SSC CGL Exam > SSC CGL Notes > General Awareness for SSC CGL > Carbon and its Compound
Carbon and its Compound | General Awareness for SSC CGL PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| The Covalent Bond |

|
| Versatile Nature of Carbon |

|
| Chemical Properties of Carbon Compounds |

|
| Important Carbon Compounds |

|
| Soaps and Detergents |

|
Introduction
Types of Compounds
- Organic Compounds
- Inorganic Compounds
Organic Compounds
- Comprised mainly of carbon and form the basis of all living organisms.
The Covalent Bond
- Carbon always forms covalent bonds.
- Covalent bonds are formed by the sharing of electron pairs between atoms.
Noble Gas Configuration of Carbon
- Carbon is tetravalent and does not form ionic bonds by losing or gaining four electrons (C4+or C4-).
- It forms bonds by sharing electrons with other atoms, such as hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, and chlorine, to achieve a stable noble gas configuration.
Examples of Covalent Bonds
- Hydrogen (H2): Single bond between hydrogen atoms.
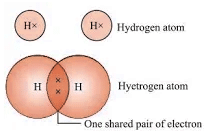
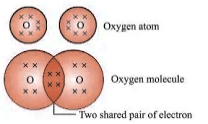
- Oxygen (O2): Double bond between oxygen atoms.
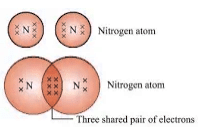
- Nitrogen (N2): Triple bond between nitrogen atoms.
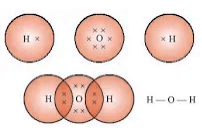
- Water (H2O): Single covalent bonds between one oxygen and two hydrogen atoms.
Physical Properties of Covalent Compounds
- Low melting and boiling points due to weak intermolecular forces.
- Poor conductors of electricity as electrons are shared between atoms, forming no charged particles.
Question for Carbon and its Compound
Try yourself:
Which type of bond is formed between two oxygen atoms in a molecule of oxygen gas (O2)?View Solution
Versatile Nature of Carbon
- Catenation: Carbon can form long chains, branched chains, and rings by bonding with other carbon atoms using single, double, or triple covalent bonds.
- Tetravalency: With four valence electrons, carbon can form bonds with four atoms, including other carbons, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, and sulfur.
Hydrocarbons
- Compounds made up of hydrogen and carbon.
- Two types: Saturated Hydrocarbons and Unsaturated Hydrocarbons.
Saturated Hydrocarbons
- Single bonds between carbon atoms.
- Example: Alkanes with the general formula CnH2n+2.
Unsaturated Hydrocarbons
- Double or triple bonds between carbon atoms.
- Alkenes: Double bonds, general formula CnH2n.
- Alkynes: Triple bonds, general formula CnH2n-2.
- Ethane (C2H6): Example of a saturated hydrocarbon.
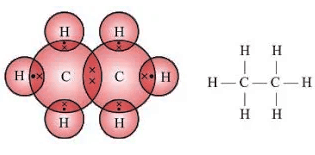
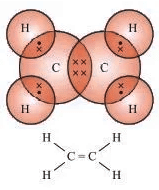
- Ethene (C2H4): Example of an unsaturated hydrocarbon (alkene).
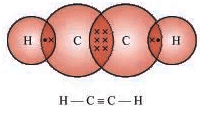
- Ethyne (C2H2): Example of an unsaturated hydrocarbon (alkyne).
Structure of Carbon Compounds
Straight (unbranched) chain
- Example: Propane (C3H8).
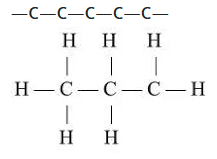
- Example: Propane (C3H8).
Branched
- Compounds with the same molecular formula but different structures are called structural isomers (phenomenon: structural isomerism).
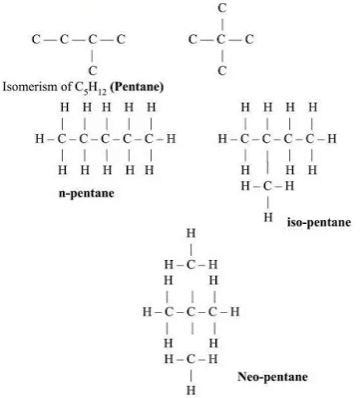
- Compounds with the same molecular formula but different structures are called structural isomers (phenomenon: structural isomerism).
Cyclic
- Example: Cyclohexane (C6H12).
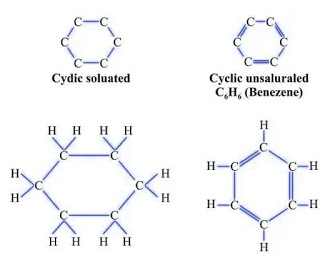
- Example: Cyclohexane (C6H12).
Functional Groups
- In hydrocarbon chains, one or more hydrogen atoms are replaced by other atoms according to their valency.
- These atoms or groups of atoms (heteroatoms) make carbon compounds reactive and determine their properties.
Homologous Series
A series of compounds with the same functional group replacing hydrogen in a carbon chain.
Example: Alcohols (CH3OH, C2H5OH, C3H7OH, C4H9OH).- Same general formula.
- Differ by a –CH2 group, with a molecular mass difference of 14 amu.
- Same chemical properties with gradual changes in physical properties.
- Identify the number of carbon atoms in the compound.
- Use suffixes or prefixes to indicate the functional group.
Chemical Properties of Carbon Compounds
Combustion:
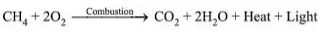
- Carbon and its compounds are used as fuels due to their ability to burn in air, releasing a lot of heat energy.
- Saturated hydrocarbons burn with a blue, non-sooty flame.
- Unsaturated hydrocarbons burn with a yellow, sooty flame due to incomplete oxidation.
Oxidation:
- Alcohols can be converted to carboxylic acids using oxidizing agents like alkaline KMnO4 or acidic potassium dichromate.
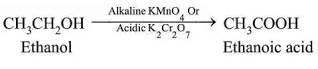
Addition Reaction:
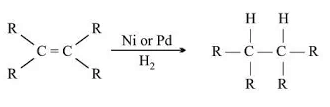
- Unsaturated hydrocarbons add hydrogen in the presence of catalysts like palladium or nickel.
- Example: Hydrogenation of vegetable oils to produce vegetable ghee.
Substitution Reaction:
- Occurs in hydrocarbons where hydrogen atoms are replaced by other atoms.

Important Carbon Compounds
Ethanol
Physical Properties
- Colourless, pleasant smell, and burning taste.
- Soluble in water, volatile, low boiling point (351 K), neutral compound.
Chemical Properties
Reaction with Sodium:
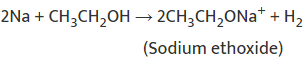 Used to test for ethanol by the evolution of H2 gas (burns with a pop sound).
Used to test for ethanol by the evolution of H2 gas (burns with a pop sound).Dehydration

Physical Properties of Ethanoic acid
- Colourless, sour taste, vinegar smell, boiling point of 391 K.
- Pure CH3COOH forms a colorless solid when frozen, called glacial acetic acid.
Chemical Properties
Esterification:
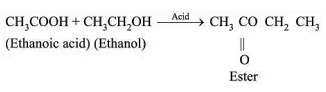
Sweet smelling ester is formed.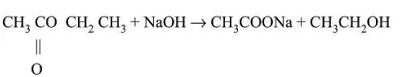
Saponification: Soap is prepared using this process.
Reaction with Base:
- NaOH + CH3COOH → CH3COONa + H2O.
Reaction with Carbonates and Hydrogen Carbonates:
- 2CH3COOH + Na2CO3 → 2CH3COONa + H2O + CO2.
- CH3COOH + NaHCO3 → CH3COONa + H2O + CO2.
Question for Carbon and its CompoundTry yourself: Which type of hydrocarbon has double or triple bonds between carbon atoms?View Solution
Soaps and Detergents
Soap: Sodium or potassium salts of long-chain carboxylic acids (e.g., C17H35COONa).
- Effective only in soft water.
Detergents: Ammonium or sulphonate salts of long-chain carboxylic acids.
- Effective in both hard and soft water.
Soap molecule has:
- Ionic (hydrophilic) part
- Long hydrocarbon chain (hydrophobic) part
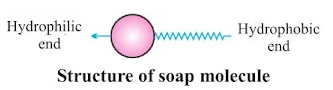
Cleansing Action of Soap
- Dirt, typically oily, attaches to the hydrophobic end of soap molecules while the hydrophilic end remains in water, forming micelles.
- Soap micelles dissolve dirt and grease, cleaning the cloth.
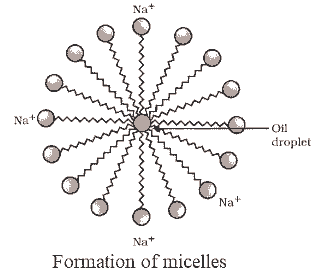
- Hard water's calcium and magnesium salts react with soap to form insoluble scum, hindering cleansing action.
- Detergents do not form scum with hard water, cleaning clothes effectively.
The document Carbon and its Compound | General Awareness for SSC CGL is a part of the SSC CGL Course General Awareness for SSC CGL.
All you need of SSC CGL at this link: SSC CGL
|
486 videos|1936 docs|395 tests
|
FAQs on Carbon and its Compound - General Awareness for SSC CGL
| 1. What is the covalent bond in carbon compounds? |  |
Ans. A covalent bond in carbon compounds is a type of chemical bond where atoms share electrons to achieve stability in their outer electron shells, allowing them to form strong bonds with other atoms.
| 2. How is the versatile nature of carbon beneficial in the formation of different compounds? |  |
Ans. The versatile nature of carbon allows it to form strong bonds with other elements, leading to the creation of a wide variety of compounds with diverse properties and functions, such as hydrocarbons, alcohols, and organic acids.
| 3. What are some important carbon compounds mentioned in the article? |  |
Ans. Some important carbon compounds discussed in the article include hydrocarbons, alcohols, organic acids, soaps, and detergents, each with unique chemical properties and uses in daily life.
| 4. How do soaps and detergents utilize carbon compounds for their cleaning properties? |  |
Ans. Soaps and detergents contain carbon compounds known as surfactants, which have both hydrophilic and hydrophobic properties. These properties allow them to interact with both water and oils, effectively removing dirt and grease from surfaces.
| 5. How do the chemical properties of carbon compounds contribute to their importance in various industries? |  |
Ans. The chemical properties of carbon compounds, such as their ability to form stable bonds and diverse structures, make them essential in industries like pharmaceuticals, plastics, and agriculture, where they are used in the production of medicines, materials, and fertilizers.
Related Searches















