MCQs
Q1. Who was the king of France when the French Revolution began?
(a) Louis XIV
(b) Louis XVI
(c) Napoleon Bonaparte
(d) Charles X
Ans: (b) Louis XVI
Louis XVI was the king of France when the French Revolution began in 1789.
Q2. Which document was created during the French Revolution to declare the rights of individuals?
(a) The French Constitution of 1791
(b) The Declaration of the Rights of Man and Citizen
(c) The Magna Carta
(d) The Bill of Rights
Ans: (b) The Declaration of the Rights of Man and Citizen
The Declaration of the Rights of Man and Citizen was created during the French Revolution to outline the natural rights of individuals.
Q3. What event marked the beginning of the French Revolution in 1789?
(a) The storming of the Bastille
(b) The execution of Louis XVI
(c) The signing of the Declaration of the Rights of Man
(d) The formation of the National Assembly
Ans: (a) The storming of the Bastille
The storming of the Bastille on 14 July 1789 marked the beginning of the French Revolution.
Q4. What was the main goal of the National Assembly in 1791?
(a) To overthrow the monarchy
(b) To draft a new constitution limiting the king’s powers
(c) To create a republic
(d) To establish a dictatorship
Ans: (b) To draft a new constitution limiting the king’s powers
The National Assembly in 1791 sought to limit the powers of the king by drafting a new constitution.
Q5. Who led the Jacobins during the French Revolution?
(a) Georges Danton
(b) Robespierre
(c) Napoleon Bonaparte
(d) Olympe de Gouges
Ans: (b) Robespierre
Robespierre led the Jacobins during the French Revolution, particularly during the Reign of Terror.
Short Q/A
Q1. Why did Louis XVI call the Estates General in 1789?
Ans: Louis XVI called the Estates General to pass proposals for new taxes due to France's empty treasury and the financial crisis caused by previous wars and the lavish court expenses.
Q2. What were the key principles of the French Revolution?
Ans: The key principles of the French Revolution were liberty, equality, and fraternity, which emphasized freedom, equal rights, and solidarity among citizens.
Q3. What led to the rise of the Jacobins during the revolution?
Ans: The Jacobins rose due to their radical approach to the revolution, advocating for the abolition of monarchy and the establishment of a republic, as well as their association with the working class and the sans-culottes.
Q4. What was the outcome of the French Revolution for women’s rights?
Ans: Although women played an active role in the revolution, they were disappointed that the Constitution of 1791 reduced them to passive citizens. They continued to fight for equal political rights, which was not fully achieved until 1946.
Q5. How did Napoleon rise to power?
Ans: Napoleon rose to power after the fall of the Jacobin government. His military successes and the political instability of the Directory allowed him to seize control and declare himself Emperor of France in 180Q4.
Activity-Based Questions
Q1. Compare the political symbols in the painting (Fig. given below) and identify the ones representing liberty, equality, and fraternity.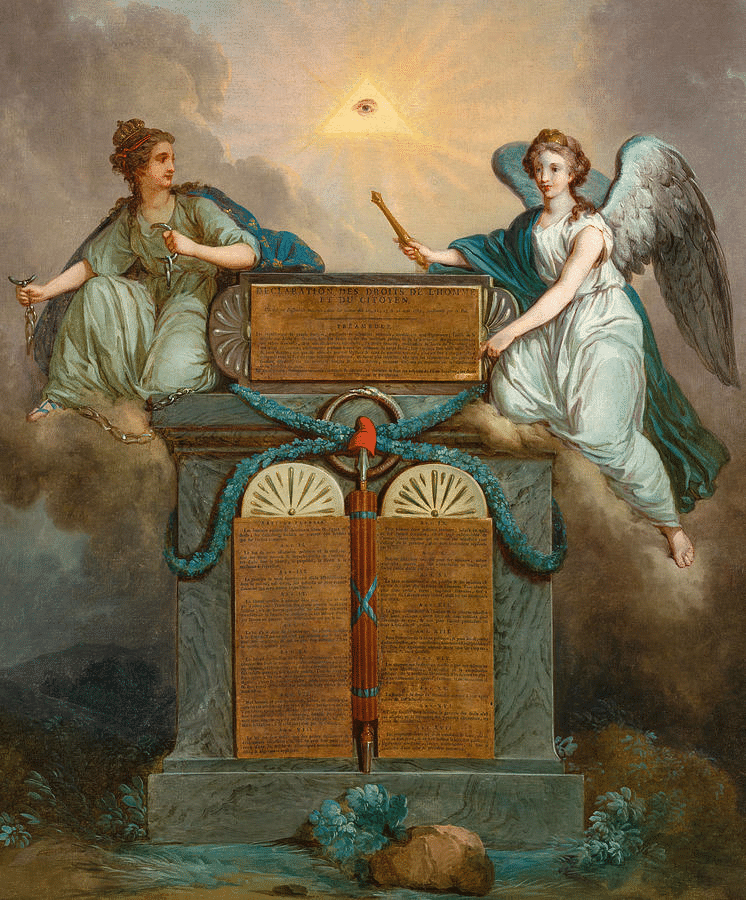
Ans: Liberty: The broken chain in the painting symbolizes freedom from oppression, representing the struggle for individual liberty and the end of tyranny.
Equality: The pyramid, often depicted as a triangle, signifies equality, symbolizing a society where all people are equal and united under a common cause.
Fraternity: The winged woman represents the law and symbolizes unity and solidarity among the people. Her presence reflects the sense of brotherhood and collective effort for the common good.
These symbols in the painting embody the core ideals of the French Revolution: liberty, equality, and fraternity, which were central to the Declaration of the Rights of Man and Citizen.
Q2. Imagine you are one of the women in the "Women Marching to Versailles" painting. Write a response to Chaumette's argument that women should focus on domestic duties.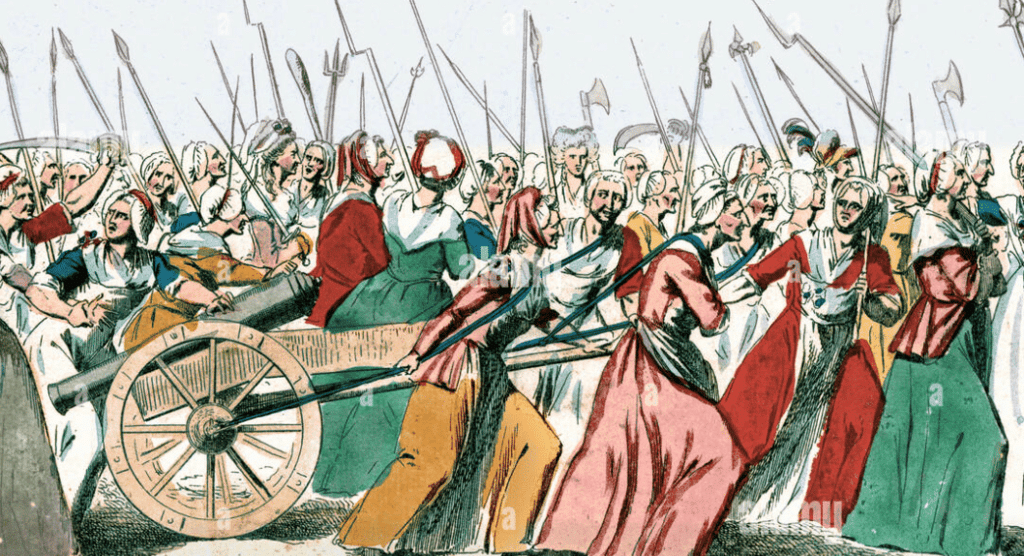
Ans: "As women, we have long been tasked with managing households, but that does not mean our roles should be limited to the private sphere. We are not just caregivers and homemakers; we are citizens with rights, and our voices deserve to be heard in the public arena. We demand the right to participate in the decisions that affect our lives, our families, and our future. We will no longer remain silent or passive in our pursuit of justice, equality, and freedom. Our contributions to society are just as valuable as those of men, and we will fight for our rightful place in shaping the future of our country."
Research-Based Question
Q1. Research how the French Revolution influenced other revolutions around the world, particularly in Latin America.
Ans: The French Revolution influenced other revolutions
- Inspiration of French Ideals: The French Revolution introduced the ideas of liberty, equality, and fraternity, which influenced revolutionary movements globally, especially in Latin America.
- Leaders' Influence: Revolutionary leaders like Simón Bolívar and José de San Martín were inspired by the French Revolution and its ideals.
- Challenge to Colonial Powers: The French Revolution's challenge to monarchies and colonial systems motivated Latin American leaders to overthrow colonial powers, such as Spain and Portugal.
- Fight for Independence: The ideals of the French Revolution encouraged the fight for independence across Latin America, leading to the eventual formation of independent republics.
- Creation of New Republics: The influence of the French Revolution played a significant role in the establishment of new, independent nations in Latin America.
Crossword
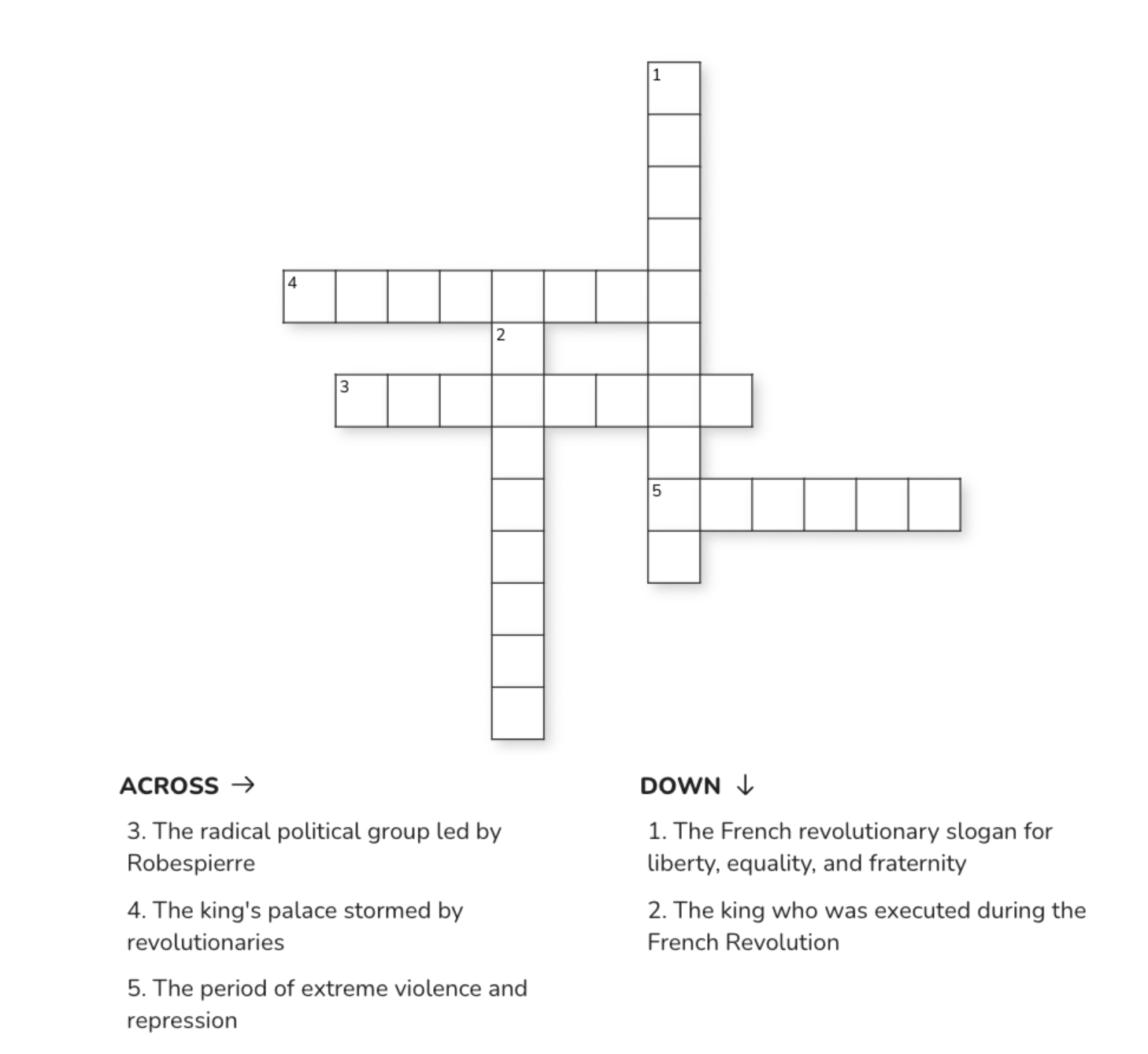 Ans:
Ans:
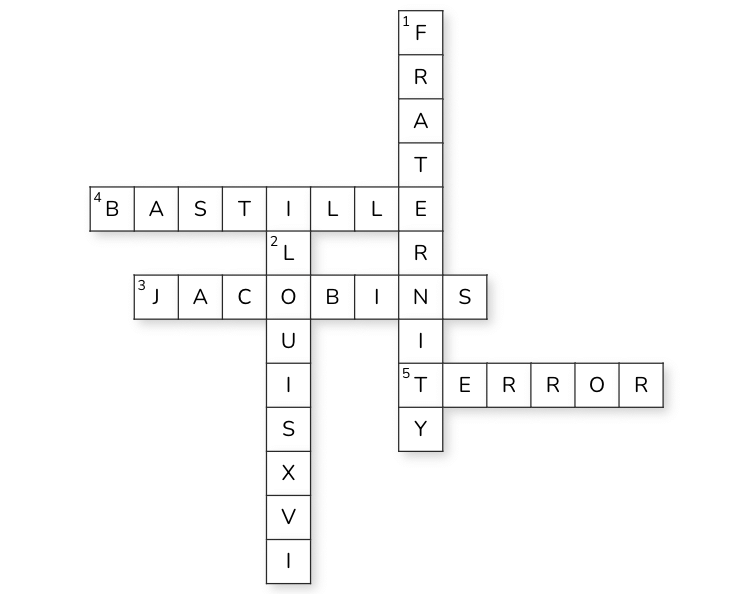





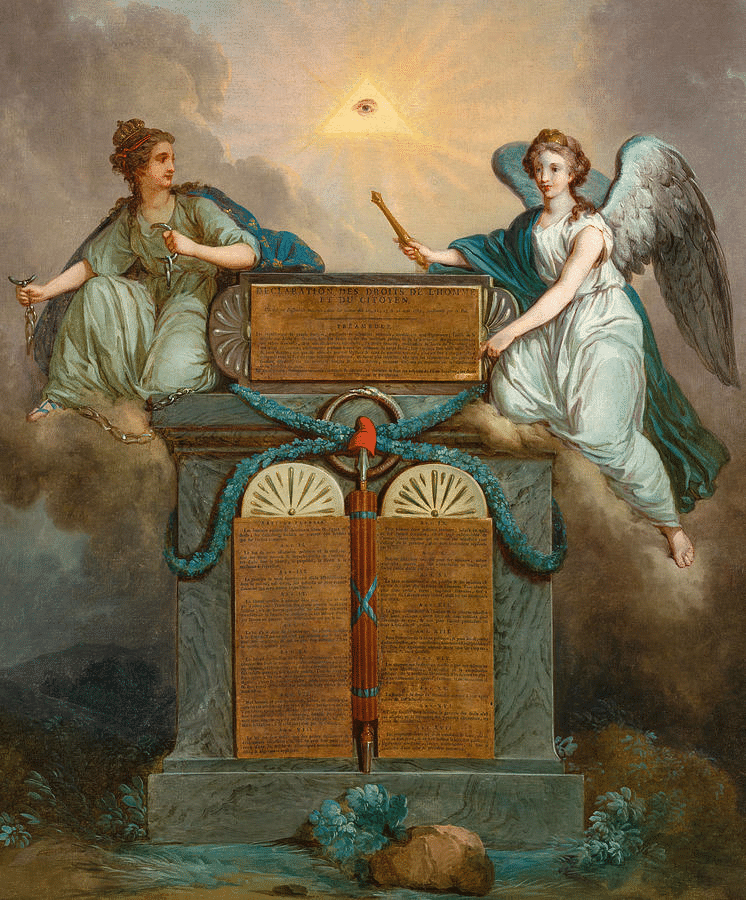

 Ans:
Ans: 





















