Biology: An Introduction | General Awareness for SSC CGL PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| Branches of Biology |

|
| Branches of Zoology |

|
| Characteristics of Living Beings |

|
Introduction
- Biology aims to explain the living world through scientific principles.
- The invention of the microscope in the 17th century led to the creation of cytology, a branch of biology focusing on the study of cells.
- Biology encompasses the study of various aspects of living beings, including their structure, functions, organization, evolution, and interactions with the environment.
- Modern biology is a broad and diverse field with numerous branches and sub-disciplines.
- It acknowledges the cell as the fundamental unit of life and genes as the basic units of heredity, which drive the synthesis and creation of new species.
- Biology, the science of living organisms, includes both plants and animals.
- Aristotle is recognized as the father of biology, and the term "biology" was first introduced by Lamarck and Treviranus in 1802.
- At the sub-atomic level, living and non-living beings are fundamentally similar, and chemical and physical principles apply to both.
Branches of Biology
The development of various tools and techniques has led to many branches of biology:
I. Basic Biology
This branch studies the fundamental principles of living organisms, including their structure and functions. It encompasses botany, zoology, and microbiology.
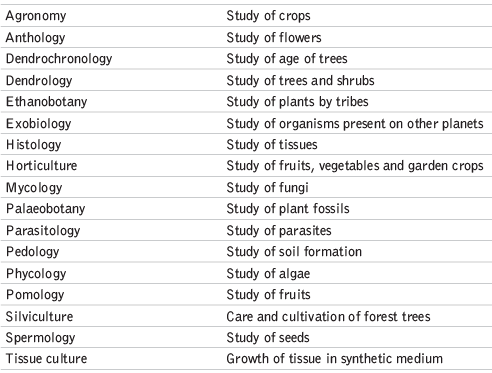
Botany: Theophrastus, known as the father of botany, documented about 500 plants in his book "Historia Plantarum."
Branches of Botany
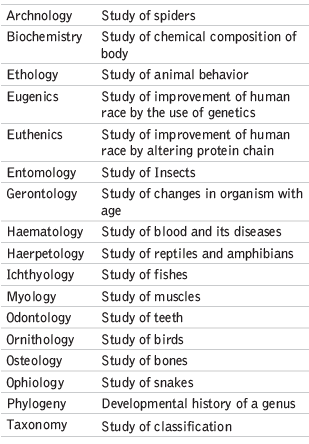
Zoology: Aristotle, also called the father of zoology and embryology, described the structure, nature, classification, and reproduction of about 500 animals in "Historia Animalium."
Branches of Zoology

Microbiology: This branch focuses on microorganisms like bacteria and viruses.
- Bacteriology: Study of bacteria.
- Virology: Study of viruses.
II. Applied Biology
This branch applies biological principles for the benefit of humankind, including agriculture, medical science, veterinary science, and pharmacy.
- Agriculture: This branch deals with farming, including soil cultivation for crops and animal rearing for food, wool, and other products.
- Medical Sciences: This branch studies human health and diseases, including their causes, prevention, control, and treatment.
- Veterinary Science: This branch focuses on the study of animals.
- Pharmacy: This branch studies medicines, including their nature, production, effects, and distribution. Hippocrates is known as the father of medicine.
Misuse of Biology
Various biological techniques have been misused against humanity:
- Amniocentesis: This technique detects fetal abnormalities by analyzing chromosomal defects or aberrations in the fetus. It can reveal the sex of the fetus, leading to increased abortions in India.
- Bioweapons: These antibiotic-resistant microorganisms, which can cause infertility, are used as bioterrorism agents.
Characteristics of Living Beings
Living organisms possess unique characteristics that distinguish them from non-living entities.
I. Cellular Structures
The cell is the fundamental building block of living organisms, serving as the structural and functional unit of life. This complex arrangement is absent in non-living things.
II. Metabolism
Metabolism is a dynamic feature of all living beings, encompassing all chemical reactions within an organism. It is divided into two phases:
- Anabolism: This constructive phase involves the formation of protoplasm and other complex substances, aiding growth and development. Examples include protein synthesis from amino acids and glucose formation through photosynthesis.
- Catabolism: This destructive phase breaks down complex molecules (nutrients) into simpler ones, releasing energy. An example is the breakdown of starch into glucose, which is further broken down into water (H₂O) and carbon dioxide (CO₂), releasing energy.
III. Nutrition
All living organisms require nutrition for growth and development. Nutrition involves the intake of food particles to provide energy and materials necessary for life-sustaining activities.
IV. Growth and Development
The life of every organism starts from a single cell, which divides to form many cells, tissues, organs, organ systems, and ultimately a complete body. This process is called growth and is a distinctive feature of living beings. Growth in living beings is fundamentally different from growth in non-living entities.
V. Reproduction
Reproduction is a key feature of living organisms, ensuring the continuity of life. For example, plants produce seeds that germinate into new plants, and mammals give birth to offspring.
VI. Sensitivity
- Living organisms are sensitive to environmental changes and have consciousness for their protection.
- They can feel hot and cold, withdraw from painful stimuli like thorns or acid, and exhibit excitability.
VII. Adaptation
Adaptation refers to an organism's ability to adjust to external environmental changes. For example, fish are adapted to live in water, while frogs are adapted to live both on land and in water.
|
478 videos|1421 docs|396 tests
|
FAQs on Biology: An Introduction - General Awareness for SSC CGL
| 1. What are the main branches of Biology? |  |
| 2. What are the branches of Zoology? |  |
| 3. What are the characteristics of living beings according to Biology? |  |
| 4. What is the significance of studying Biology for SSC CGL exam? |  |
| 5. How can knowledge of Biology help in cracking the SSC CGL exam? |  |
















