Planning Chapter Notes | Business Studies (BST) Class 12 - Commerce PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| What is Planning? |

|
| Importance of Planning |

|
| Limitations of Planning |

|
| Planning Process |

|
| What is a Plan? |

|
| Types of Plan |

|
What is Planning?
Planning refers to the process of setting goals, determining actions to achieve those goals, and outlining the resources needed to execute those actions effectively. It involves making decisions in advance about what needs to be done, when it needs to be done, and how it will be done to achieve desired outcomes.
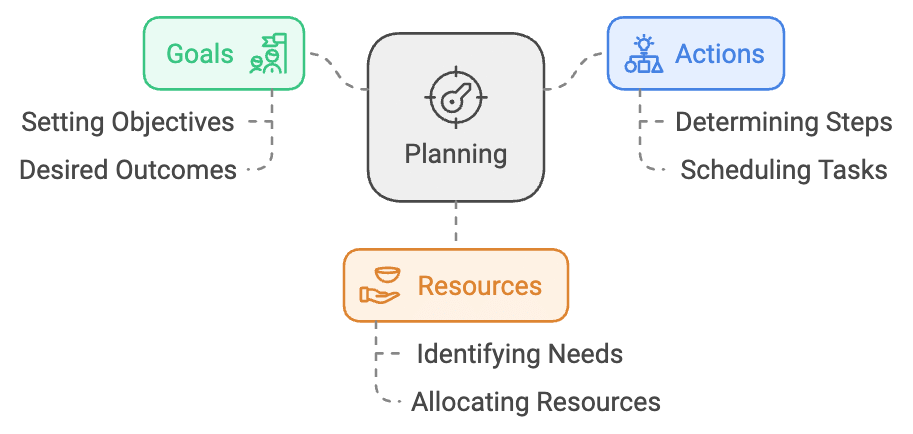
Key Features of Planning
The planning function of management has some special features. These features cast enlightenment on its scope and nature.
- Goal-oriented: Planning is focused on achieving specific objectives or goals. It involves identifying what the organization wants to accomplish within a certain timeframe.
- Future-oriented: Planning is concerned with future events and outcomes. It involves forecasting and anticipating future conditions to make informed decisions in the present.
- Systematic process: Planning involves a systematic approach that includes analyzing the current situation, setting objectives, identifying alternative courses of action, evaluating those alternatives, and selecting the best course of action.
- Flexibility: Plans should be flexible enough to adapt to changes in the external environment or unforeseen circumstances. This allows organizations to adjust their strategies as needed to achieve their goals.
- Continuous process: Planning is an ongoing process that requires regular review and adjustment. As circumstances change, plans may need to be modified to remain relevant and effective.
- Coordination: Planning helps in coordinating various activities and resources within an organization. It ensures that different departments or individuals work together towards common goals.
- Decision-making: Planning provides a framework for making decisions by providing a clear direction and criteria for evaluating alternatives.
- Resource allocation: Planning involves determining the resources (such as manpower, finances, and materials) required to achieve goals and allocating them efficiently.
Importance of Planning
(a) Planning provides directions: By stating in advance how the work is to be done planning provides direction for action. If there was no planning, employees would be working in different directions and the organization would not be able to achieve its goals efficiently.
(b) Planning reduces the risk of uncertainty: Planning is an activity that enables a manager to look ahead, anticipate change, consider the impact of change, and develop appropriate responses.
(c) Planning reduces wasteful activities: Planning serves as the basis for coordinating the activities and efforts of different departments and individuals whereby useless and redundant activities are mentioned.
(d) Planning promotes innovative ideas: Planning is the first function of management. Managers get the opportunity to develop new ideas and new ideas can take the shape of concrete plans.
(e) Planning facilities decision making: Under planning, targets are laid down. The manager has to evaluate each alternative and select the most viable option.
(f) Planning establishes standards for controlling: Planning provides the standards against which the actual performance can be measured and evaluated. Control is blind without planning. Thus planning provides the basis for control.
Limitations of Planning
1. Internal Limitations:
- Planning leads to rigidity: Planning discourages an individual’s initiative &creativity. The managers do not make changes according to the changing business environment. They stop taking or giving suggestions and new ideas. Thus detailed planning may create a rigid in the organization.
- Planning may not work in a dynamic environment: Planning is based on anticipation of future happenings and since the future is uncertain and dynamic, therefore, future anticipations are not always true.
- Planning involves huge costs: When plans are drawn up, huge cost is involved in their formulation.
- Planning is time-consuming: Sometimes plans to be drawn up take so much time that there is not much time left for their implementation.
- Planning does not guarantee success: The success of an enterprise is possible only when plans are properly drawn and implemented. Sometimes managers depend on previously tried successful plans, but it is not always true that a plan that has worked before will work effectively again.
- Planning reduces creativity: In planning, work is to be done as per pre-determined plans. It is decided in advance what is to be done, how it is to be done, and who is going to do it. Moreover, planning is done by top management which leads to a reduction of creativity of other levels of management.
2. External Limitations: These are those limitations of planning that arise due to external factors over which an organization has no control.
- Changes in Government policies way lead to failure of planning.
- Natural calamities such as floods; earthquakes etc. also adversely affect the success of planning. Changes in the strategies of competitors also leads to failure of planning many times.
- Regular technological changes may affect planning. Changes in the Economic and Social Conditions also reduce the effectiveness of planning.
Planning Process
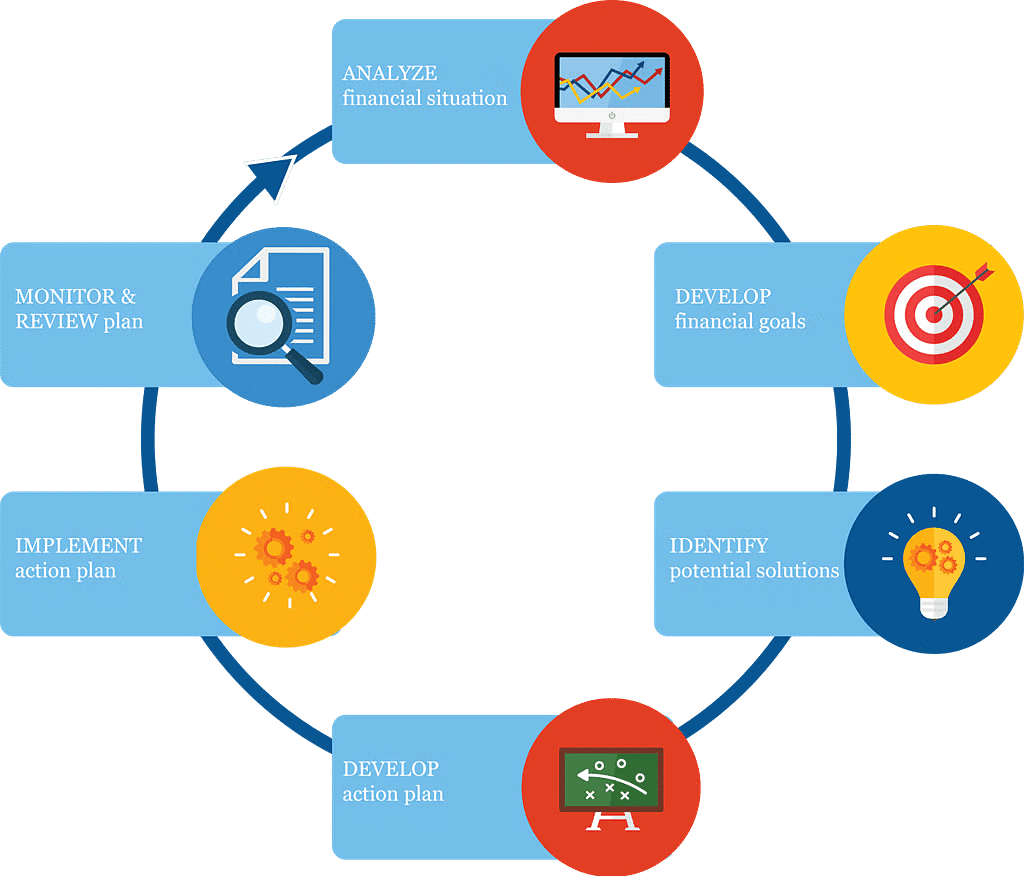
(a) Setting Objectives: The first and foremost step is setting objectives. Objectives may be set for the entire organization and each department.
(b) Developing premises: Planning premises are the assumptions about the likely shape of events in the future. It forecasts the obstacles, problems or limitations in the path of effective planning because of which the plans may deviate. Planning premises supply relevant facts & information relating to the future.
(c) Identifying alternative courses of action: Once objectives are set and premises are developed. Then the next step would be to act upon them. All the alternative courses of action should be identified. (d) Evaluating alternative Courses: The next step is to weigh the pros and cons of each alternative. Each course will have many variables which have to be weighed against each other.
e) Selecting an alternative: After comparison and evaluation, the best alternative is chosen for reaching the organization's objectives. Based on merits, demerits, resources, and consequences, the best plan has to be adopted, which must be the most feasible, profitable, and with the best negative consequences.
(f) Implementing the plan: Once the plans are developed they are put into action. Successful implementation of the plan ensures understanding and wholehearted cooperation of all the employees. (g) Follow-up action: To see whether plans are being implemented, and activities are performed according to schedule. In case of any deviations, changes are made in the plans.
What is a Plan?
A Plan is a specific action proposed to help the organization achieve its objectives. It is a document that outlines how goals are going to be met. The importance of developing plans is evident from the fact that there may be more than one means of reaching a particular goal. So with the help of logical plans, the objectives of an organization can be achieved easily.
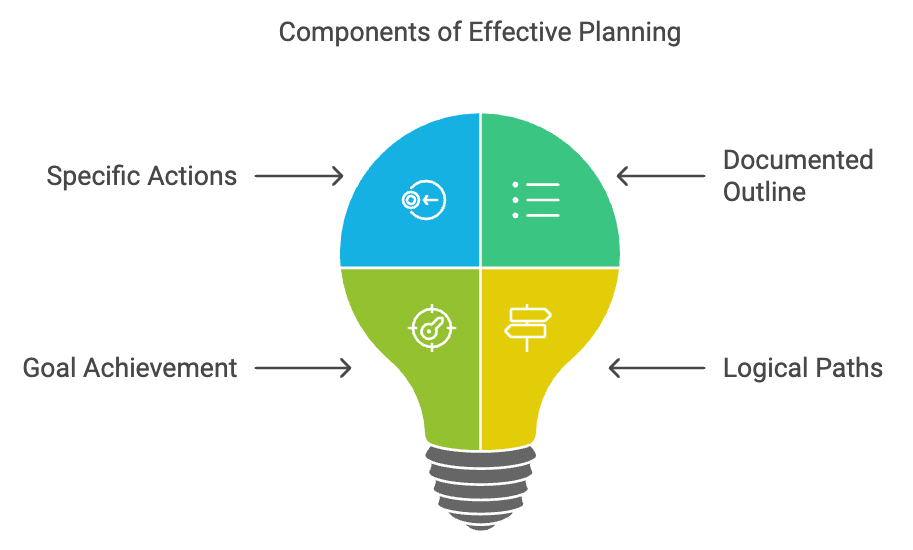
Types of Plan
1. Single-use plans
A Single-use plan in a business refers to a plan developed for a one-time project or event that has one specific objective. It applies to activities that do not reoccur or repeat. It is specifically designed to achieve a particular goal. Such a plan is developed to meet the needs of a unique situation. The length of a single-use plan differs greatly depending on the project in question, as a single event plan may only last one day while a single project may last one week or months. For example, an outline for an advertising campaign. After the campaign runs its course, the short-term plan will lose its relevance except as a guide for creating plans.
Types of Single Use Plan:
(a) Programme: A program is a single-use plan containing detailed statements about the project outlining the objectives, policies, procedures, rules, tasks, and physical and human resources required to implement any course of action.
(b) Budget: A budget is a statement of expected results expressed in numerical terms for a definite period in the future.
2. Standing Plans
Standing plans are used over and over again because they focus on organizational situations that occur repeatedly. They are usually made once and retain their value over years while undergoing revisions and updates. That is why they are also called repeated-use plans. For example, a Businessman plans to establish a new business Entrepreneur drafts a business plan before opening the doors to their business, and they can use their plan to guide their efforts for years into the future.
Types of Standing Plans
- Objectives: Objectives are defined as ends for the achievement of which an organization goes on working. They may be designed as the desired future position that the management would like to reach. The first and foremost step of the planning process is setting organizational objectives. Examples: increasing sales by 10%, Getting a 20% return on Investment, etc. Objectives should be clear and achievable.
- Strategy: Strategies refer to those plans that an organization prepares to face various situations, threats, and opportunities. When the managers of an organization prepare a new strategy for the business, it is called internal strategy, and when some strategies are prepared to respond to the strategies of the competitors, then such strategies are called external strategies. Examples are the selection of the medium of advertisement, the selection of the channel of distribution, etc.
- Policy: Policies refer to the general guidelines that bring uniformity in decision-making for the achievement of organizational objectives. They provide directions to the managers of an organization. They are flexible as they may be changed as per requirement. For example, selling goods on a cash basis only, and reserving some posts for women in the organization. They indicate which work is to be done in which sequence/way. They help in the performance of work. Procedures are guides to action. Example: Process adopted in the Selection of Employees.
- Rule: Rules are specific statements that tell what is to be done and what is to be done in a specified situation. They help in indicating which points are to be kept in mind while performing task/work. Rules are rigid which ensures discipline in the organization. Example: ‘No smoking on the office premises’. Violation of rules may invite penalty.
- Method: Methods are standardized ways or manners in which a particular task has to be performed. There may be many ways/methods of completing a task but that method/way must be selected by which work can be done early at the minimum possible cost. Methods are flexible. For example, various methods of training are adopted by an organization to train its employees like apprenticeship training, vestibule training, etc.
- Procedure: Procedures are detailed steps outlining how to perform activities in a specific order. For instance, there might be a procedure for requisitioning supplies before production. They are meant for insiders to follow, and they enforce policies and objectives within a broader framework.
- Programme: Programmes provide detailed descriptions of projects, including objectives, policies, procedures, rules, tasks, resources needed, and the budget for implementation. They encompass all activities and align with the organization's policy to support the overall business plan. Every aspect, such as procedures, rules, and budgets, is meticulously planned within the overarching policy framework.
- Budget: A budget is a numerical plan that predicts future outcomes. For instance, a sales budget forecasts product sales by region for a specific month. It helps compare actual results with expected ones and allows for corrective action. Budgeting is part of planning as it involves forecasting. Cash budgeting, for example, helps manage cash flow by estimating inflows and outflows over a period. The net cash position is calculated by subtracting outflows from inflows, determining a surplus or deficit. Businesses must maintain adequate cash reserves while avoiding excess, which earns little to no return. Planning cash needs requires careful assessment.
Basis of Difference Single-use Plans and Standing Plans
1. Meaning- A single-use plan in a business project one-time r event that is used over and over again has the same objective. because they focus on organizational situations that occur repeatedly.
2. Objective - Single-use plans are developed to carry out a course of action for activities that are not likely to be repeated in future time.
3. Scop - Single-use plans generally have a narrow scope and encompass plans generally a specific project or involve more than one event.
department function.
4. Stability - Single-use plans are discarded when the situation, project, or stable and used event is occurring again modifications or updating.
5. Example -Budget for Annual General Recruitment and selection with necessary
Standing Plans-
1. Meaning- A standing plan in a business refers to plans developed for using over and over again with has same objective. because they focus on organizational situations that occur repeatedly.
2. Objective -Standing plans however are to carry out a course of action developed for activities occur regularly over some time.
3. Scop -Standing encompasses a wider scope targeting more than one department function or business.
4. Stability -Standing plans are relatively stable and used over and over modifications or updates.
5. Example - Recruitment and selection procedure for a particular post in a company.
|
51 videos|324 docs|74 tests
|
FAQs on Planning Chapter Notes - Business Studies (BST) Class 12 - Commerce
| 1. What is the definition of planning in a business context? |  |
| 2. Why is planning considered important for organizations? |  |
| 3. What are some limitations of planning? |  |
| 4. What steps are involved in the planning process? |  |
| 5. What are the different types of plans used in organizations? |  |
















