Basic Concepts of Auditing | Crash Course for UGC NET Commerce PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| What is Auditing? |

|
| Objectives of Auditing |

|
| Importance of Auditing |

|
| Types of Audit |

|
| Duties of an Auditor |

|
| Auditing – Important Short Notes |

|
What is Auditing?

- Auditing is an independent examination of financial information of any organization, regardless of its nature or size, with the purpose of expressing an opinion on it.
- The term "Audit" originates from the Latin word "Audire," which means "to hear." It involves verifying the financial status presented in financial statements.
- It aims to evaluate accounts to confirm whether financial statements offer an accurate representation of the financial status and performance of the organization.
- Auditing also serves as an intelligent and critical assessment of the accuracy, reliability, and sufficiency of accounting data and statements.
- According to R.K. Mautz, auditing focuses on validating accounting information to ensure the precision and trustworthiness of accounting statements and reports.
Objectives of Auditing
The objectives of auditing evolve with advancements in business practices. These objectives can be categorized as:
- Main Objective
- Subsidiary Objectives
Main Objective
The primary goal of auditing is to ascertain the reliability of financial statements, including the financial position and profit and loss accounts. The aim is to ensure that the accounts provide a true and fair representation of the business and its transactions. Auditing also aims to confirm that, at a specific date, both the profit and loss account and the balance sheet accurately reflect the financial standing of the business. Therefore, the main objective is to form an independent judgment on the reliability of accounts and the truthfulness and fairness of the financial status and results of operations.
Subsidiary Objectives
Detection and Prevention of Fraud:
- Fraud detection and prevention rank among the key subsidiary objectives of auditing. Fraud involves intentional misrepresentation of financial information and can encompass activities such as manipulation, falsification, or alteration of financial records; misappropriation of assets; misapplication of accounting policies; recording transactions without evidence; and concealing the impact of transactions from records.
Detection and Prevention of Errors:
- Another critical objective of auditing involves identifying and preventing errors in financial statements. Through auditing, efforts are made to ensure that there is no misrepresentation in financial statements. These errors can be identified by thoroughly examining and verifying the books of accounts, vouchers, ledger accounts, and other relevant documents.
Importance of Auditing
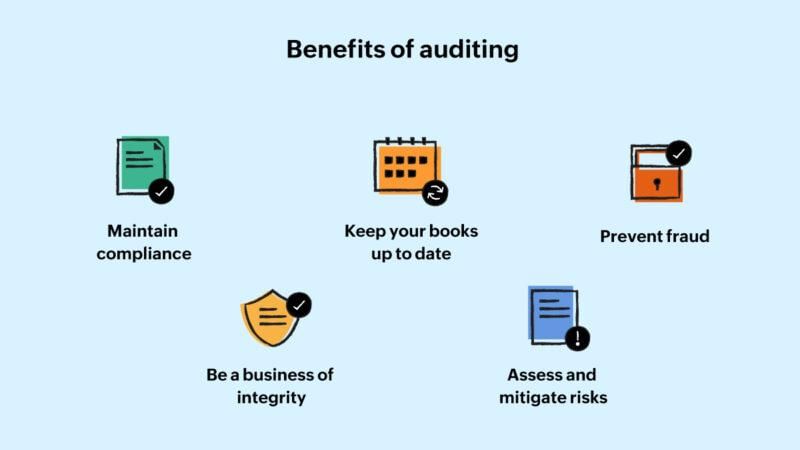 Auditing holds significant importance for all types of organizations, evident by the practice being widespread even among entities not mandated by the Companies Act of 1956 to undergo audits.
Auditing holds significant importance for all types of organizations, evident by the practice being widespread even among entities not mandated by the Companies Act of 1956 to undergo audits.
Auditing is deemed essential for both commercial and non-commercial entities. Here are key roles and benefits of auditing:
Roles of Auditing:
- Audited accounts aid sole traders in determining their business's value for potential sales.
- Auditors provide financial advice to management.
- Auditing helps prevent and detect errors and fraud within the organization.
- Long and short term creditors rely on audited financial statements while deciding on extending credit to businesses.
- Tax authorities use audited statements to assess income tax, sales tax, and wealth tax liabilities of businesses.
- Audited accounts serve as a foundation for calculating purchase considerations in cases of mergers and acquisitions.
- Auditing safeguards workers' interests by providing useful data for resolving trade disputes related to wages or bonuses.
Types of Audit
The various types of audits can be categorized based on Ownership, Time, and Objectives. Let's delve into these categories in detail below:
On the basis of Ownership
- Audit of Proprietorship: In this type of audit, the owner personally decides to have the financial statements and accounts audited. The sole trader has the authority to determine the extent of the audit and appoint an auditor.
- Audit of Partnership: When it comes to partnerships, the Partnership Deed, established through mutual agreement among partners, typically mandates the audit of financial statements. Subsequently, an auditor is selected with the consensus of all partners.
- Audit of Companies: Auditing the accounts of companies in India is a legal requirement under the Companies Act. A chartered accountant with professional qualifications is mandated to audit a company's accounts.
- Audit of Trusts: Trust audits are obligatory due to the distribution of trust income among beneficiaries, which may lead to potential fraud and income misappropriation. The audit of trusts is enforced as per the stipulations of the trust deed and the Public Trust Act.
- Audit of Accounts of Cooperative Societies: According to the Cooperative Societies Act 1912, auditing the accounts of cooperative societies is mandatory. The auditor must be well-versed in the specific act governing the cooperative society.
- Government Audit: The government of India maintains a dedicated department for auditing government offices and departments known as the Accounts and Audit Department, overseen by the Comptroller and Auditor General of India.
On the basis of Time
- Interim Audit: An interim audit occurs between two annual audits and may involve a comprehensive check of accounts for a portion of the year.
- Continuous Audit: A continuous audit is carried out consistently throughout the year or at regular short intervals.
- Final Audit: A final audit is conducted after the financial year closes. It typically starts after the end of the financial period and continues until completion.
- Balance Sheet Audit: A balance sheet audit involves verifying different elements on the balance sheet such as assets, liabilities, reserves and surplus, provisions, and the profit and loss balance.
On the basis of Objectives
- Internal Audit: Internal audit refers to the examination of accounts by the internal staff of a business. It is a review process within an organization that assesses accounts, finances, and other operations to offer both protective and constructive services to management.
- Cost Audit: Cost audit is the process of ensuring the accuracy of cost accounts and adherence to cost accounting plans. It involves a detailed examination of the costing system, techniques, and accounts to ensure the accuracy of financial records.
- Secretarial Audit: Secretarial audit focuses on verifying a company's compliance with various provisions of the Companies Act and other relevant laws. The secretarial audit report typically includes a detailed analysis of legal compliance.
(a) Ensuring adherence to the regulations outlined in the Companies Act.
(b) Obtaining necessary approvals from authorities like the central government and company law board. - Tax Audit: Verification process crucial for validating the accuracy of tax-related documents. Focuses on income returns, invoices, debit and credit notes, as well as current and fixed assets.
- Independent Audit: Carried out by an impartial and qualified auditor. Goal is to assess whether financial statements accurately represent the financial status and profits.
Qualities of an Auditor
An auditor needs to possess specific qualities to excel in their role. Let's explore these key attributes:
- Qualified Chartered Accountant: An auditor must hold the necessary qualifications as a chartered accountant.
- Comprehensive Accountancy Knowledge: Understanding the principles and practices across all facets of accountancy is crucial for an auditor.
- Knowledge of Financial Management: Adequate familiarity with financial management, industrial administration, and business organization is essential.
- Technical Acumen: The auditor should grasp the technical intricacies of the business they are auditing.
- Honesty: Integrity is paramount; the auditor must be honest in their dealings.
- Certification Integrity: Before certifying any information, auditors must ensure they have reasonable belief and exercise due care and skill.
- Confidentiality: It's crucial for auditors to maintain the confidentiality of their clients' information.
- Work Ethic: Auditors should be hardworking, systematic, and methodical in their approach.
- Listening Skills: Being a good listener and open to considering others' viewpoints is essential for effective auditing.
Qualifications of an Auditor
To become an auditor, certain qualifications must be met. Here are the key points simplified for better understanding:
- A person can be appointed as an auditor of a company only if they are a chartered accountant.
- If a firm, including a limited liability partnership, is designated as the auditor of a company, only the partners who are chartered accountants are allowed to act and sign on behalf of the firm.
Rights of an Auditor
An auditor, when appointed to review a firm's financial records, is granted several rights and responsibilities. These include:
- Right to access the books of accounts: This privilege allows the auditor to examine the financial records of the firm.
- Right to obtain the information and explanations: The auditor can request necessary details and clarifications to perform a thorough audit.
- Right to receive notice: The auditor should be notified about meetings and relevant information concerning the audit process.
- Right to seek legal and technical advice: To ensure accuracy and compliance, auditors have the right to consult legal and technical experts.
- Right to remuneration: Auditors are entitled to fair compensation for their services rendered.
- Right to sign the audit report: After completing the audit, the auditor can affix their signature to the final report.
- Right to be indemnified: Auditors have the right to be protected or compensated for any losses incurred during the audit process.
Duties of an Auditor
The duties and responsibilities of an auditor, particularly under section 143 (1), are crucial aspects to comprehend.
Duties under section 143 (1):
Let's delve into the obligations an auditor holds under section 143 (1):
- Duty to plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance: Auditors must meticulously plan and execute audits to ensure reasonable certainty regarding the financial statements' accuracy.
- Duty to comply with auditing standards: Adherence to established auditing standards is imperative to maintain audit quality and integrity.
- Duty to exercise professional judgment: Auditors are expected to apply their expertise and judgment while conducting audits.
- Duty to prepare and present the audit report: After completing the audit, auditors must compile and present a comprehensive audit report.
Duties under section 143 (2):
- The auditor must inform the members of the company about the accounts he has examined and all financial statements to be presented at the company's general meeting.
Duties under section 143 (3):
- Obtain all necessary information and explanations for the audit.
- Verify if the company has maintained the required books of accounts as per the law.
- Assess the adequacy and effectiveness of the company's internal financial control system.
- Confirm whether the company's balance sheet and profit and loss account match the records in the report.
Auditing – Important Short Notes
Audit Programme:
- The Audit Programme serves as a structured plan outlining the steps to be taken to form an opinion on financial statements.
Audit Note Book:
- An audit note book is like a journal kept by audit staff to jot down mistakes, uncertainties, and challenges encountered during an audit.
- Its purpose is to note down points that require clarification with either the client or the chief auditor.
- The audit note book is also used to record important details to include in the auditor's report.
Audit Working Papers:
- Audit working papers are collections of analysis, summaries, comments, and correspondence created by an auditor during the fieldwork of an audit.
- These papers contain crucial information about the accounts being audited.
Internal Control:
- Internal control is a comprehensive concept that oversees various aspects, encompassing the management system's regulation. It incorporates a series of inspections and regulations within a business to ensure its smooth and cost-effective functioning.
- The term 'Internal Control' is expansive, addressing the oversight of the entire management framework. It entails multiple checks and balances implemented in a business to guarantee its effective and efficient operation.
Internal Check:
- Internal check is a process that involves various facets.
- It oversees the management system comprehensively.
- Internal check enforces numerous inspections and regulations within a business to ensure its efficient and economical performance.
Vouching:
- Vouching is the process where an auditor examines documentary evidence to confirm the accuracy of entries in the financial records.
- It involves the auditor inspecting evidence that supports the transactions recorded in the books of accounts.
- Essentially, vouching is a method used by auditors to verify the truthfulness of the entries in the financial statements.
Investigation:
- Investigation consists of a detailed inquiry into the background of the financial records, focusing on the technical, financial, and economic standing of the business.
- It entails a thorough examination of the books with a specific goal in mind.
Verification:
- Verification involves confirming the ownership, valuation, and existence of items on a balance sheet typically done at the end of the year. It's essentially about proving the accuracy or validity of the information.
Valuation:
- Valuation is the process of determining the precise value of an asset based on its utility. It plays a crucial role in audits by ensuring the accuracy of the balance sheet, validating the estimation of asset and liability values. Auditors ensure that the values reported on the balance sheet are correct, neither inflated nor undervalued.
|
237 videos|236 docs|166 tests
|
FAQs on Basic Concepts of Auditing - Crash Course for UGC NET Commerce
| 1. What is the main objective of auditing? |  |
| 2. Why is auditing important for businesses? |  |
| 3. What are the different types of audits that can be conducted? |  |
| 4. What are the duties of an auditor during an audit process? |  |
| 5. What are some key concepts of auditing that one should be aware of for the UGC NET exam? |  |















