Mechanical Engineering Exam > Mechanical Engineering Notes > Mechanical Engineering SSC JE (Technical) > Simple Stresses in Machine Parts
Simple Stresses in Machine Parts | Mechanical Engineering SSC JE (Technical) PDF Download
SIMPLE STRESSES IN MACHINE PARTS
- The machine parts are subjected to various forces which may be due to either one or more of the following:
- Energy transmitted
- Weight of Machine
- Frictional resistance
- Inertia of reciprocating parts
- Change of temperature
- Lack of balance of moving parts
- The following types of the load are important from the design point of view :
- Dead or steady load : A load is said to be a dead or steady load, when it does not change in magnitude or direction.
- Live or variable load : A load is said to be a live or variable load, when it changes continually.
- Suddenly applied or shock loads : A load is said to be a suddenly applied or shock load, when it is suddenly applied or removed.
- Impact load : A load is said to be an impact load, when it is applied with some initial velocity.
- When a body is subjected to two equal and opposite axial pulls P (also called tensile load) then the stress induced at any section of the body is known as tensile stress.

The ratio of the increases in length to the original length is known as tensile strain.
Tensile stress st = P/A and tensile strain = 

and
Young’s Modulus;

P = Tensile or compressive force acting on the body
A = Cross-sectional area of the body
ℓ = original length
dℓ = Change in length
Question for Simple Stresses in Machine PartsTry yourself: What is the term used to describe a load that changes continually?View Solution
- When a body is subjected to two equal and opposite forces, acting tangentially across the resisting section, as a result of which the body tends to shear off the section, then the stress produced is called shear stress. The corresponding strain is known as shear strain and it is measured by the angular deformation accompanying the shear stress.
- Shear stress,


- All lap joints and single cover plate butt joints are in single shear, while the butt joints with double cover plates are in double shear.
- In case of shear, the area involved is parallel to the external force applied.
- A localised compressive stress at the surface of contact between two members of a machine part, that are relatively at rest is known as bearing stress or crushing stress.The bearing stress is taken into account in the design of riveted joints, cotter joints, knuckle joints etc.
- Bearing stress


d = diameter of rivet
t = thickness of the plate
d.t = projected area of the rivet
n = number of rivet per pitch length in bearing.
- Barba established a law that in tension similar test pieces deforms similarly and two STUDENT CORNER test pieces are said to be similar if they have the same value of ℓ /√A, where ℓ is the gauge length and A is the cross-sectional area.
- When designing machine parts, it is desirable to keep the stress lower than the maximum or ultimate stress at which failure of the material takes place. This stress is known as the working stress or design stress.
- The ratio of the maximum stress to the working stress is known as factor of safety.

- For ductile materials :

- For brittle materials :

- The selection of proper factor of safety to be used in designing any machine component depends upon a number of consideration such as the material, mode of manufacture, type of stress, general service conditions and shape of the parts.
- Thermal stresses
- Whenever there is some increase or decrease in the temperature of a body, it causes the body to expand or contract. If the body is allowed to expand or contract freely, with the rise of fall of the temperature, no stresses are induced in the body. Such stresses are known as thermal stresses.
Let,ℓ = original length of the body t = change in temperature (increase or decrease) a = coefficient of thermal expansion Increase in length = dℓ = ℓ.a.t.
If ends of body are fixed to rigid supports, then compressive strain.
- Whenever there is some increase or decrease in the temperature of a body, it causes the body to expand or contract. If the body is allowed to expand or contract freely, with the rise of fall of the temperature, no stresses are induced in the body. Such stresses are known as thermal stresses.

Thermal stress s =Î .E =a .t.E
Thermal stress is independent of length and cross - section dimensions.
- When a body composed of two of different materials having different coefficient of thermal expansion, then due to the rise in temperature, the material with higher coefficient of thermal expansion will be subjected to compressive stress whereas material with low coefficient of thermal expansion will be subjected to tensile stress.
- When a thin tyre is shrunk on to a wheel of diameter D, its internal diameter is little less than that of wheel diameter. When tyre is heated, its circumference (pd) will increases to (pD). In this condition, it is slipped on to the wheel. When it cools it wants to return to its original circumference (pd), but the wheel, if it assumed to be rigid, prevents it from doing so.

- This strain is known as circumferential or hoop strain.
- Circumferential or hoop stress,

- When a tensile force act along the length of the bar, the length of the bar is increased by dl and the diameter decreases by an amount dd. The strain in the direction of force is known as linear strain and an opposite kind of strain in every direction at right angles to it, is known as lateral strain.
- Poisson’s Ratio

- When a body is subjected to three mutually perpendicular stresses, of equal intensity then the ratio of the direct stress to the corresponding volumetric strain is known as bulk modulus (K).

- Relation between Bulk modulus and young’s modulus :

- Relation between young’s modulus and modulus of rigidity :

- Relation between E, G and K
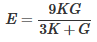
The document Simple Stresses in Machine Parts | Mechanical Engineering SSC JE (Technical) is a part of the Mechanical Engineering Course Mechanical Engineering SSC JE (Technical).
All you need of Mechanical Engineering at this link: Mechanical Engineering
|
5 videos|103 docs|59 tests
|
FAQs on Simple Stresses in Machine Parts - Mechanical Engineering SSC JE (Technical)
| 1. What are simple stresses in machine parts? |  |
Ans. Simple stresses in machine parts refer to the stresses that develop in a machine part due to the application of an external force or load. These stresses can be either tensile, compressive, or shear stresses.
| 2. How are simple stresses calculated in machine parts? |  |
Ans. Simple stresses in machine parts can be calculated using the formula σ = F/A, where σ represents the stress, F denotes the applied force, and A is the cross-sectional area of the machine part.
| 3. What are the factors that affect simple stresses in machine parts? |  |
Ans. The factors that affect simple stresses in machine parts include the amount of force applied, the geometry of the machine part, the material properties of the part, and the type of load applied.
| 4. What is the significance of analyzing simple stresses in machine parts? |  |
Ans. Analyzing simple stresses in machine parts is essential to ensure that the machine part can withstand the load applied to it without breaking or experiencing any deformation. This analysis helps in designing efficient and safe machine parts.
| 5. What are the common types of machine parts that experience simple stresses? |  |
Ans. Some of the common types of machine parts that experience simple stresses include bolts, screws, shafts, gears, and bearings. These parts are subjected to different types of loads and stresses, and analyzing these stresses helps to ensure their safe and efficient operation.
Related Searches























