Boxes and Sketches Class 5 Notes Maths Chapter 9
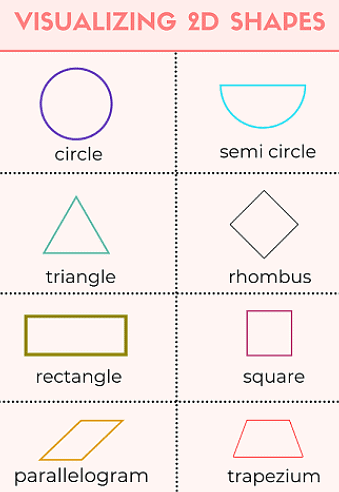
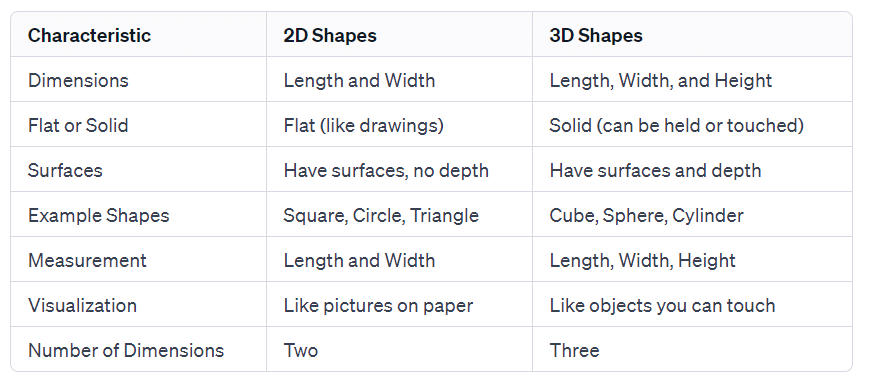
2D Shapes
- 2D means two-dimensional, like having width and height.
- Shapes in 2D are flat, like a piece of paper.
- Examples include rectangles and circles; they don't have depth.
- Dimensions are like measurements in different directions.
- In 2D, we talk about length, and width (or breadth), but no depth or height.
- 2D objects can't be physically held; they're just flat on a surface.
3D Shapes
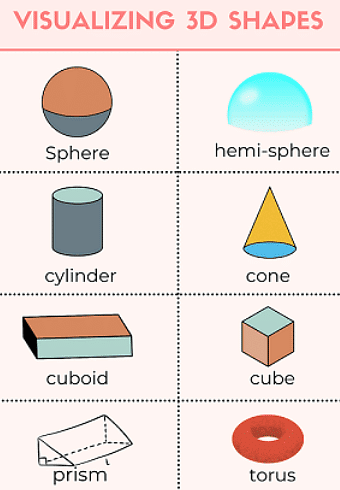
- 3D shapes have faces, edges, and vertices.
- Faces are like the sides of the shape, and they can be flat or curved.
- Cubes have six faces, while spheres have only one.
- Edges are where two faces meet. Cubes have 12 edges, but spheres, like balls, have none.
- Vertices are like corners where edges meet.
- Pyramids can change based on their base shape. A square-based pyramid has five faces, and a triangle-based pyramid has four.
Properties of 2D Shapes
Circle
- A circle is a 2D closed shape with no sides or edges made out of a curved line.
- A circle is made up of several different pieces, such as radius, diameter, and circumference.
- Examples include Coins, wheels, and pizzas.
 Circle
Circle
Triangle
- .A triangle is a closed shape that has three sides, three vertices, and three angles.
- It is a polygon with inner angles summing 180 degrees.
 Triangle
Triangle
Square
- A square is a two-dimensional form having four equal sides and each angle equal to 90 degrees.
- Examples include a loaf of bread and a chessboard.
 Square
Square
Rectangle
- A rectangle is a two-dimensional object having four sides that are equal and parallel, and all four angles measure 90 degrees.
- Examples include Tabletops, blackboards, and cardboard.
 Rectangle
Rectangle
Properties of 3D Shapes
Sphere
- A sphere has only one curved surface.
- For example, planets, balls, globes, etc.
 Sphere
Sphere
Hemisphere
A hemisphere has a single face, one curved surface, and one edge.
- For example, a scoop of ice cream, cups, etc.
 Hemisphere
Hemisphere
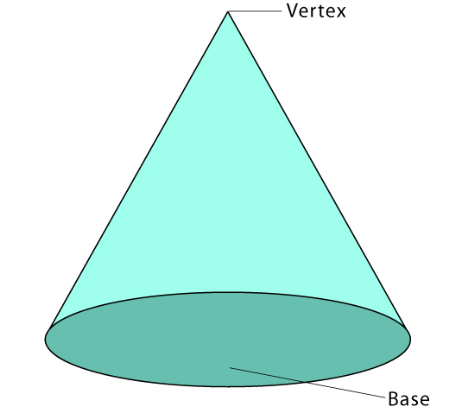
Cone
- A cone has a single face, one curved surface, one edge, and one vertex.
- For example, ice cream cones, traffic cones, etc.
 Cone
Cone
Cube
- A cube is a solid three-dimensional object. It has six faces, twelve edges, and eight vertices.
- For example, ice cubes, gift boxes, etc.
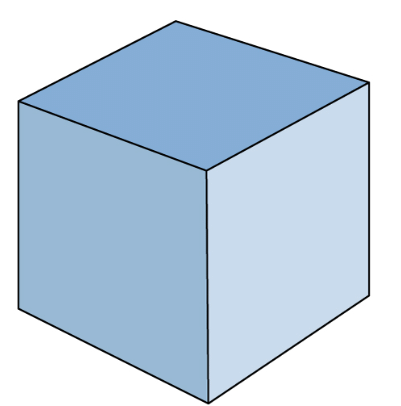 Cube
Cube
Cylinder
- A cylinder is made up of two faces, one curved surface, and two edges.
- For example, battery, test tube, etc.
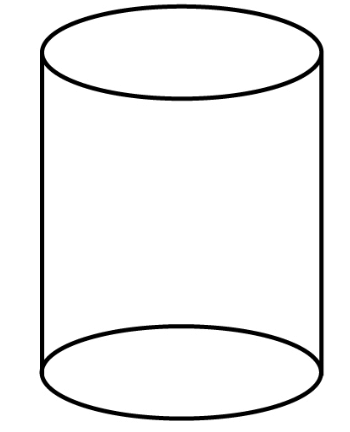 Cylinder
Cylinder
Solved Examples of 2D and 3D Shapes
Example 1: Each cube and cuboid contains _____ plane surfaces,______ edges, and _____vertices.
Sol: six, twelve, eight
Example 2: Which of the following is a 3D shape?
Cone, Square, Sphere, Cuboid, Cylinder, Parallelogram
Solution: Cone, Sphere, Cuboid, Cylinder.
Example 3: State whether the following are true or false.
(a) A three-dimensional shape has 3 dimensions.
(b) Three-dimensional shapes are also called flat shapes.
(c) Three-dimensional shapes occupy space.
(d) All three-dimensional shapes have flat faces.
Sol: (a)True
(b) False. Three-dimensional shapes are also called solid shapes.
(c) True
(d) False. The sphere is a three-dimensional shape with no flat face.
2D Shapes vs 3D Shapes
2D to 3D shape
- A triangle, like a drawing on paper, becomes a pyramid or a cone when we turn it into a 3D shape.
- Think of a circle, like a flat picture, turning into a sphere when it becomes a 3D shape.
- Imagine a square, a flat shape, transforming into a cube, like a real block you can hold, in 3D.
- A rectangle, like a drawing on paper, changes into a cuboid, like a box you can touch, in 3D.
2D representation of 3D objects
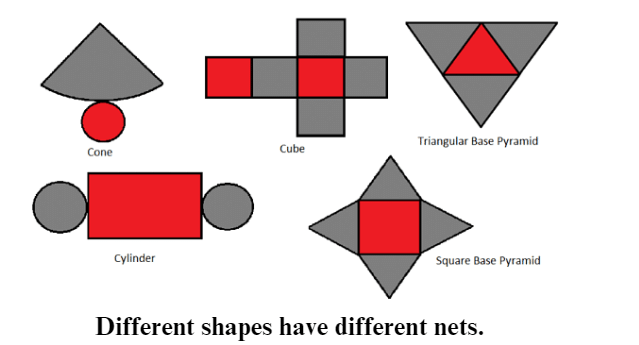
- A net is like a flat paper plan that shows how a 3D shape looks when you unfold it.
- Imagine it's like a pattern you use to make a paper model of a 3D figure.
- Think of a box. It's a solid 3D object shaped like a rectangular block.
- Other shapes have their own nets too, like puzzles to make different 3D shapes.
Floor Maps
- The floor map is like a picture of a house.
- It shows where the doors and windows are in the house.
- The front side of the house is where the door is.
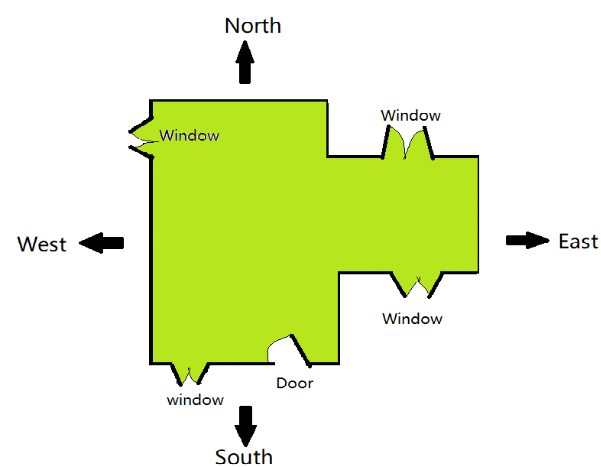
- On the front side, there are two windows.
- We can't see how big the house is or how tall the windows are from the floor map.
Deep Drawings
- A deep drawing of a home is a special way of drawing that shows how long, wide, and tall the house is.
- It's like making the house look real in a picture.
- This kind of drawing is called a 3D depiction of a house map.
- Below is an example of a deep drawing of the given floor map.
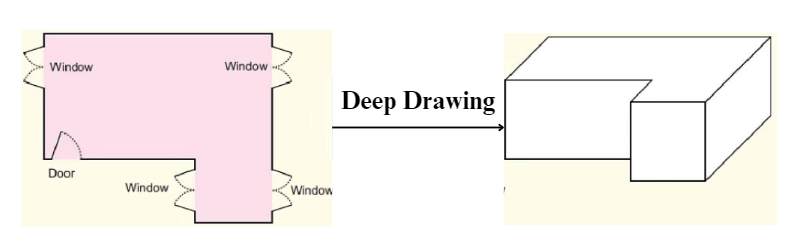
Deep Drawing of a Cube and Cuboid
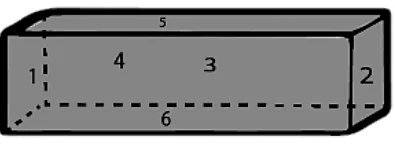
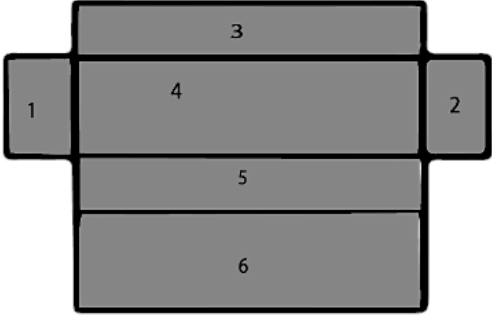
- Cuboid: A cuboid is a three-dimensional (3D) object with six faces. A cuboid has variable lengths, widths, and heights. A cuboid has eight corners and twelve edges.
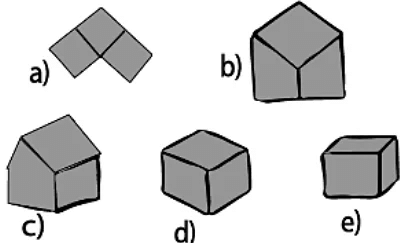
- Cube: It is a 3D shape with 6 faces, 12 edges, and 8 vertices. The above drawing of a cube shows shapes that fold into a cube.
Visualization of 3-dimensional Shapes
- A three-dimensional item or shape can appear differently from multiple locations (or sides), allowing it to be drawn from various viewpoints; this is known as visualizing a solid shape.
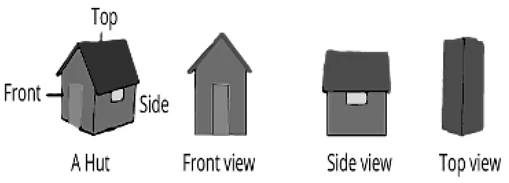
- The front view of a hut, as illustrated above, is a combination of a square with a conical top, while the side and top views are a combination of two rectangular surfaces.
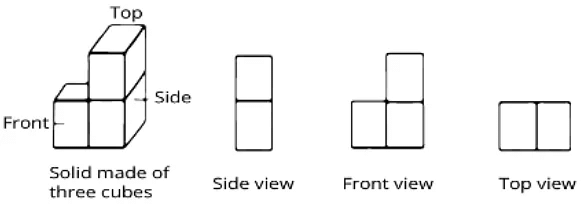
- In the image above, one side of a solid has two square surfaces that are vertically connected, the front view has three square surfaces that are arranged in an L shape, and the top view has two square surfaces that are horizontally connected.
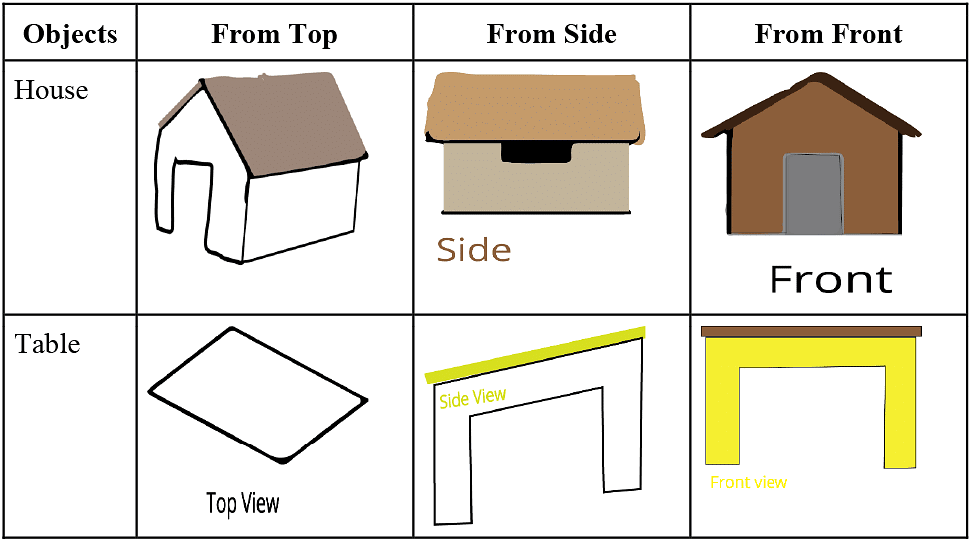
|
31 videos|192 docs|41 tests
|
FAQs on Boxes and Sketches Class 5 Notes Maths Chapter 9
| 1. What are 2D shapes? |  |
| 2. What are 3D shapes? |  |
| 3. What are some properties of 2D shapes? |  |
| 4. What are some properties of 3D shapes? |  |
| 5. How can 2D shapes be represented in 3D? |  |
















