CBSE Sample Question paper - 10 Economics, Class 12 | Sample Papers for Class 12 Commerce PDF Download
Class - XII
Economics
TIME: 3 Hrs.
M.M: 80
General Instructions :
1. This question paper contains two parts :
Part A : Macro Economics (40 marks)
Part B : Indian Economic Development (40 marks).
2. All questions in both sections are compulsory. Marks for questions are indicated against each question.
3. Question No. 1-10 and 18-27 (including two Case Based Questions) are very short answer questions carrying 1 mark each. They are required to be answered in one word or one sentence each.
4. Case Based Questions (CBQ’s) are Question No. 7-10 and Question No. 25-27.
5. Question No. 11-12 and 28-29 are short answer questions carrying 3 marks each. Answers to them should not normally exceed 60-80 words each.
6. Question No. 13-15 and 30-32 are also short answer questions carrying 4 marks each. Answers to them should not normally exceed 80-100 words each.
7. Question No. 16-17 and 33-34 are long answer questions carrying 6 marks each. Answers to them should not normally exceed 100-150 words each.
8. Answers should be brief and to the point and the above word limit be adhered to as far as possible.
9. There is no overall choice. However, an internal choice has been provided in 2 questions of one mark, 2 questions of three marks, 2 questions of four marks and 2 questions of six marks. Only one of the questions have to be attempted.
10. In addition to this, separate instructions are given with each section and question, wherever necessary
PART — A
Q.1. Goods purchased for the following purpose are final goods:
(i) For satisfaction of wants
(ii) For investment in firm
(iii) Both (i) and (ii)
(iv) None of the above
Ans. (iii) Both (i) and (ii).
OR
Name the ‘economic assistance’ given by the government to the firms and households, with a motive of general welfare.
(i) Taxes
(ii) Rent
(iii) Subsidies
(iv) Remittances
Ans. (iii) Subsidies
Q.2. In the present COVID-19 times, many economists have raised their concerns that Indian economy may have to face a deflationary situation, due to reduced economic activities in the country.
Suppose you are a member of the high powered committee constituted by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI).
You have suggested that as the supervisor of commercial banks, ___________ (restriction/release) of the money supply be ensured, by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI).
Ans. release
Q.3. Which measure of money supply is considered as aggregate monetary resources of the country?
(i) M1
(ii) M2
(iii) M3
(iv) M4
Ans. (iii) M3
Q.4. Of which the Real GDP is considered as an index?
(i) Welfare of people
(ii) Happiness of people
(iii) GDP in Real terms
(iv) All of the above
Ans. (i) welfare of people
Q.5. What are demand deposits?
(i) Demand deposits are the deposits which can be with drawn on demand by the depositors from banks.
(ii) Demand deposits are the deposits which cannot be withdrawn on demand by the depositors from banks.
(iii) Demand deposits are the loans which can be taken from banks.
(iv) Demand deposits are the deposits where fixed amount needs to be given every month and the matured amount can be withdrawn during maturity period.
Ans. (i) Demand deposits are the deposits which can be withdrawn on demand by the depositors from banks.
Q.6. An Indian real estate company receives rent from Google in New York. This transaction would be recorded on ___________ side of ___________ account. (Fill up the blanks with correct alternative)
(i) credit, current
(ii) debit, capital
(iii) credit, capital
(iv) debit, current
Ans. (i) credit, current
Q.7. Read the following news report and answer Question 7 on the basis of the same:
Due to the Covid-19 situation, there has been a fall in the savings of the people, and they are spending the savings. This has led to the consumption to be done by the reduction of the savings. In order to control the situation the government has announced various stimulus packages to revive the economy and proving employment through road and railway building projects. Still the desired savings or ex-ante savings that is required for the functioning of the economy has reduced. It is seen that the private consumption expenditure, private investment expenditure and ex-ante savings has reduced the aggregate demand in the economy.
Q. Desired saving during an accounting year is called:
(i) ex-ante saving
(ii) ex-post saving
(iii) actual saving
(iv) none of these
Ans. (i) ex-ante saving
Q.8. In a situation of S < I:
(i) fall in expenditure through ‘S’ < rise in expenditure through ‘I’
(ii) fall in expenditure through ‘S’ > rise in expenditure through ‘I’
(iii) AD > AS
(iv) both (i) and (iii)
Ans. (iv) both ( i) and (iii).
Q.9. The relation between K and MPC is
(i) Indirect
(ii) Direct
(iii) No relation
(iv) It depends on Income
Ans. (ii) Direct
Q.10. The impact of ‘Excess Demand’ under Keynesian theory of income and employment, in an economy are : (choose the correct alternative)
(i) decrease in income, output, employment and general price level
(ii) decrease in nominal income, but no change in real output
(iii) increase in income, output, employment and general price level
(iv) no change in output/employment but increase in general price level.
Ans. (iv) no change in output/employment but increase in general price level.
Q.11. If the real GDP is Rs. 400 and nominal GDP is Rs. 450, calculate the Price Index (base = 100).
OR
Distinguish between final goods and intermediate goods. Give an example of each.
Ans. Given : Real GDP = Rs. 400
Nominal GDP = Rs. 450
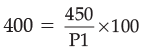
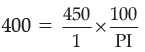
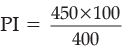
Price index (PI) = Rs. 112.50
OR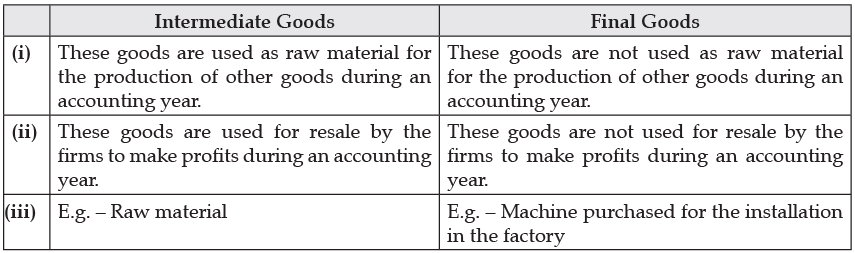
Q.12. By giving reasons, classify the following into intermediate or final goods.
(i) Machine purchased by a dealer of machines.
(ii) A car purchased by a household.
Ans. (i) Machine purchased by a dealer is an intermediate good because it is meant for resale to someone.
(ii) A car purchased by a household is a final good as it is used for self-consumption.
Q.13. What is Government Budget? Explain how taxes and subsidies can be used to influence the allocation of resources.
Ans. Government Budget is a statement showing estimated government expenditures and receipts during a financial year. Government can encourage production of selected goods and services by providing tax concessions. For example, electricity generation etc. Government can also give subsidies to enterprises who are willing to undertake production in backward areas etc. In this way, government budget can be used to influence allocation of resources in the country. Increasing taxes and reducing subsidies will have the opposite effects.
Detailed Answer :
Government Budget is an annual statement, showing item-wise estimates of receipts and expenditures during a fiscal year.
Reallocation of Resources :
(i) The government aims to reallocate resources according to economic and social priorities through its budgetary policy.
(ii) Government encourages the production of certain commodities by giving subsidies or tax reliefs,e.g., government encourages the use of ‘khadi products’ by providing subsidies.
(iii) Government can discourage the production of harmful goods like liquor or cigarettes, by imposing heavy excise duties or taxes. In India, we use progressive taxation, i.e., higher taxes from rich people and distribute these receipts through various welfare activities.
Q.14. In an economy C= 200 + 0.5 Y is the consumption function where C is the consumption expenditure and Y is the national income. Investment expenditure is Rs. 400 crores.
Is the economy in equilibrium at an income level Rs. 1500 crores? Justify your answer.
OR
Define :
(i) Ex-Ante Savings
(ii) Full Employment
Ans. Given, Consumption function (C) = 200 + 0.5Y, Investment (I) = 400, Level of income (Y) = 1500
At Equilibrium level :
AD = AS
Y = C+I
thus, Y = (200 + 0.5Y) + 400
Y – 0.5 Y = 600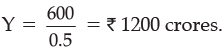
The equilibrium level of income = Rs. 1200 crores.
The given income (Rs. 1500 crores) is greater than equilibrium level of income (Rs. 1200 crores). Therefore, the economy is not in equilibrium.
Or
(i) Ex-ante savings : Ex ante savings refers to the planned savings of an economy at different levels of income.
(ii) Full employment : It refers to a situation, where all the willing and capable resources get a gainful job at prevailing wage rate. It is a situation where there is no involuntary unemployment.
Q.15. Explain the concept of Money Supply.
OR
Explain ‘government’s banker’ function of the central bank.
Ans. The Supply of Money means the total stock of money (paper notes, coins and demand deposits of banks) in circulation held by the public at any particular point of time.
Thus, two components of money supply are: (i) Currency (paper notes and coins), and (ii) Demand Deposits of Commercial Banks.
Money supply or supply of money means total amount of money available in an economy. In other words, money supply refers to the volume of money held by the people in the country for transactions or settlement of debts.
OR
Central bank acts as a banker, agent and financial advisor to the government.
It keeps the accounts of all government banks and manages government treasuries.
The loans are given to the government without any interest for short terms.
It also transfers Government Funds. It also buys and sells securities, treasury bills on behalf of the government.
Being the apex bank of the country, it advices the government from time to time on economic, financial and monetary matters.
Q.16. Explain the distinction between Revenue receipts and Capital receipts in a government budget. Give their components.
Ans. Revenue receipts are receipts which neither create a liability nor lead to reduction in assets whereas Capital Receipts are the receipts which either create a liability or reduce assets of the government.
Components of Revenue Receipts are :
– Tax revenue receipts (direct and indirect taxes)
– Non-tax revenue receipts.
Components of Capital Receipts are:
– recovery of loans
– borrowings and other liabilities
– other capital receipts like disinvestment.
Detailed Answer :
The difference between Revenue Receipts and Capital Receipts is :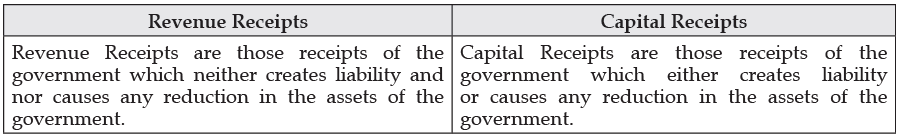
Components of Revenue Receipts :
(i) Tax Receipts : Tax is the compulsory payment made to the government. All the receipts from tax sources are termed as tax receipts. Tax can be of two types: Direct Tax and Indirect Tax. The burden of Direct Taxes cannot be shifted from where as the burden of indirect taxes can be shifted from one party to another. Example: Goods and Service Tax.
(ii) Non Tax Receipts : Non-tax receipts are the receipts of the government from all the sources other than tax sources. Example: Fees, forfeitures, etc.
Components of Capital Receipts :
(i) Borrowings : Borrowings from external and internal sources by the government are capital receipts since they created liability for the government.
(ii) Disinvestment : Disinvestment means withdrawing the current investment of government in public sector undertaking and giving it to private sectors. Disinvestment is capital receipt because it reduces assets of the government.
(iii) Dissaving : Dissaving is a co component of Capital receipts since it reduces assets of government.
Q.17. (a) Calculate National Income from the following data:

(b) "While Calculating National Income Net Exports" are included which is the difference between Imports and Exports." Justify the statement.
OR
Differentiate between National Income at Current Prices and National Income at Constant Prices. Which of the two presents a better view of the economic growth of economy and Why?
Ans. (a) N. I. = (i) + (iii) + (v) - (viii) - (ix) - (iv) + (vii)
= 900 + 400 + 250 - 20 - 30 - 100 + (- 40)
= Rs. 1,360 crore.
(b) Exports form a part of National Income because exports are provided by the producers of the domestic territory of the country. Exports are as a matter of fact are a part of domestic production. Now Imports on the other hand are a burden on the domestic production. So, the net exports that is the difference between the two is included in the calculation of National Income.
OR
National income at Constant Prices : When National product is estimated on the basis of prices prevailing in the base year, it is called national income at constant prices or real national income.
National Income at Current Prices: When national product is estimated on the basis of prices prevailing in the current year, it is called national income at current prices or nominal national income.
National income at constant prices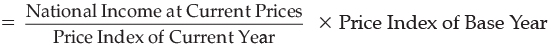
National income at constant prices reflects the real growth of an economy because it increases only when there is an increase in real national output over a period of time.
National income at current prices may increase due to increase in prices of goods and services during the current year, thus it does not reflect the true picture of economic growth.
Part - B
Q.18. ___________ was the Indian Finance Minister in 1991, acknowledged for his capabilities to steer away the economic crisis looming large on the erstwhile Indian Economy. (Choose the correct alternative)
(i) Dr. Subramanian Swamy
(ii) Dr. Manmohan Singh
(iii) Pranab Mukherjee
(iv) Dr. Urjit Patel
Ans. (ii) Dr. Manmohan Singh
Q.19. 5 year plans were formulated by ______________ in India.
(i) Planning Commission
(ii) UPSC
(iii) Finance Commission
(iv) NCERT
Ans. (i) Planning Commission
Q.20. Read the following statements - Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Choose one of the correct alternatives given below:
Assertion (A) : All before demonetisation has occurred in the context of hyperinflation, wars, political upheavals or other extreme circumstances.
Reason (R) : Discontinuing the big notes boosted the economy Alternatives:
(i) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A)
(ii) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A)
(iii) Assertion (A) is true but Reason (R) is false.
(iv) Assertion (A) is false but Reason (R) is true.
Ans. Assertion (A) is true but Reason (R) is false.
Q.21. Estimation of poverty in urban areas is at the consumption of per day calories is—
(i) Less than 2000
(ii) Less than 2100
(iii) Less than 2400
(iv) Less than 2200
Ans. (ii) Less than 2100
Q.22. From the set of events/systems given in column I and corresponding relevant fact given in column II, about China, choose the correct pair of statement :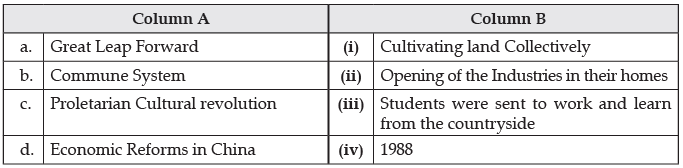
Alternatives :
(i) a - i
(ii) b - ii
(iii) c - iii
(iv) d – iv
Ans. (iii) C – iii
Q.23. When was The Great Leap Forward (GLF) Campaign launched in China?
(i) 1960s
(ii) 1950s
(iii) 1970s
(iv) 1990s
Ans. (ii) 1950s
Q.24. Read, the following hypothetical Case Study, carefully and answer the question number 24 on the base of the same.:
In order to produce in an Economy, there are the four factors, i.e., land, labour, capital and entrepreneur are required. It is the duty of the government to help and nurture all the factors. Moreover the major investment needs to be done on Capital. There are two types of Capital, namely Physical and Human Capital. In order to increase the physical capital the government needs to invest in infrastructure and acquisition of new technologies. These leads to generation of employment, leading to the reduction in the problem of unemployment, that the country like India is suffering with.
There are different types of unemployment present in India, namely seasonal, disguised, industrial, fictional and many other. Most of the employment problems can be solved if the government focuses on investment in education to improve the quality of Human Capital, and for skill development, increase in efficiency and productivity and overall growth of the economy, for all the three sectors in the economy.
Q. Why do we need to invest in human capital?
(i) Skill development
(ii) Increase efficiency
(iii) Increase Productivity
(iv) All of the above
Ans. (iv) All of the above
Q.25. Mention the state that has achieved prosperity in Agriculture and Horticulture?
Ans. Punjab/Haryana/Himachal Pradesh.
Q.26. The rural banking structure in India consists of a set of multi-agency institutions. ___________ (Regional Rural Banks / Small Industries Development Bank of India) is expected to dispense credit at cheaper rates for agricultural purposes to farmers.
Ans. Regional Rural Banks
Q.27. Read, the following hypothetical Case Study, carefully and answer the question number 27 on the base of the same.
Since after Independence, the condition of the labour workforce has been improving in India, All the factors such as education policy and health care has led to the improvement of the work force. The growth of population has had posed some serious threats in the Economy with respect to the employment generation.
The prospects of the Rural development have been improving with the respect of the growth of many financial institutions in the rural areas. The NABARD oversees all the regional rural banks and regulates them for the proper functioning of the Rural Economy.
There have been many skill development initiatives taken by the government of India to improve the Human Capital as well.
Q. Identify the correctly matched item from Column A to that of Column B: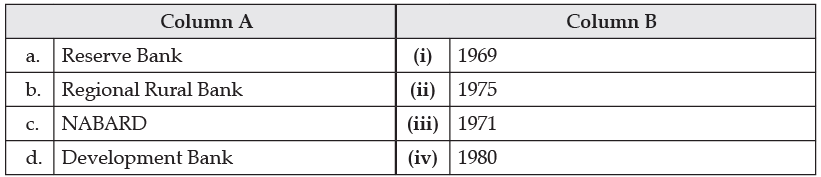
(i) a – (i)
(ii) b – (ii)
(iii) c – (iii)
(iv) d - (iv)
Ans. (ii) (b)Regional Rural Bank (ii) 1975
Q.28. “During colonial period, India was a semi-feudal economy.” Justify.
Or
State the trend in the contribution of different sectors in India’s total employment.
Ans. It is true that during colonial period, India was semi-feudal economy because :
(i) At the time of independence, there were two aspects of the Indian economy. The Britishers introduced a new type of land tenure system in India which gave birth to two classes-Zamindars or landlords and landless tenants or cultivators.
(ii) The landlords were very cruel to the cultivators. They used to charge very high rate of rent and land revenue. That’s why feudal relations (landlord tenant relations) appeared in this system.
(iii) In the middle of 19th century, capital investment was made in many new sectors like cotton textile, jute, sugar, tea, rubber and coffee plantation, etc. This created two classes-capitalists and labourers. So, at the time of independence, features of both (feudal and capitalist) appeared in this system.
OR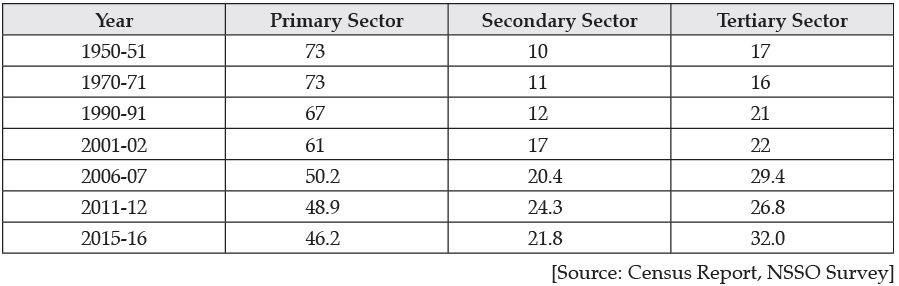
The trend in the employment of various sectors in employment can be summarised from the above data as :
Primary Sector : The employment in the primary sector has been on a constant decline from 73% in 1950-51 to 46.2% in 2015-16.
Secondary Sector : The employment in the secondary sector has increased from 10% in 1950-51 to 21.8% in 2015-16.
Tertiary Sector: The employment in the tertiary sector has increased from 17% in 1950-51 to 32% in 2015-16.
Q.29. Why are children not included in working population?
Ans. Working population means able-bodied persons and adults. Children are unable to perform productive activities.
Use of children in work is equivalent to denying them childhood. Children’s right to playing and schooling should be respected. It is doubly criminal to turn them into dull adults and old persons.
In every civilised society, children’s rightful place is school and playground. Hence, children are not included in working population for the purpose of employment.
Q.30. A“griculture sector appears to be adversely affected by the economic reform process.” Explain the given statement.
Ans. The agricultural sector was adversely affected by the reform process in the following manner :
(i) Public investment in agriculture sector especially in infrastructure like irrigation, power etc. has been reduced in the reform period
(ii) Reduction of fertilizer subsidy has increased the cost of production affecting thereby the small and marginal farmers.
(iii) Increased international competitiveness due to liberalisation and reduction of import duties.
(iv) Shift from food crops to cash crops due to export-oriented policy in agriculture led to a rise in prices of food-grains.
Q.31. Explain co-operative marketing societies.
Ans. These societies have been set up to improve agricultural marketing. The farmers make such societies themselves. In 1964, National Agricultural Co-operative Marketing Federation of India or NAFED was set up. The main objective of NAFED was to establish the co-ordination among co-operative societies. These societies have made much progress in the states of Punjab, Haryana, Maharashtra, Uttar Pradesh etc.
The farmers get the following benefits from them:
(i) Free from intermediaries
(ii) Reasonable price of the produce and loans on cheap rate of interest
(iii) Storage facilities
(iv) Free from exploitation
Q.32. Discuss the external sector comparison of India and China.
Ans. The comparison of external sectors of both the countries can be made as under :
(i) Exports and imports : Exports and imports of China are 8 and 6 times higher in comparison to India respectively.
(ii) Share in world's export : China's share in world's exports is 8% against 1% in India. It means India's share in world's export is also lower in comparison to China.
(iii) Foreign exchange reserves : Foreign exchange reserves are also 6 times higher in China in comparison to India.
(iv) Bilateral trade : Bilateral trade between India and China rose by 18.63% year by year to hit $ 84.44 billion.
Q.33. Study the following chart showing the Growth of Employment and Gross Domestic Product and analyse the trend of the two variables from 1990-2012.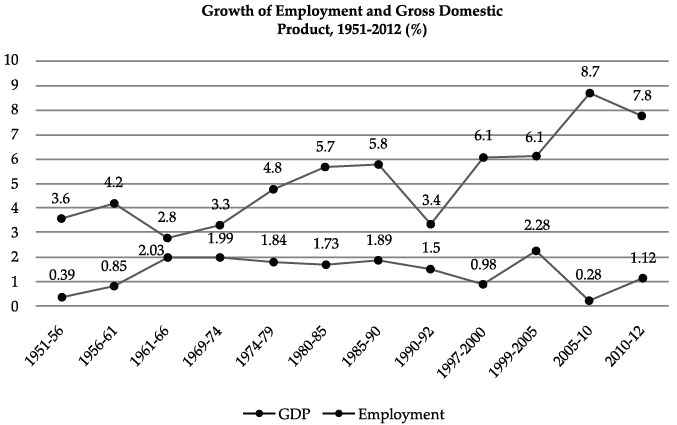
OR
Write down the causes of rural in indebtedness in India?
Ans. The period between 1990 to 2012 had been a significant one. Introduction of Economic Reforms in India has changed everything in India. Variables shown in the given graph show that GDP growth rate has taken an upwards tread over the years whereas the situation of Employment growth rate has seen major fluctuations while going down in overall trend.
GDP growth rate has increased from a meagre 3.4% in 1991 to 7.8% in 2012. However the employment growth rate has shown declining trends from 1.5% in 1991 to 1.12% in 2012. Between the period 1999-2005 the employment generation rate was at peak since independence i.e. 2.28% p.a. with the corresponding GDP growth rate standing at a decent 6.1% p.a.
The gap between the two variables is maximum between the period 2005-10 when the employment growth rate hit the lowest in history of Independent India i.e. 0.28%. In the same period the GDP growth rate had hit the highest level since independence to the tune of 8.7% p.a. Indian economy has witnessed the peculiar phenomena of 'jobless growth' over all these years. Learning from the situation government had put in serious efforts on employment front and brought it to a level of 1.12% p.a. between the period 2010-12.
In all the period between 1990-2012 has been a real roller coaster ride for the Indian economy on the two fronts of GDP and Employment Growth rate.
OR
The main causes are as under :
(i) Poverty: In fact, annual income of the farmers is very low. So, they always live below poverty line.
They have to borrow money for many purposes.
(ii) Unproductive expenditure: Most of the farmers borrow to celebrate social customs like marriages, religious festivals, etc. Births and deaths also lead to unproductive expenditure.
(iii) Litigation: The farmers borrow for litigation also. Litigation is always very expensive which adds to the problem of indebtedness.
(iv) To make improvement on land: The farmers mostly borrow to make improvement on land. It is a positive thinking, but it needs to be done by saving and not by borrowing.
(v) Inherited debt: It is called ancestral debt also. A farmer also inherits the debts of his father along with the land. It contributes a lot in rural indebtedness.
(vi) Illiteracy: The farmers are illiterate. The moneylenders encourage the farmers to borrow. They make a plan to mortgage their land. They charge higher rate of interest. The farmers are unable to repay the debt. Ultimately they take away the land of the farmers.
Q.34. State, giving valid reasons whether the following statements are true or false. (i) Since independence, the benefits of the increase in economic growth in India have trickled down to the people at the bottom of population pyramid.
(ii) Human Capital Formation gives birth to innovation, invention and technological improvements.
(iii) There exists an inverse correlation between infrastructural growth and national income.
Ans. (i) The given statement is false as there have been different factors (like massive rate of growth of population, unequal distribution of wealth, skewed benefits accruing from green revolution etc.) due to which benefits of increase in the Gross Domestic Product have not trickled down completely to the people at the bottom of population pyramid.
(ii) The given statement is true. Human Capital Formation (investment in education/health) not only increases the productivity of the available human resources but also stimulates innovations and creates ability to adopt and adapt to the new technologies.
(iii) The given statement is false, as generally, there exists a positive correlation between infrastructural growth and national income. Infrastructure is the support system for an economy which facilitates greater productive activities, higher levels of output/income and improvement of quality of life in an economy.
|
130 docs|5 tests
|
FAQs on CBSE Sample Question paper - 10 Economics, Class 12 - Sample Papers for Class 12 Commerce
| 1. What is the CBSE sample question paper for Class 12 Economics? |  |
| 2. How can I access the CBSE sample question paper for Class 12 Economics? |  |
| 3. Are the questions in the CBSE sample question paper for Class 12 Economics similar to the actual exam? |  |
| 4. How can solving the CBSE sample question paper for Class 12 Economics benefit students? |  |
| 5. Can the CBSE sample question paper for Class 12 Economics be used as the sole study material? |  |





















