Class 9 Science Chapter 5 Case Based Questions - The Fundamental Unit of Life
(I) Read the given passage and answer the questions based on the passage and related studied concepts.
Although the cell is the basic structural and functional unit of all organisms, cells differ enormously in size, shape, and function. Some are free living, independent organisms, while others are immovable fixed as part of tissues of multicellular organisms. All cells exchange materials with their immediate environment and therefore, have a plasma membrane that controls which substances are exchanged by allowing some materials to pass through it while slowing or stopping others. The cytoplasm is protected from the environment, yet still can exchange materials with it. Within the cytoplasm, cells differ in the type and number of organelles. Prokaryotic cells have the simplest structure with each independent cell lacking any internal membrane organelles, including the lack of a nuclear membrane to separate the genetic chromosome material from the rest of the cytoplasm. More typical and more specialized are the eukaryotic cells, with a double nuclear membrane and membrane organelles specialised to fit their function. Since no one cell would have all organelles possible, observing a variety of animal cells will give you an idea of the similarities and differences among cells.
Q1: State two differences between Prokaryotic cell and Eukaryotic cell.
Ans: Differences between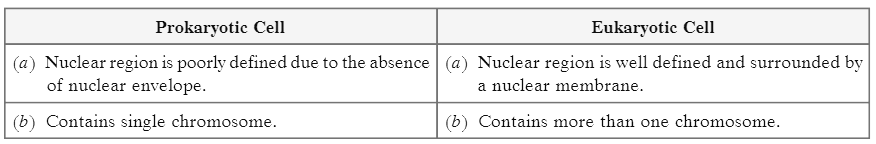
Q2: Name a cell organelle found only in plant cell and name its type.
Ans: Plastids are organelles found exclusively in plant cells. They are classified into two main types:
- Chromoplasts - These contain pigments and give colour to the plant.
- Leucoplasts - These are colourless and primarily serve as storage for substances like starch and oils.
Among chromoplasts, those that contain chlorophyll are known as chloroplasts, which are essential for photosynthesis.
Q3: What is the function of Golgi body?
Ans: The Golgi body is a vital organelle in the cell with several key functions:
- It acts as the cell's secretory organelle, packaging and dispatching materials.
- It is involved in the formation of lysosomes and peroxisomes.
- It modifies proteins and lipids received from the endoplasmic reticulum (ER).
- It plays a role in the synthesis of complex sugars from simpler ones.
Q4: What is the function of Endoplasmic Reticulum(ER)?
Ans: The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) serves essential functions in the cell, including:
- Assisting in the synthesis of proteins through the rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER), which has ribosomes on its surface.
- Facilitating the production of lipids in the smooth endoplasmic reticulum (SER), crucial for cell function.
- Acting as a transport network for materials, especially proteins, within the cell.
- Providing a structural framework for various biochemical activities.
In liver cells, the SER also plays a vital role in detoxifying substances.
(II) Read the given passage and answer the questions based on the table and related studied concepts.
Plant and animal cells have several differences and similarities. For example, animal cells do not have a cell wall or chloroplasts but plant cells do. Animal cells are mostly round and irregular in shape while plant cells have fixed, rectangular shapes. Plant and animal cells are both eukaryotic cells, so they have several features in common, such as the presence of a cell membrane, and cell organelles, like the nucleus, mitochondria and endoplasmic reticulum. Given below a comparison of Animal Cells and Plant Cells shown in the table.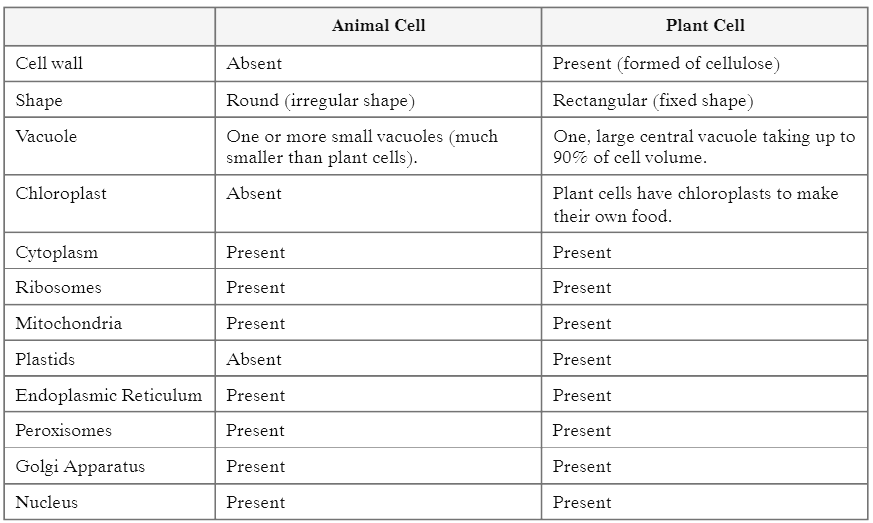
Ans: Plant and animal cells have several differences and similarities:
- Animal cells lack a cell wall and chloroplasts, while plant cells possess both.
- Animal cells are typically round and irregular, whereas plant cells are fixed and rectangular.
- Both types are eukaryotic, sharing features like a cell membrane and organelles such as the nucleus, mitochondria, and endoplasmic reticulum.
Below is a comparison of animal and plant cells:
- Cell Wall: Present in plant cells, absent in animal cells.
- Chloroplasts: Present in plant cells, absent in animal cells.
- Shape: Fixed in plant cells, irregular in animal cells.
|
84 videos|541 docs|60 tests
|
FAQs on Class 9 Science Chapter 5 Case Based Questions - The Fundamental Unit of Life
| 1. What is the fundamental unit of life? |  |
| 2. What are the main differences between plant and animal cells? |  |
| 3. What is the function of the cell membrane? |  |
| 4. How do cells obtain energy? |  |
| 5. What role do organelles play in a cell? |  |






















