Class 9 Science Chapter 2 Case Based Questions - Is Matter Around Us Pure??
(I) Read the given passage and answer the questions that follow based on the passage and related studied concepts.
A pure substance consist of single type of particles. Mixture consist of more than one kind of pure form of matter. Mixtures can be separated by physical methods but pure substances especially compounds cannot be separated into chemical constituents by physical methods. Pure substance has same composition throughout. Soil and soft drinks are mixtures. Mixtures can be separated by various methods depending upon nature of substance present in it. Solution is a homogeneous mixture.
Q1: Name the process by which pure NaCl can be obtained from salt solution.
Ans: The process to obtain pure NaCl from a salt solution is known as crystallisation.
Q2: What are alloys-compounds or mixtures?
Ans: Alloys are homogeneous mixtures made from two or more metals or a combination of a metal and a non-metal. They cannot be separated into their individual components through physical methods. Key points about alloys:
- They retain the properties of their constituent materials.
- Alloys can have varying compositions.
- For example, brass is an alloy consisting of approximately 30% zinc and 70% copper.
Q3: What is size of particles in solution?
Ans: The size of particles in a solution is typically less than 1 nm (10-9 metres).
- These particles are so small that they cannot be seen with the naked eye.
- Due to their tiny size, they do not scatter light, making the path of light invisible in a solution.
- Particles in a solution cannot be separated by filtration.
- When left undisturbed, the particles do not settle, indicating that a solution is stable.
Q4: What is solute and solvent in cold drinks?
Ans: In cold drinks, the components are classified as follows:
Solutes: These are substances that dissolve in the solvent. In cold drinks, common solutes include:
- Carbon dioxide (CO2) gas
- Sugar
- Preservatives
Solvent: This is the substance that dissolves the solutes. In cold drinks, the solvent is: Water
(II) Study the table showing melting points and boiling points of certain compounds. Answer the questions based on the table and related studied concepts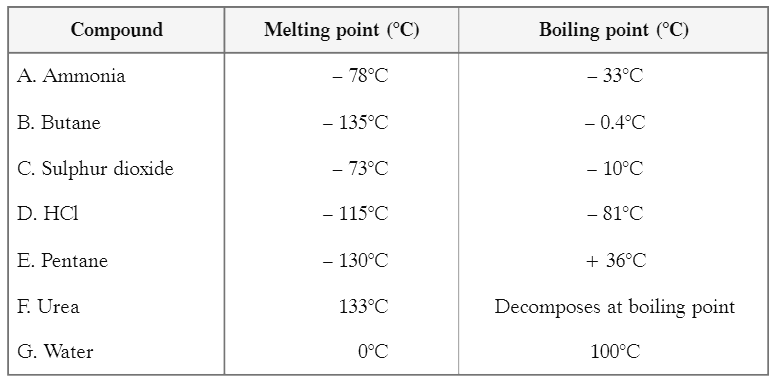 Q1: Which one of the given substances may be separated by using a water condenser?
Q1: Which one of the given substances may be separated by using a water condenser?
Ans: Pentane can be separated using a water condenser because:
- The temperature of the water condenser is 25°C.
- The boiling point of pentane is 36°C.
Since the boiling point of pentane is higher than the temperature of the condenser, it can be effectively condensed and separated.
Q2: How can gases be separated that are present in air?
Ans: The separation of gases present in air can be achieved through fractional distillation of liquid air.
Q3: If sample of urea has melting point 129°C, then:
(a) It is impure
(b) It is pure
(c) It can not be predicted
(d) The compound is not urea
Ans: (a) It is impure
Q4: Which of the following will have boiling point 100°C?
(a) Distilled water
(b) Sea water
(c) River water
(d) Well water
Ans: (a) Distilled water will have boiling point 100°C.
|
84 videos|544 docs|60 tests
|
FAQs on Class 9 Science Chapter 2 Case Based Questions - Is Matter Around Us Pure??
| 1. What is meant by 'pure substances' in the context of matter? |  |
| 2. How can we differentiate between pure substances and mixtures? |  |
| 3. What are the methods to separate components of a mixture? |  |
| 4. Can you provide examples of pure substances and mixtures from everyday life? |  |
| 5. Why is it important to understand the difference between pure substances and mixtures in science? |  |

















