Bernoulli's Equation | Fluid Mechanics for Mechanical Engineering PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Equations of Motion |

|
| Euler’s Equation of Motion |

|
| Bernoulli’s Equation for Incompressible Real Fluid |

|
| The Momentum Equation |

|
| Solved Numericals |

|
Equations of Motion
According to Newton’s second law of motion, the net force Fx acting on a fluid element in the direction of x is equal to mass m of the fluid element multiplied by the acceleration ax in the x − direction. Thus, mathematically Fx = m ax In the fluid flow, the following forces are present:- Fg, gravity force
- Fp, the pressure force
- F ν , the force due to viscosity
- Fc, force due to compressibility
- Ft, fore due to turbulence of flow
Thus , net force Fx, = (Fg )x + (Fp)x + (Fν)x + (Ft)x + (Fc)x
- If the force due to compressibility, FC is negligible, the resulting net force
Fx =(Fg)x + (Fp)x + (Fν)x + (Ft)x and equations of motion are called “Reynold’s equations of motion” - For flow where (Ft) is negligible, the resulting equations of motion are known as “Navier − Stokes equation”.
- Fx = (Fg )x + (Fp )x+ (Fv )x (Navier Stoke’s equation.) This equation is useful in analysis of viscous flow.
- If the flow is assumed to be ideal, viscous force (Fν) is zero and equations of motion are known as “Euler’s equations of motion”.
Fx = (Fg )x + (Fp )x
Euler’s Equation of Motion
This is Equation of motion in which the force due to gravity and pressure are taken into consideration Euler’s Equation is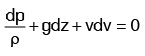 Bernouli’s equation is obtained by integrating the Euler’s equation of motion as
Bernouli’s equation is obtained by integrating the Euler’s equation of motion as 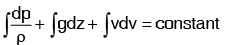 This equation is applicable for steady, irrotational flow of incompressible fluids.
This equation is applicable for steady, irrotational flow of incompressible fluids.If flow is incompressible, ρ is constant i.e. independent of pressure (hence p is treated as constant).
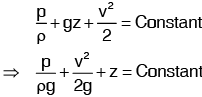
Above equation is Bernoulli’s equation in which:
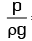 = pressure energy per unit weight of fluid or pressure head
= pressure energy per unit weight of fluid or pressure head
v2 / 2g = Kinetic energy per unit weight or kinetic head
z = potential energy per unit weight or potential head
Assumptions:
The following are the assumptions made in the derivation of Bernoulli’s equation:(i) The fluid is ideal, i.e. viscosity is zero
(ii) The flow is steady
(iii) The flow is incompressible
(iv) The flow is irrotational
Bernoulli’s Equation for Incompressible Real Fluid
Bernoulli's equation is originally derived under the assumption that the fluid is inviscid (non-viscous) and, therefore, frictionless. However, real fluids are viscous and resist flow, resulting in energy losses. These losses must be accounted for when applying Bernoulli's equation to real fluids. The modified Bernoulli's equation for real fluids, accounting for these losses between points 1 and 2, is given as: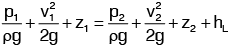 Where hL is loss of energy per unit weight of fluid between points 1 and 2.
Where hL is loss of energy per unit weight of fluid between points 1 and 2.Practical Applications of Bernoulli’s Equation
Bernoulli's equation is applied in all problems of incompressible fluid flow where energy considerations are involved e.g.(i) Venturimeter
(ii) Orifice m eter
(iii) Pitot − tube
The Momentum Equation
The momentum equation is derived from the law of conservation of momentum, which states that the net force acting on a fluid mass is equal to the change in momentum of the fluid flow per unit time in that direction. The momentum equation can be expressed as follows: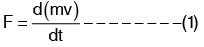 Where F is the force on a fluid mass m.
Where F is the force on a fluid mass m. Above equation is known as the “momentum principle” Equation (1) may also be written as
F. dt = d (mv)
Which is known as the “impulse − momentum equation”.
Force exerted by a flowing fluid on Pipe − Bend
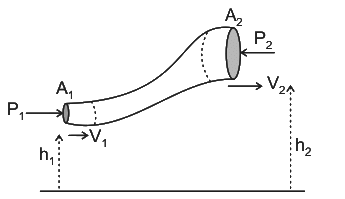
The impulse momentum equation is used to determine the resultant force exerted by a flowing fluid on a pipe bend. Consider two sections (1) and (2) as shown in fig.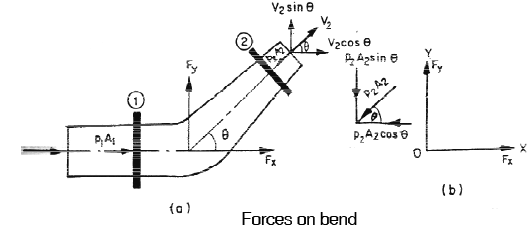 Let, V1 = Velocity of flow at section (1)
Let, V1 = Velocity of flow at section (1) p1 = pressure intensity at section (1)
A1 = area of cross section of pipe at section (1) and
V2, p2.,A2 = corresponding values of velocity, pressure and area at section (2)
Let Fx and Fy be the components of the forces exerted by the flowing fluid on the bend in x and y direction respectively. Then
Fx = ρ Q (V1 − V2 cosθ ) + p1 A1 − p1 A2 cosθ
Fy = ρ Q (−V2 sin θ) − p2 A2 sin θ
The resultant force (FR) acting on the bend =
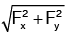
And the angle made by the resultant force with horizontal direction is given by tanθ = Fy / Fx
Solved Numericals
Q1. Water flows in a horizontal tube (see figure). The pressure of water changes by 700 Nm−2 between A and B where the area of cross section are 40 cm2 and 20 cm2, respectively. Find the rate of flow of water through the tube. (density of water = 1000 kgm−3)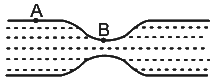 Ans: In fluid dynamics, Bernoulli's principle states that an increase in the speed of a fluid occurs simultaneously with a decrease in static pressure or a decrease in the fluid's potential energy.
Ans: In fluid dynamics, Bernoulli's principle states that an increase in the speed of a fluid occurs simultaneously with a decrease in static pressure or a decrease in the fluid's potential energy.
From Bernoulli's equation
PA + 1/2ρV2A = PB + 1/2ρV2B
Calculations:
Given:
Δ P = 700 Nm-2
aA = 40 cm2
aB = 20 cm2
From the continuity equation
aAVA = aBVB
Putting values of area, we will get,
2VA = VB
From Bernoulli's equation
PA + 1/2ρV2A = PB + 1/2ρV2B
Δ P = 1/2ρ(V2B - V2A)
= 1/2103(4V2A - V2A)
700 × 2 = 103 (3 V2A)
V2A =
VA = 7/15m/s
= 7/15
The volume of the flow = aA × vA = 40 × 7/15
= 2732.5 cm3/s
Q2. If the flow speeds of the upper and lower surfaces of the wings of an aeroplane are 260m/s and 250m/s, the wings cover an area of 500 m2 then what would be the lift generated (in kN)? (take density of air as 1kg/m3)
Ans:
- Bernoulli's principle states that the sum of pressure energy, kinetic energy, and potential energy per unit volume of an incompressible, non- viscous fluid in a streamlined irrotational flow remains constant along a streamline.
- This means that in steady flow the sum of all forms of mechanical energy in a fluid along a streamline is the same at all points on that streamline.
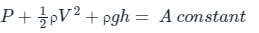
Assume Ptop = pressure at the top, Pbottom = Pressure at the bottom, Vtop = Velocity at the top of the wing, Vbottom = Velocity at the bottom
- Given - Vtop = 260 m/s, Vbottom = 250 m/s, A = 500 m2, and ρ = 1 kg/m3
- Assuming the height difference between the upper and lower surface of the wings to be zero.
- Hence the gravitational potential energy can be neglected then the equation of Bernoulli's theorem becomes
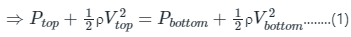
- In order for the lift to occur Pbottom > Ptop
- Hence equation 1 can be rewritten as
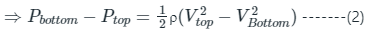
The lift force can be found out using the equation
⇒ F = ΔP A -----(3)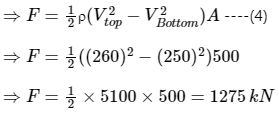
Q3. The pressure of water in a pipe when water is not flowing is 3 × 105 Pa and when the water flows the pressure falls to 2.5 × 105 Pa. Find the speed of flow of water (in m/s)?
Ans:
- Bernoulli's principle states that the sum of pressure energy, kinetic energy, and potential energy per unit volume of an incompressible, non- viscous fluid in a streamlined irrotational flow remains constant along a streamline.
This means that in steady flow the sum of all forms of mechanical energy in a fluid along a streamline is the same at all points on that streamline. From Bernoulli's principle
From Bernoulli's principle
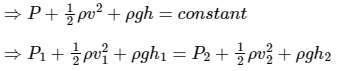
Given:
Initial velocity (v1) = 0 m/s, Initial pressure (P1) = 3 × 105 Pa, and Final pressure (P2) = 2.5 × 105 Pa
According to Bernoulli's principle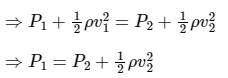
Above equation can be written as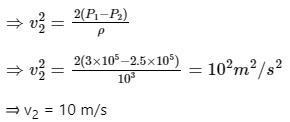
|
56 videos|154 docs|75 tests
|




















