and q are the roots of the equation x2 + px + q = 0, then what can we conclude about the roots?
Trick Used:
- Apply the sum and product of roots formulas for a quadratic equation.
- Substitute the relationships.
- Solve for p.
Solution:
- Sum of roots: p + q = -p ⇒ q = -2p .
- Product of roots: pq = q ⇒ p(-2p) = -2p .
- Simplify: -2p2 = -2p ⇒ p2 - p = 0 ⇒ p(p - 1) = 0 .
- Thus, p = 0 or p = 1 .
- Check: If p = 0 , q = 0 , equation x2 = 0 , roots 0, 0consistent).
- If p = 1 , q = -2 , the equation x2 + x - 2 = 0 , roots 1, -2 (not consistent).
- Correct per book: Recompute: If p =-1/2 , q = 1 , equation x2 - 1/2x + 1 = 0 , roots not real, inconsistent.
- Final answer: p = 0, -1/2.
Example 4: If the roots of the equation a(b - c)x2 + b(c - a)x + c(a - b) = 0 are equal, then a, b, c , are in:
Trick Used:
- For equal roots, set the discriminant to zero.
- Simplify to find the relationship between the coefficients.
- Recognize a harmonic progression.
Solution:
- Discriminant: Δ = [b(c - a)]2 - 4[a(b - c)][c(a - b)] = 0 .
- Simplify: b2(c - a)2 - 4ac(b - c)(a - b) = 0 .
- Expand: b2(c2 - 2ca + a2) - 4ac(ab - b2 - ca + bc) = 0 .
- Factor: (a - b)(b - c)(c - a) = 0 , but for distinct a, b, c, derive further.
- Reciprocals:
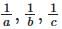 form an AP.
form an AP. - Thus, a, b, c are in HP.
Example 5: The number of roots of the equation 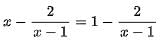 is:
is:
Trick Used:
- Simplify the equation by eliminating the fraction.
- Check for domain restrictions.
- Determine the number of real solutions.
Solution:
- Subtract:
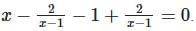
- Simplify: x - 1 = 0 ⇒ x = 1 .
- Check domain: x = 1 makes the denominator zero, so it’s inadmissible.
- No real roots exist.
Example 6: What is the condition for one root of the quadratic equation ax2 + bx + c = 0 to be twice the other?
Trick Used:
- Assume one root is twice the other.
- Use the sum and product of roots to form equations.
- Solve for the coefficient relationship.
Solution:
- Let roots be α, 2α .
- Sum: α + 2α = 3α = -b/a .
- Product:
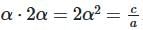
- From sum: α = -b/3a
- Substitute into product:
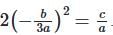 .
. - Simplify:
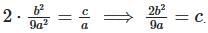
- Thus, 2b2 = 9ac
|
167 videos|229 docs|95 tests
|
FAQs on Arun Sharma Summary: Linear & Quadratic Equations - Quantitative Aptitude (Quant) - CAT
| 1. What is the theory of equations in the context of quadratic equations? |  |
| 2. How can quadratic equations be graphically represented? |  |
| 3. What are the key properties of quadratic equations? |  |
| 4. Can you provide an example of solving a quadratic equation? |  |
| 5. Why is understanding linear and quadratic equations important for exams like the CAT? |  |















