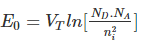Electrical Engineering (EE) Exam > Electrical Engineering (EE) Notes > Electrical Engineering SSC JE (Technical) > P-N Junction Diode - 1
P-N Junction Diode - 1 | Electrical Engineering SSC JE (Technical) - Electrical Engineering (EE) PDF Download
What is a P-N Junction?
A p-n junction is an interface or a boundary between two semiconductor material types, namely the p-type and the n-type, inside a semiconductor.
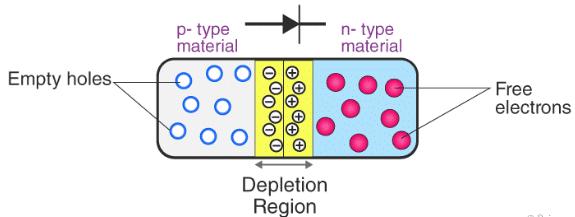 Unbiased P-N Junction
Unbiased P-N Junction
- The p-side or the positive side of the semiconductor has an excess of holes and the n-side or the negative side has an excess of electrons.
- In a semiconductor, the p-n junction is created by the method of doping. The process of doping is explained in further detail in the next section.
Formation of P-N Junction
- As we know, if we use different semiconductor materials to make a p-n junction, there will be a grain boundary that would inhibit the movement of electrons from one side to the other by scattering the electrons and holes and thus we use the process of doping.
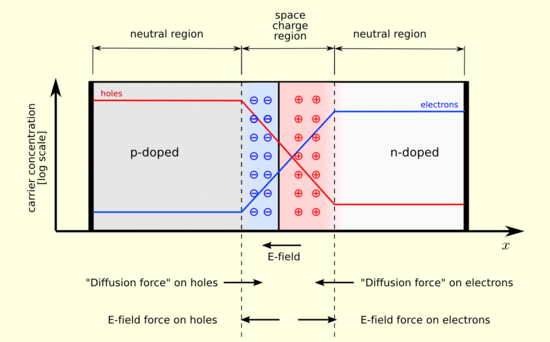 P-N Junction Formation
P-N Junction Formation - We will understand the process of doping with the help of this example. Let us consider a thin p-type silicon semiconductor sheet. If we add a small amount of pentavalent impurity to this, a part of the p-type Si will get converted to n-type silicon.
- This sheet will now contain both the p-type region and n-type region and a junction between these two regions. The processes that follow after the formation of a p-n junction are of two types – diffusion and drift.
- As we know, there is a difference in the concentration of holes and electrons at the two sides of a junction, the holes from the p-side diffuse to the n-side, and the electrons from the n-side diffuse to the p-side. This gives rise to a diffusion current across the junction.
- Also, when an electron diffuses from the n-side to the p-side, an ionized donor is left behind on the n-side, which is immobile. As the process goes on, a layer of positive charge is developed on the n-side of the junction.
- Similarly, when a hole goes from the p-side to the n-side, an ionized acceptor is left behind in the p-side, resulting in the formation of a layer of negative charges in the p-side of the junction. This region of positive charge and negative charge on either side of the junction is termed the depletion region.
- Due to this positive space charge region on either side of the junction, an electric field direction from the positive charge towards the negative charge is developed. Due to this electric field, an electron on the p-side of the junction moves to the n-side of the junction.
- This motion is termed the drift. Here, we see that the direction of the drift current is opposite to that of the diffusion current.
Question for P-N Junction Diode - 1Try yourself:The p-region has a greater concentration of __________ as compared to the n-region in a P-N junction.
View Solution
Biasing Conditions for the P-N Junction Diode
There are two operating regions in the P-N junction diode, P-type & N-type.
There are three biasing conditions for P-N junction diode and this is based on the voltage applied:
- Zero bias: There is no external voltage applied to the P-N junction diode.
- Forward bias: The positive terminal of the voltage potential is connected to the p-type while the negative terminal is connected to the n-type.
- Reverse bias: The negative terminal of the voltage potential is connected to the p-type and the positive is connected to the n-type.
1. Forward Bias
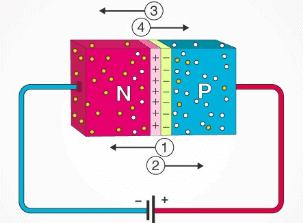 Forward Bias of the P-N Junction
Forward Bias of the P-N Junction
- In the figure, 1 represents battery induced electric field, 2 represents Build-in electric field, 3 represents conventional current, and 4 represents Electron current.
- When the p-type is connected to the positive terminal of the battery and the n-type to the negative terminal then the P-N junction is said to be forward-biased. When the P-N junction is forward biased, the built-in electric field at the P-N junction and the applied electric field are in opposite directions.
- When both the electric fields add up the resultant electric field has a magnitude lesser than the built-in electric field. This results in a less resistive and thinner depletion region.
- The depletion region’s resistance becomes negligible when the applied voltage is large. In silicon, at the voltage of 0.6 V, the resistance of the depletion region becomes completely negligible and the current flows across it unimpeded.
2. Reverse Bias
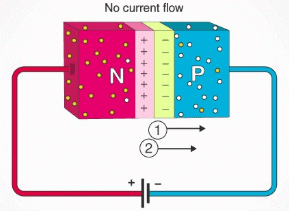 Reverse Bias of the P-N Junction
Reverse Bias of the P-N Junction
- In the figure, 1 represents a battery-induced electric field, and 2 represents Build-in electric field.
- When the p-type is connected to the negative terminal of the battery and the n-type is connected to the positive side then the p-n junction is said to be reverse biased. In this case, the built-in electric field and the applied electric field are in the same direction.
- When the two fields are added, the resultant electric field is in the same direction as the built-in electric field creating a more resistive, thicker depletion region.
- The depletion region becomes more resistive and thicker if the applied voltage becomes larger.
P-N Junction Formula: The formula used in the p-n junction depends upon the built-in potential difference created by the electric field is given as:
where E0 is the zero bias junction voltage, VT is the thermal voltage of 26mV at room temperature, ND and NA are the impurity concentrations, ni is the intrinsic concentration
Question for P-N Junction Diode - 1Try yourself: What happens when a P-N junction is forward biased?View Solution
How does current flow in the P-N junction diode?
- The flow of electrons from the n-side towards the p-side of the junction takes place when there is an increase in the voltage.
- Similarly, the flow of holes from the p-side towards the n-side of the junction takes place along with the increase in the voltage.
- This results in the concentration gradient between both sides of the terminals. Because of the formation of concentration gradient, there will be a flow of charge carriers from higher concentration region to lower concentration region.
- The movement of charge carriers inside the p-n junction is the reason behind the current flow in the circuit.
V-I Characteristics of P-N Junction Diode
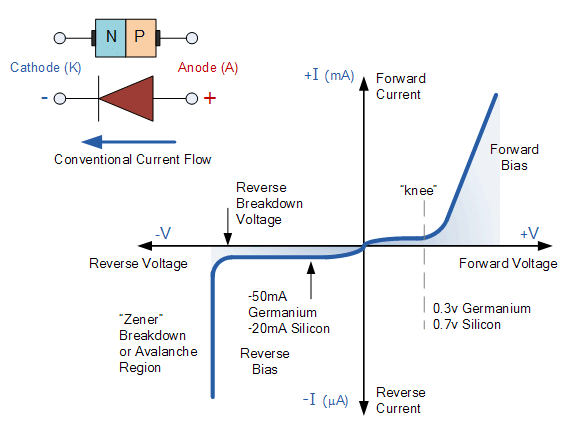
[Intext Question]
Applications of P-N Junction Diode
- P-n junction diode can be used as a photodiode as the diode is sensitive to the light when the configuration of the diode is reverse-biased.
- It can be used as a solar cell.
- When the diode is forward-biased, it can be used in LED lighting applications.
- It is used as a rectifier in many electric circuits and as a voltage-controlled oscillator in varactors.
The document P-N Junction Diode - 1 | Electrical Engineering SSC JE (Technical) - Electrical Engineering (EE) is a part of the Electrical Engineering (EE) Course Electrical Engineering SSC JE (Technical).
All you need of Electrical Engineering (EE) at this link: Electrical Engineering (EE)
|
23 videos|98 docs|42 tests
|
FAQs on P-N Junction Diode - 1 - Electrical Engineering SSC JE (Technical) - Electrical Engineering (EE)
| 1. What is a P-N Junction? |  |
Ans. A P-N junction is the interface between a P-type semiconductor and an N-type semiconductor, forming a diode. It is a crucial component in electronic devices, allowing the flow of electric current in only one direction.
| 2. How is a P-N Junction formed? |  |
Ans. A P-N junction is formed by bringing a P-type semiconductor, which has an excess of holes, in contact with an N-type semiconductor, which has an excess of electrons. This results in the diffusion of majority carriers from one side to the other, creating a depletion region at the junction.
| 3. What are the biasing conditions for the P-N Junction diode? |  |
Ans. The P-N junction diode can be forward biased, where the P-side is connected to the positive terminal of a voltage source, or reverse biased, where the N-side is connected to the positive terminal. In forward bias, current flows easily, while in reverse bias, only a negligible current flows.
| 4. How does current flow in the P-N junction diode? |  |
Ans. In a P-N junction diode, current flows when the diode is forward biased, allowing majority carriers to move across the junction and recombine. In reverse bias, the depletion region widens, preventing significant current flow due to the absence of majority carriers.
| 5. What are the applications of P-N Junction diode? |  |
Ans. P-N junction diodes are commonly used in various applications such as rectification, signal demodulation, voltage regulation, light-emitting diodes (LEDs), solar cells, and temperature sensors. Their ability to control the flow of current makes them versatile components in electronic circuits.
Related Searches