Boolean Logic | Computer Science for Class 11 - Humanities/Arts PDF Download
Introduction to Boolean Logic
Every day we may cross a path of many situation like “Should I do this or not?”, “Should I do switch on laptop or not?”. These types of questions having answer either “Yes” or “No”. So these kind of situation is binary decision.
Now lets consider following examples:
- Scahin Tendulker is the only player who scored 100 centuries in Circket.
- 56 – 4 = 52
- Ahmedabad is biggest district of Gujarat.
- What do you feel about lockdown extension?
In these sentences 1, 2 are TRUE and sentence 3 is False, where as sentence 4 cannot be answered in TRUE or FALSE. Hence sentences which can be answered in TRUE or FALSE are known as logical statements or truth functions.
The result of truth functions are stored in TRUE or FALSE values are known as truth values. This can be written as 0 and 1 in logical constant where 1 means TRUE and 0 means FALSE. These values can be stored in variables are known as logical variables or binary valued variables.
Boolean logic refers to Boolean Algebra which values of variables are the truth values true or false. These values have two states either on or off denoted by 0 or 1.
Truth Table
A truth table represents a Boolean function or expression with all possible input and output results in tabular form.
If the result is always 1 or true or high, is called Tautology, whereas the result is false or 0(zero) or low is known as Fallacy. The number of rows in the truth table is computed as 2n.
Rules of writing Truth table:
- Check the number of variables of expression.
- Make column for each input variable.
- Make column for each logical expression.
- Write 0’s in first half for the number of rows in first column and then second column respectively.
- Continue the same pattern until the last column.
- Compute result for each operation by considering the input values of variables written in each row.
Logical Operations: Logical operations can be applied of truth functions. These operations carried out by logical operators with operands.
Logical Operators: In this section of notes Boolean Logic Computer Class 11 we are going to discuss the logical operators used in Boolean logic.
NOT: It handles only a single variable. The operation performed by NOT is known as complementation. To denote NOT operator bar symbol is used. 
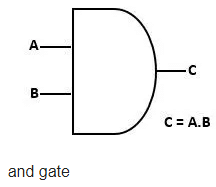
AND: It is a binary operator that operates on two variables and the result of the AND operator is known as logical multiplication. To denote AND operator dot(.) symbol is used. The truth table for AND operator looks like as following: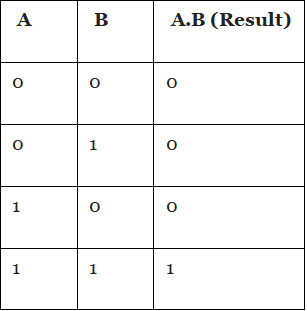
AND operator accepts two input variables A and B with values 0 and 1 respectively. the result calculated as follows:
Row 1: A=0, B = 0 , 0 x 0 = 0
Row 2: A = 0, B = 1, 0 x 1 = 0
Row 3 : A = 1. B = 0, 1 x 0 = 0
Row 4: A = 1, B = 1, 1 x 1 = 1
The result of A.B also written as AB.
In short the AND operator returns TRUE or 1 when both input are 1, rest all results will be 0. True is also considered as high, and False as low.
OR
It is also a binary operator that operates on two variables. The result of the OR operator is also known as logical addition. The symbol is used for OR is plus (+). The truth table for the OR operator looks as follows: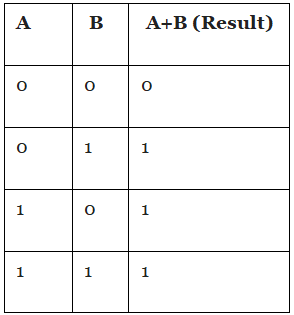
OR operator accepts two input variables A and B with values 0 and 1 respectively. the result calculated as follows:
Row 1: A = 0, B = 0 , 0 + 0 = 0
Row 2: A = 0, B = 1, 0 + 1 = 1
Row 3: A = 1, B = 0, 1 + 0 = 1
Row 4: A = 1, B = 1, 1 + 1 = 1
In short the OR operator returns TRUE or 1 when any one input value is 1, otherwise 0. True is also considered as high, and False as low.
After getting familiar with logical operations for notes Boolean Logic Computer Class 11 you should learn about operator precedence.
Precedence of Boolean Operator
- NOT (First Priority)
- AND (Second Priority)
- OR (Third Priority)
Rules for evaluating boolean expression
- Evaluate the Boolean Expression from left to right.
- Evaluate the expression in parenthesis.
- Now consider the priorities of operator given above.
Logic Gates
A logical gate is a logical circuit that takes one or more inputs and produces result. It uses three operators AND, OR and NOT known as AND Gate, OR Gate and NOT Gate. These are fundamentals gates.
NOT Gate
A NOT gate has only one input. It is known as inverter gate. It is used for electronic inverter devices. It produces the reverse result of an input. The output is always negation or complement of an input signal.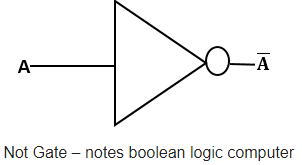
AND Gate

OR Gate
OR refers like A or B. It is considered as inclusive “or”. The output is true if either one or two inputs are “true”. It both false it produce false result.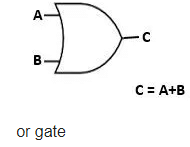
Some more gates are available with OR and AND gates followed by inverter, N or X is written in front of name of gate. They are as follow:
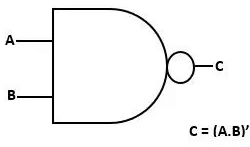
NAND Gate
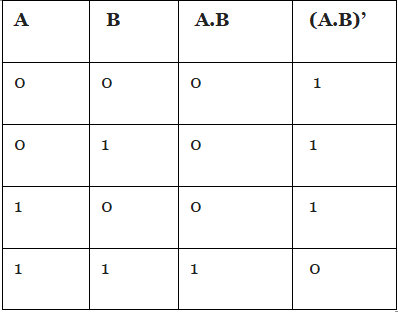
It stands for NOT AND that produce reverse result of AND gate. The truth table for NAND Gate is as following:
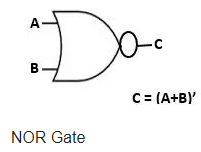
NOR Gate
It stands for NOT OR. It produces reverse output than the OR gate. The truth table for NOR Gate is as follows: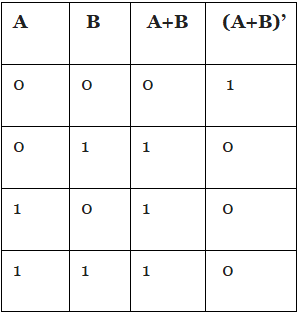
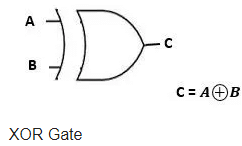
XOR Gate
It produces high output if the input of 1s is odd, otherwise false.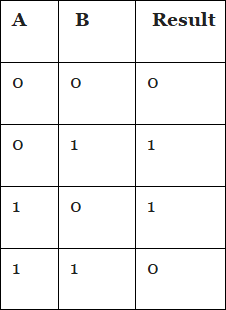
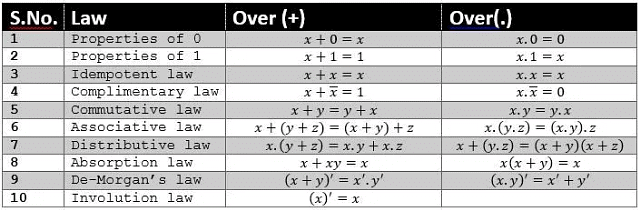
Basic Laws
|
20 videos|20 docs|5 tests
|

|
Explore Courses for Humanities/Arts exam
|

|