Detailed Notes: Averages | Quantitative Aptitude (Quant) - CAT PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| Definition |

|
| Weighted Mean |

|
| Real Facts About Average |

|
| Average Speed |

|
| Instructions for the next 3 questions: |

|
Introduction
- This chapter forms the backbone concept of most questions in the Quantitative Aptitude & Data Interpretation sections. This is a crucial chapter & quick solving methods in this concept will help you save time - which is an essential factor for your success.

- Let's try to have a quick look asks question to its aspirants, through this 2019 question.Question for Detailed Notes: AveragesTry yourself:PYQ (CAT 2019) The average of 30 integers is 5. Among these 30 integers, there are exactly 20 which do not exceed 5. What is the highest possible value of the average of these 20 integers?View Solution
- This question helps you get the idea of how the questions are asked from this chapter.
Definition
Simple Average (or Mean) is defined as the ratio of the sum of the quantities to the number of quantities.


Here x1, x2, x3, ----------- xn represent the n values of a quantity under consideration &  is the mean. Average or mean is said to be a measure of central tendency.
is the mean. Average or mean is said to be a measure of central tendency.
Example: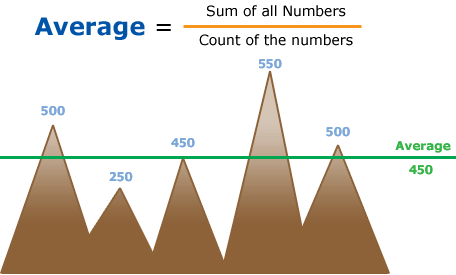 Average Formula
Average Formula
Let us take a very simple example of the first five natural numbers 1, 2, 3, 4 & 5:
Now let’s add 2 more 3’s to these 5 numbers:
Example 1. If a person with age 45 joins a group of 5 persons with an average age of 39 years. What will be the new average age of the group?
- Total age will be 45 + 5× 39 = 240. And there will be 6 persons now.
So, the average will be 240/6 = 40.
(or)Since, 45 is 6 more than 39, by joining the new person, the total will increase by 6 and so the average will increase by 1.
So, the average is 39 + 1 = 40.
Example 2. Two students with marks 50 and 54 leave class VIII A and move to class VIII B. As a result, the average marks of class VIII A fall from 48 to 46. How many students were there initially in class VIII A?
- The average of all the students of class VIII A is 46, excluding these two students.
- They have 4 and 8 marks more than 46. So, with the addition of these two students, 12 marks are adding more, and hence the average is increasing 2.
- There should be 6 students in that class, including these two. This is the initial number of students.
Example 3. The average of x successive natural numbers is N. If the next natural number is included in the group, the average increases by:
(a) Depends on x
(b) Depends on the starting number of the series
(c) Both (1) and (2)
(d) 
(e) None of these
Correct Answer is Option (d)
The average of consecutive numbers is the middle number. If one more number is added to the list, the middle number moves 0.5 towards the right. So the answer is (d).
Weighted Mean
- If somebody asks you to calculate the combined average marks of both the sections of class X, A and B when both sections have 60% and 70% average marks respectively?
- Then your answer will be 65%, but this is wrong as you do not know the total number of students in each section. So to calculate the weighted average, we have to know the number of students in both sections.
- Let N1, N2, N3, …. Nn be the weights attached to variable values X1, X2, X3, …….. Xn respectively. Then the weighted arithmetic mean, usually denoted by:

- For any two different quantities taken in different ratios. The weighted average is just like a see-saw. More the ratio of a quantity more will be the inclination of the average from mid-value towards the value with more ratios.
Example 4. The average marks of 30 students in a section of class X are 20 while that of 20 students of the second section is 30. Find the average marks for the entire class X.
We can do the question by using both the Simple average & weighted average method.
Real Facts About Average
- If each number is increased/decreased by a certain quantity n, then the mean also increases or decreases by the same quantity.
- If each number is multiplied/ divided by a certain quantity n, then the mean also gets multiplied or divided by the same quantity.
- If the same value is added to half of the quantities and the same value is subtracted from the other half quantities, then there will not be any change in the final value of the average.
Average Speed
- It is the total distance traveled divided by the time it takes to travel the distance.
 Average Speed Formula
Average Speed Formula
- If d1 & d2 are the distances covered at speeds v1 & v2 respectively and the time taken are t1 & t2 respectively, then the average speed over the entire distance (x1 + x2) is given by:
Tip: Average Speed can never be double or more than double of any of the two speeds. - If both the distances are equal i.e. d1 = d2 = d then,
 {i.e. Harmonic mean of two velocities}
{i.e. Harmonic mean of two velocities} - But if both the time taken are equal i.e. t1 = t2 = t then,
Average speed = {i.e. Algebraic mean of two velocities}
{i.e. Algebraic mean of two velocities}
Example 5. The average of 10 consecutive numbers starting from 21 is:
The average is simply the middle number, which is the average of 5th & 6th no. i.e, 25 & 26 i.e. 25.5
average is 0.41 kg. If the lightest apple weights 0.2 kg, what is the weight of heaviest apple?
Instructions for the next 3 questions:
There are 60 students in a class. These students are divided into three groups A, B, C of 15, 20 & 25 students each. The groups A & C are combined to form group D.
|
191 videos|131 docs|110 tests
|
FAQs on Detailed Notes: Averages - Quantitative Aptitude (Quant) - CAT
| 1. What is the definition of average in statistics? |  |
| 2. How is the weighted mean different from the regular mean? |  |
| 3. What are some real-world applications of averages? |  |
| 4. How do you calculate average speed? |  |
| 5. Why is understanding averages important in data analysis? |  |

|
Explore Courses for CAT exam
|

|