Working with Windows | Year 1 Computing IGCSE (Cambridge) - Class 1 PDF Download
1. Navigating the Windows Operating System Interface
The Windows operating system is one of the most popular operating systems used in personal computers. It provides a graphical user interface (GUI) that allows users to interact with the computer using icons, windows, and menus.
Key Features of the Windows Interface:
- Start Menu: The Start menu is a central hub for accessing programs, settings, and files. It can be opened by clicking the Start button located at the bottom left corner of the screen.
- Taskbar: The taskbar is the horizontal bar at the bottom of the screen that displays open programs, system notifications, and quick-access tools like volume and battery control.
- Windows: In Windows OS, multiple applications can run at the same time, each in its own window. These windows can be moved, resized, and minimized to fit the user's preferences.
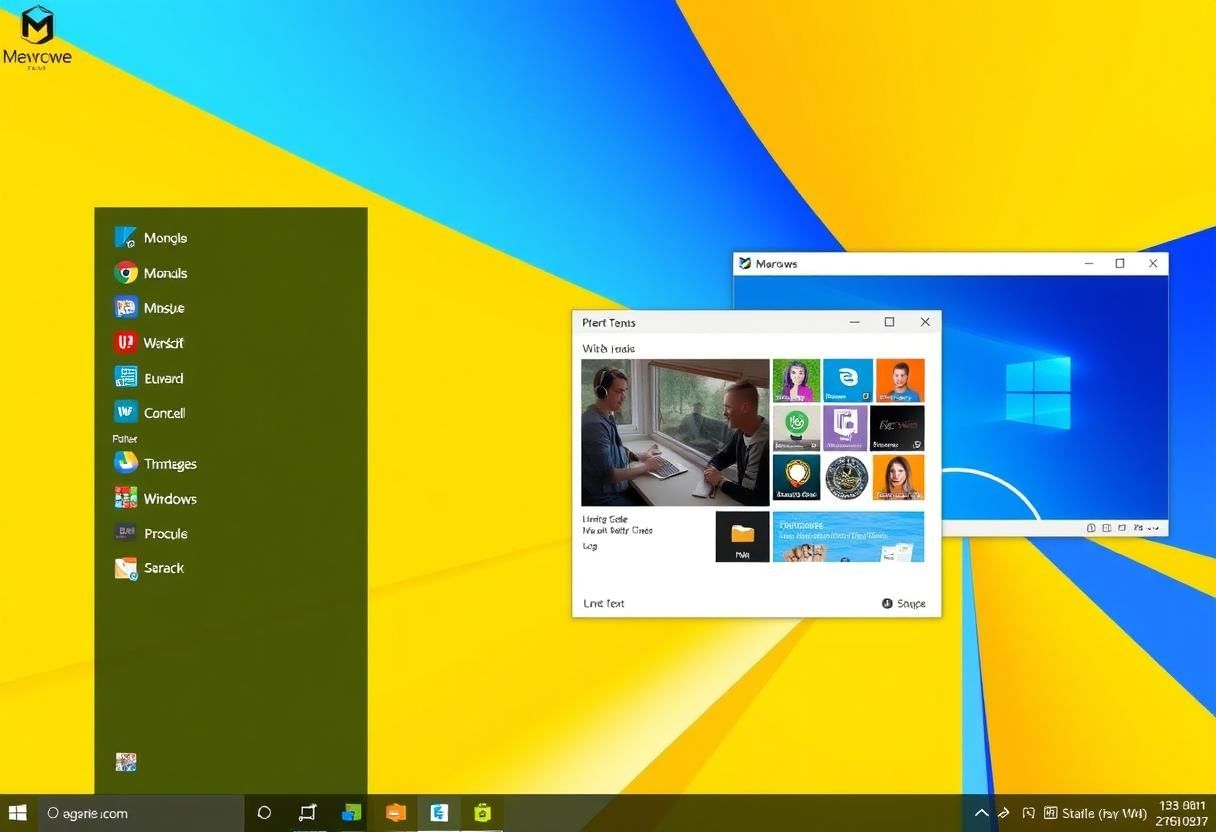 User Interface
User Interface
2. Understanding Desktop, Taskbar, and Start Menu
The Desktop
The desktop is the primary screen that appears when you log into Windows. It serves as the workspace where you can place files, folders, and shortcuts to applications. The desktop provides a visual overview of your current work environment.
The Taskbar
The taskbar runs across the bottom of the screen and contains icons for open applications, as well as shortcuts to frequently used programs. It also provides system icons such as the clock, battery status, and network connection. You can access the taskbar by moving your mouse to the bottom of the screen.
Key functions of the taskbar include:
- Quick Access: The taskbar allows you to pin frequently used applications for quick access.

- System Tray: The system tray shows notifications and status icons for system functions like Wi-Fi, sound, and battery life.
- Start Menu Access: The Start menu button on the taskbar opens the Start menu.
The Start Menu
The Start menu is a crucial part of the Windows interface. It allows users to access programs, settings, and files. You can open the Start menu by clicking the Start button located in the lower-left corner of the screen. The Start menu is divided into two main sections:
- Live Tiles: Display dynamic content like news, weather, or calendar events.
- All Apps: A list of installed applications and settings that can be accessed directly.
3. Managing Windows: Opening, Minimizing, Maximizing, and Closing
Opening Windows
In Windows, you can open a program or file by double-clicking its icon either on the desktop, taskbar, or Start menu. Programs can also be opened by typing their name into the Start menu search bar and selecting the application.
Minimizing Windows
The minimize button, usually located in the top-right corner of a window, reduces the window to a button on the taskbar. This allows you to hide a window temporarily and continue working with other programs without closing it.
Maximizing Windows
Clicking the maximize button in the top-right corner of a window enlarges it to fill the entire screen. You can also double-click the title bar of the window to maximize it.
Closing Windows
The close button (represented by an "X" in the top-right corner) will close the window. If the window has unsaved work, you will usually be prompted to save your changes before closing the program.
4. Using File Explorer to Manage Files and Folders
What is File Explorer?
File Explorer is a built-in application in Windows that allows you to browse, organize, and manage your files and folders. It provides a graphical interface for accessing and manipulating data stored on your computer's hard drive or connected devices like USB drives.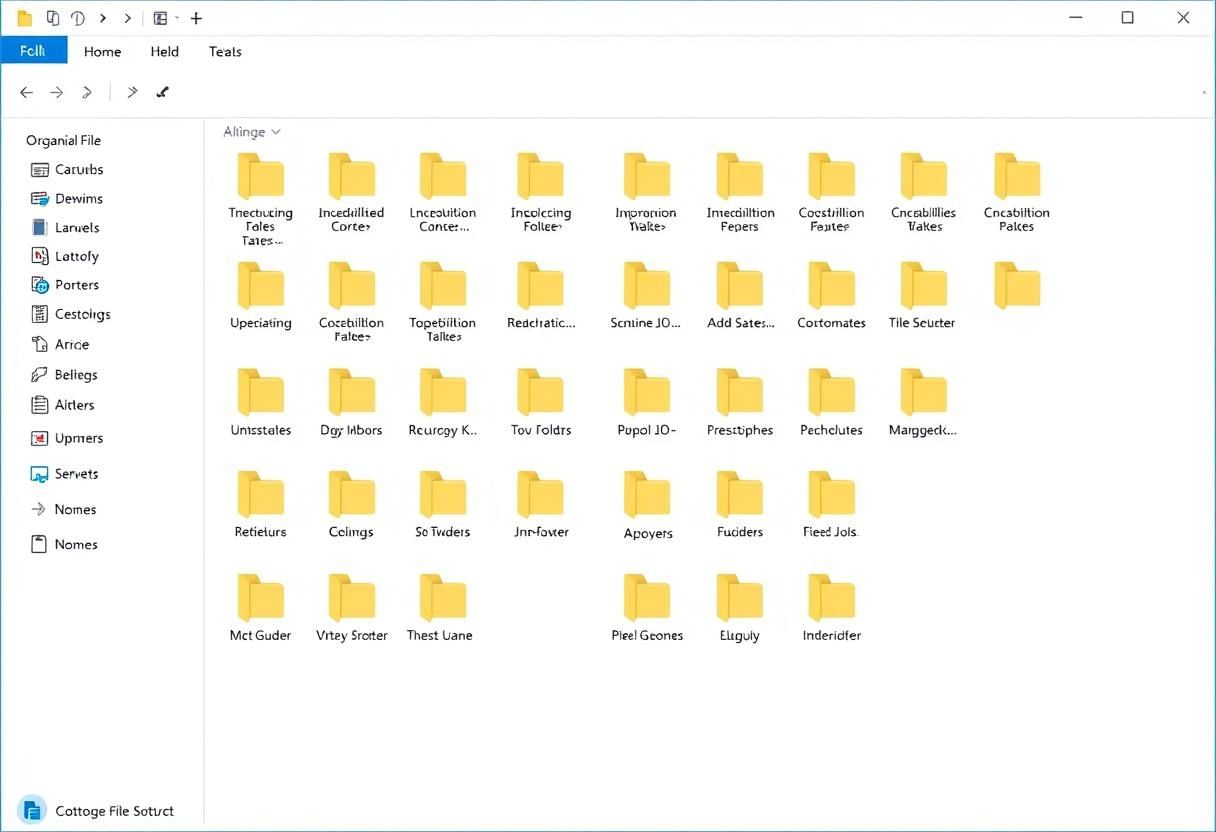
Basic Functions of File Explorer:
- Navigation: You can navigate through your computer’s file system by clicking on the folders and drives listed in the left pane. The right pane displays the contents of the selected folder or drive.
- Creating and Managing Folders: You can create new folders, rename existing ones, and organize files by dragging and dropping them into the appropriate folders.
- Search Function: File Explorer has a built-in search feature that allows you to find specific files by typing keywords into the search bar at the top right of the window.
- File Operations: You can copy, paste, cut, delete, or rename files and folders using the right-click context menu or the ribbon options at the top of the window.
Accessing Different Locations in File Explorer:
- This PC: Provides access to all the drives and storage devices connected to the computer, such as hard drives and external drives.
- Quick Access: A section that provides shortcuts to frequently accessed folders and files, making it easier to reach important locations quickly.
- Network: Allows you to access files on other devices that are connected to the same network, such as shared folders or networked printers.
File Explorer Views:
File Explorer offers different views for displaying files and folders, such as:
- Icon View: Displays files and folders as large or small icons.
- List View: Displays files and folders as a list with details like size and date modified.
- Details View: Shows more detailed information about the files, such as file type, size, and date of creation.
- Tiles View: Shows files with a preview of their contents, such as images or documents.
|
12 docs|6 tests
|
FAQs on Working with Windows - Year 1 Computing IGCSE (Cambridge) - Class 1
| 1. What is the purpose of the Windows Taskbar? |  |
| 2. How can I customize my Windows desktop background? |  |
| 3. What are the steps to open, minimize, maximize, and close a window in Windows? |  |
| 4. How do I create a new folder in File Explorer? |  |
| 5. What is the difference between minimizing and maximizing a window? |  |
















