Small Business Chapter Notes | Business Studies (BST) Class 11 - Commerce PDF Download
Introduction
Small Business enterprises exist in every country of the world. However, in a developing country like India, they occupy a special place in the industrial structure because they provide better employment opportunities, better utilization of local resources, and equitable distribution of national income.
Meaning
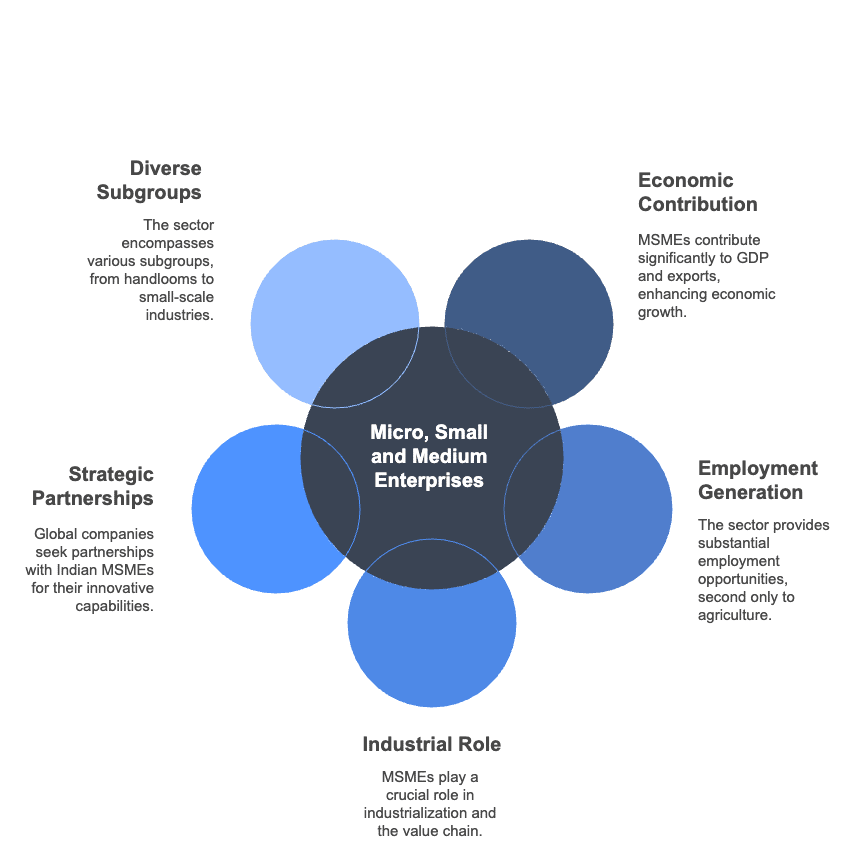
- Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises (MSME) contribute significantly to the development process and act as a vital link in the industrialisation in terms of production, employment and exports for economic prosperity by widening the entrepreneurial base and use of local raw materials and indigenous skills.
- MSME dominate the industrial scenario in the country with a sizeable proportion of the labour force and tremendous export potential.
- MSMEs play a significant role in economic growth and contribute approximately 29.7 per cent of GDP and 49.66 per cent of exports.
- The sector offers employment to nearly 60 million people through 28.5 million enterprises, after the agriculture sector.
- MSMEs are complementary to large industries as ancillary units and form an integral part of value chain for building a conducive environment for indigenous skills, grassroots innovations and entrepreneurship development.
- This sector produces a wide range of products, from simple consumer goods to high-precision, sophisticated finished products.
- Recognising the potential of this sector for national development, this industry segment is encouraged in both pre-reform and post-reform periods to fulfil the objective of self-reliance and rural industrialisation.
- In India, the MSME consists of both ‘traditional’ and ‘modern’ small industries.
- This sector has eight subgroups. They are:
- handlooms
- handicrafts
- coir
- sericulture
- khadi and village industries
- small scale industries
- powerlooms
- The Khadi and Village Industries and Coir segment is another major contributor to the growth of the MSME.
- Many global companies are increasingly looking to Indian MSMEs for strategic partnerships of mutual benefit due to the innovative capabilities in niche of low-cost manufacturing and local skills and capabilities.
Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises
- It is essential to understand how size is defined in our country concerning MSME (Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises) establishments.
- Various factors can be used to measure the size of business units, including:
- the number of people employed in the business,
- the capital invested in the business,
- the turnover of the business.
- The definition that the Government of India uses for MSMEs is based on the amount invested in plant and machinery and the business's turnover.
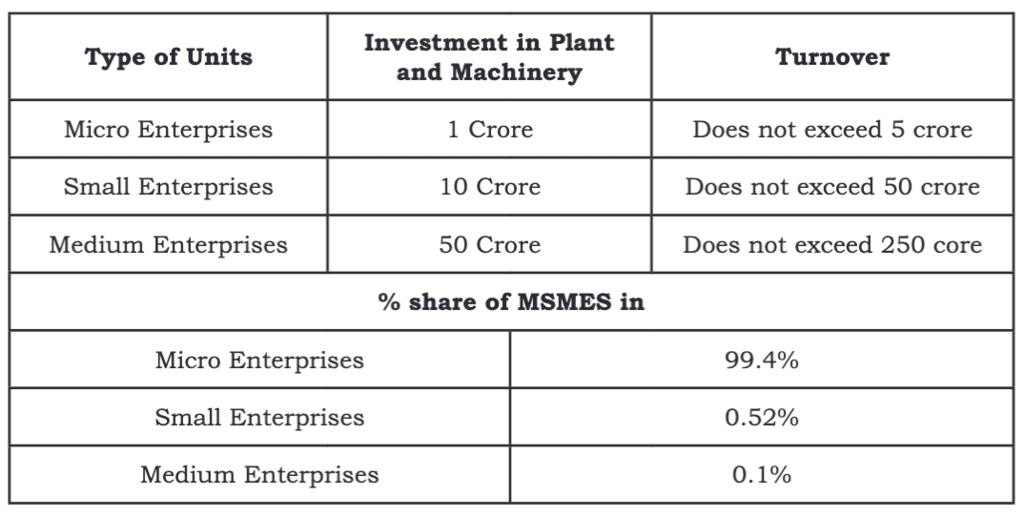
- This measure considers the socio-economic situation in India, where capital is limited, but labor is plentiful.
- The growth of a large services sector has led the government to include more types of businesses, covering both the Small Scale Industries (SSI) sector and related service businesses.
- As small businesses grew into medium-sized enterprises, they needed to adopt more advanced technologies to stay competitive in a rapidly globalizing world.
- Therefore, it became important to address the needs of micro, small, and medium enterprises and provide them with a unified legal framework.
- The MSMED Act, 2006 was enacted starting October 2006, addressing issues related to definitions, credit, marketing, and technology upgrades for these enterprises.
- This Act also covers medium-sized enterprises and those related to services.

Role of MSMEs in India (With Special Reference to Rural Areas)
- MSME play a vital role in the socio-economic growth of India.
- The focus on MSME has always been a key part of India’s industrial plans.
- Development of MSME helps stop rural people from moving to cities for jobs.
- They also help reduce income differences and promote industry spread across various regions.
- The Indian government views MSME and rural industrial growth as crucial for achieving faster industrial progress and creating more job opportunities in rural and less developed areas.
Key contributions of MSME
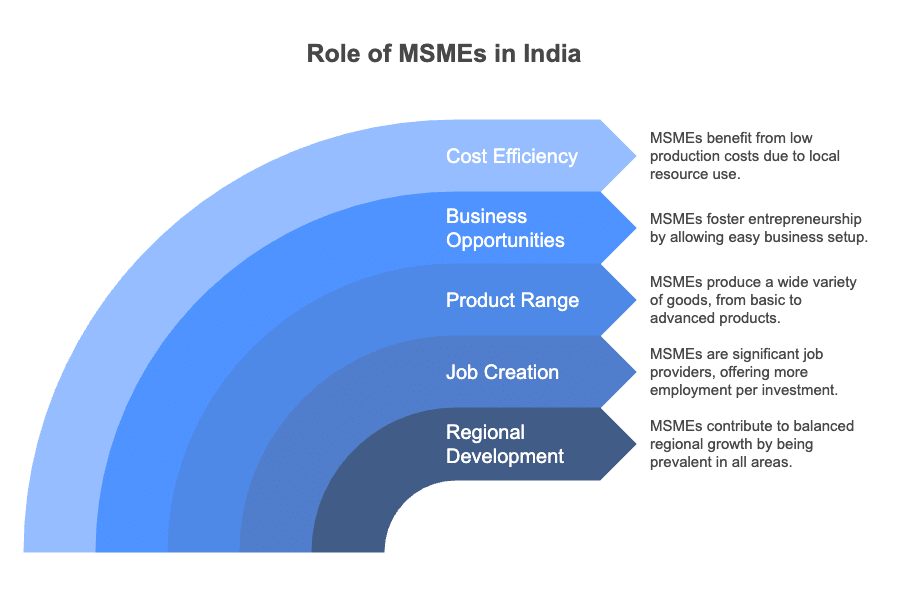
- Their role in balanced regional development is significant, as small industries make up 95% of all industrial units in India.
- MSME are the second largest providers of jobs, following the agriculture sector. They offer more jobs per unit of money invested compared to larger industries, making them more labor-focused and using less capital. This is beneficial for a country like India that has many workers.
- MSME produce a wide range of goods, including:
Everyday items like clothing, stationery, soaps, utensils, and more.
Advanced products such as electronic devices, medical equipment, teaching tools, air conditioners, and pharmaceuticals.
Additionally, traditional products like handlooms and handicrafts are important for their value in exports. - MSME that create simple products using basic technologies can be set up anywhere in the country. They can thrive without needing specific locations, allowing all regions to benefit from industrial growth. This greatly supports the balanced development of India.
- MSMEs create many chances for starting a business. People’s hidden skills and talents can be turned into business ideas that require only a small amount of money to start and have very few formal requirements to launch a small enterprise.
- MSMEs also benefit from low production costs. Resources available in the local area are usually cheaper, which helps to keep the costs of setting up and operating small businesses low due to fewer ongoing expenses. In fact, the low production costs that small businesses have give them a competitive advantage.
- Because these organizations are small in size, they can make quick and timely decisions without needing to consult many people, unlike larger organizations. This allows them to take advantage of new business opportunities when they arise.
Problems Of Small Scale Industries
- The potential of MSMEs is often not fully recognized due to various challenges related to their size and operations.
- Let's look at some of the main issues that small businesses face, whether they are located in urban or rural areas.
- MSMEs are at a clear disadvantage compared to larger industries.
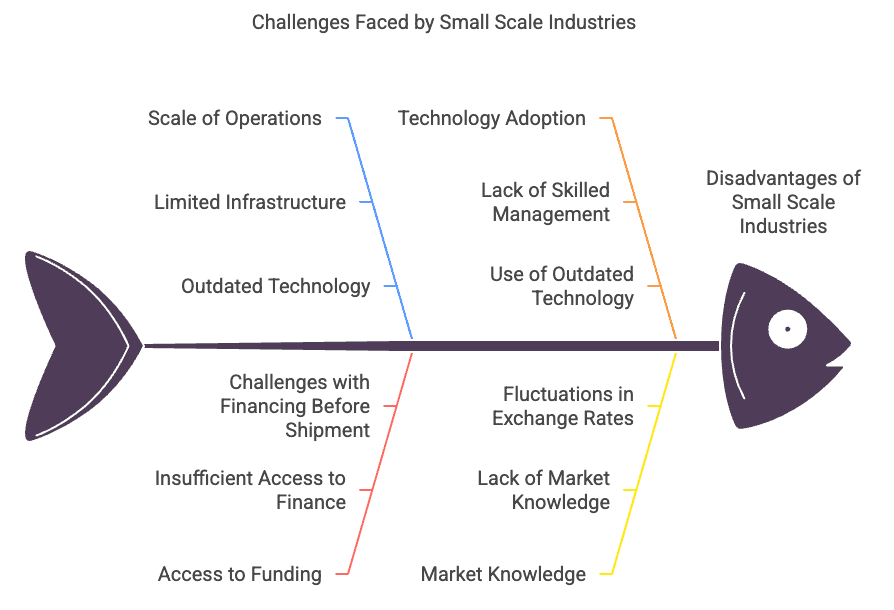
- Some of the challenges include:
- The scale of operations
- Access to funding
- Ability to adopt modern technology
- Getting necessary raw materials
- These challenges lead to several significant problems:
- Being located in remote areas with limited infrastructure
- Lack of skilled management
- Low-quality products
- Use of outdated technology
- Insufficient access to finance
- Small-scale exporters face specific issues as well:
- Not having enough information about foreign markets
- Lack of market knowledge
- Fluctuations in exchange rates
- Meeting quality standards
- Challenges with financing before shipment
In general the small businesses arefaced with the following problems:
(i) Finance
- One major issue faced by MSMEs is the lack of sufficient funds to manage their operations.
- Typically, these businesses start with a small amount of capital.
- Many small businesses often do not have the necessary creditworthiness to obtain funds from capital markets.
- As a result, they rely heavily on local financial sources and often fall victim to exploitation by moneylenders.
- These businesses frequently struggle with insufficient working capital.
- This lack of capital can be due to delayed payments owed to them or their money being tied up in unsold inventory.
- Banks usually do not provide loans without adequate collateral, guarantees, or margin money, which many of these businesses cannot offer.
(ii) Raw materials
- Another major issue for MSMEs is the difficulty in obtaining raw materials.
- If the necessary materials are not available, they have to settle for lower quality or pay more money to get good quality materials.
- Their bargaining power is quite low because they buy in small amounts.
- They also cannot afford to take risks by buying in bulk since they lack storage facilities for these materials.
- Due to a general scarcity of metals, chemicals, and extractive raw materials in the economy, the small-scale sector suffers the most.
- This situation leads to a waste of production capacity for the economy and results in the loss of potential production units.
(iii) Managerial skills
- Small businesses are often run by a single individual.
- This person may not have all the management skills needed to operate the business effectively.
- Many entrepreneurs in small businesses have good technical knowledge.
- However, they often struggle with marketing their products or services.
- These business owners may also lack enough time to handle all aspects of running their business.
- Additionally, they might not have the resources to hire professional managers.
(iv) Marketing
- Marketing is a crucial activity because it helps generate revenue.
- To market products successfully, it's essential to have a deep understanding of what the customer needs and wants.
- Often, small businesses struggle with marketing, making it a weak point for them.
- As a result, these small organizations often rely heavily on middlemen.
- Sometimes, middlemen take advantage of small businesses by offering low prices and making delayed payments.
- Additionally, direct marketing can be challenging for small firms because they may not have the required infrastructure in place.
(v) Quality
- Many MSMEs do not follow the necessary quality standards.
- Instead, they focus on reducing costs and keeping prices low.
- These businesses often lack the resources needed to invest in quality research.
- They also struggle to maintain the industry standards.
- There is a lack of expertise to improve their technology.
- Maintaining good quality is one of their biggest challenges when competing in global markets.
(vi) Capacity utilisation
- Many companies have to work below their full potential because of a lack of strong marketing skills or insufficient demand.
- This situation results in higher operating costs for these firms.
- Over time, these increased costs can lead to business failure or even closure.
- As companies struggle to attract customers, they may find it hard to stay afloat.
- When businesses operate at less than full capacity, they miss out on potential profits.
- This cycle of reduced activity and rising costs can create a path towards financial difficulties.
(vii) Global competition
- Apart from the issues mentioned earlier, MSMEs have their own worries, especially in today's world of globalization.
- These small and medium enterprises are not just facing competition from medium and large industries.
- They are also competing against multinational companies, which are much larger in terms of both size and business volume.
MSME and Entrepreneurship Development
- Entrepreneurship is the act of starting and running your own business, different from being employed or working in a profession.
- A person who starts their own business is known as an entrepreneur.
- The business that the entrepreneur creates is referred to as an enterprise.
- Entrepreneurship not only provides self-employment for the entrepreneur but also plays a big role in creating and expanding job opportunities and professional paths for others.
- This process of entrepreneurship is very important for the overall economic development of a country.
- Every nation, whether it is developed or developing, requires entrepreneurs.
- In a developing country, entrepreneurs are needed to kickstart the development process.
- In contrast, developed countries rely on entrepreneurship to maintain and grow their economy.
- In India today, there is a decline in job opportunities in the public sector and large-scale businesses.
- At the same time, there are many opportunities arising from globalization that can be taken advantage of.
- Entrepreneurship can significantly help India become a strong economic power.
- The need for entrepreneurship is evident based on the roles that entrepreneurs play in relation to economic growth and their businesses.
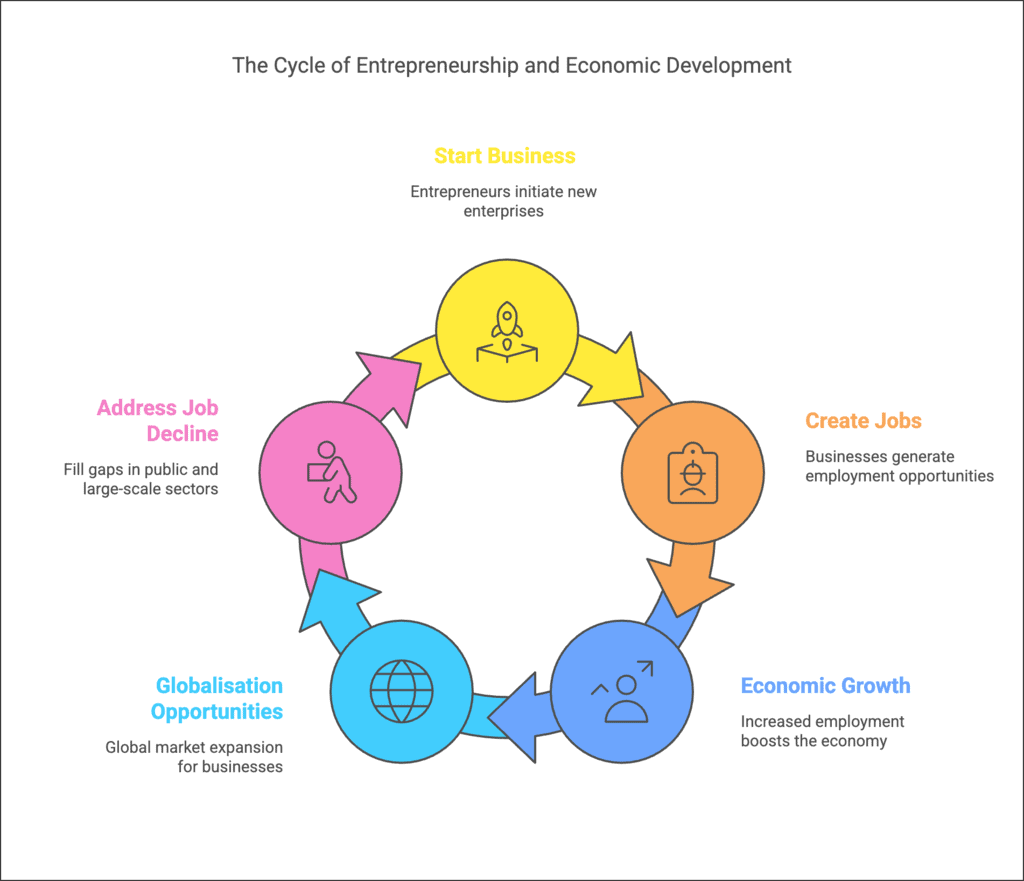
The following are the characteristicsof entrepreneurship:
(i) Systematic Activity
- Entrepreneurship is not a mysterious gift or charm and something that happens by chance!
- It is a systematic, step-by-step and purposeful activity.
- It has certain temperamental, skill and other knowledge and competency requirements that can be acquired, learnt and developed, both by formal educational and vocational training as well as by observation and work experience.
- Such an understanding of the process of entrepreneurship is crucial for dispelling the myth that entrepreneurs are born rather than made.
(ii) Lawful and Purposeful Activity
- The main goal of entrepreneurship is to run a legal business.
- It is essential to recognize this point because some people might try to justify illegal activities as being part of entrepreneurship, claiming that both involve taking risks.
- However, the true aim of entrepreneurship is to create value that benefits both personal profit and the community.
(iii) Innovation
- From a company's perspective, innovation can either save costs or increase revenue.
- If it achieves both, it is highly appreciated.
- Even if it does neither, it is still valued because innovation should become a regular practice.
- Entrepreneurship is a creative process as it involves creating value.
- By combining different resources, entrepreneurs create goods and services that satisfy society's needs and desires.
- Every act of entrepreneurship leads to the generation of income and wealth.
- Entrepreneurship is also creative because it brings about innovationthrough:
- New products
- Identifying new markets
- Finding new sources for supplies
- Technological advancements
- Introducing new organizational methods to improve efficiency
- These improvements aim to do things in a way that is better, cheaper, faster, and with minimal impact on the environment.
(iv) Organisation of Production
- Production involves creating things in a specific form, place, and time for personal use, and it requires the combined use of different factors of production: land, labor, capital, and technology.
- An entrepreneur identifies a business opportunity and brings together these resources to form a productive enterprise or firm.
- It is important to note that an entrepreneur may not actually own any of these resources; often, they only have a business idea that they share with those who can provide the resources.
- In an economy with a strong financial system, the entrepreneur needs to persuade funding institutions. Once they secure the necessary capital, they can enter into contracts for equipment, materials, utilities (like water and electricity), and technology.
- At the heart of organizing production is the understanding of how to find and use these resources effectively, including knowing where they are located and how to combine them in the best way.
- An entrepreneur must have strong negotiation skills to gather these resources in a way that benefits the enterprise the most.
(v) Risk-taking
- It is commonly thought that entrepreneurs take significant risks.
- Yes, people who choose to become entrepreneurs face greater risks compared to those in regular jobs or professions because there is no guaranteed reward.
- For instance, when someone leaves a stable job to start their own business, they often think about whether they can earn the same income.
- To an outside observer, leaving a secure and promising job may seem like a high risk, but the individual is actually making a calculated decision.
- They have confidence in their skills, believing that they can turn a 50% chance of success into a 100% success.
- Entrepreneurs tend to steer clear of situations with higher risks because they dislike failing, just like anyone else.
- They also avoid lower-risk situations because they find that running a business should be exciting and enjoyable.
- For entrepreneurs, risk is not just about money; it becomes a personal matter where underperformance leads to feelings of displeasure and distress.
Intellectual Property Rights
- Over the past two decades, intellectual property rights have grown to a stature from where it plays a major role in the development of the global economy.
- Intellectual property is everywhere, i.e., the music you listen to, the technology that makes your phone work, the design of your favourite car, the logo on your sneakers, etc.
- It exists in all the things you can see— all are the products of human creativity and skill, such as inventions, books, paintings, songs, symbols, names, images, or designs used in business, etc.
- All inventions of creations begin with an ‘idea’. Once the idea becomes an actual product, i.e., Intellectual Property, one can apply to the authority concerned under the Government of India for protection.
- Legal rights conferred on such products are called ‘Intellectual Property Rights’ (IPR).
- Hence, Intellectual property (IP) refers to products of the human mind; hence, just like other types of property, the owners of IP can rent, give or sell it to other people.
- Specifically, Intellectual property (IP) refers to the creations of the human mind, like inventions, literary and artistic works, symbols, names, images and designs used in business.
- Intellectual property is divided into two broad categories: industrial property, which includes inventions (patents), trademarks, industrial designs and geographical indications, while the other is copyrights, which includes literary and artistic works, such as novels, poems, plays, films, musical works, artistic works, such as drawings, paintings, photographs and sculptures and architectural designs.
- The most noticeable difference between intellectual property and other forms of property is that intellectual property is intangible, i.e., it cannot be defined or identified by its own physical parameters.
- The scope and definition of intellectual property is constantly evolving with the inclusion of newer forms.
- In recent times, geographical integrated circuits and undisclosed indications, protection of plant varieties, information have been brought under the protection of semi-conductors and umbrella of intellectual property.
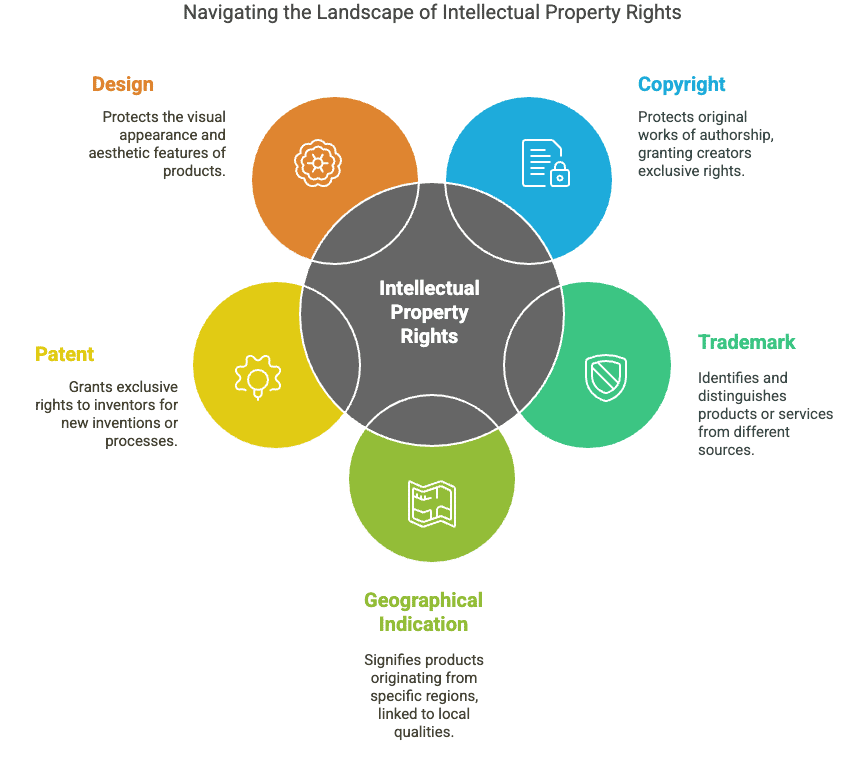
- The following types of Intellectual Property Rights are recognised in India: Copyright, Trademark, Geographical Indication, Patent, Design, Plant Variety, Semiconductor Integrated Circuit Layout Design.
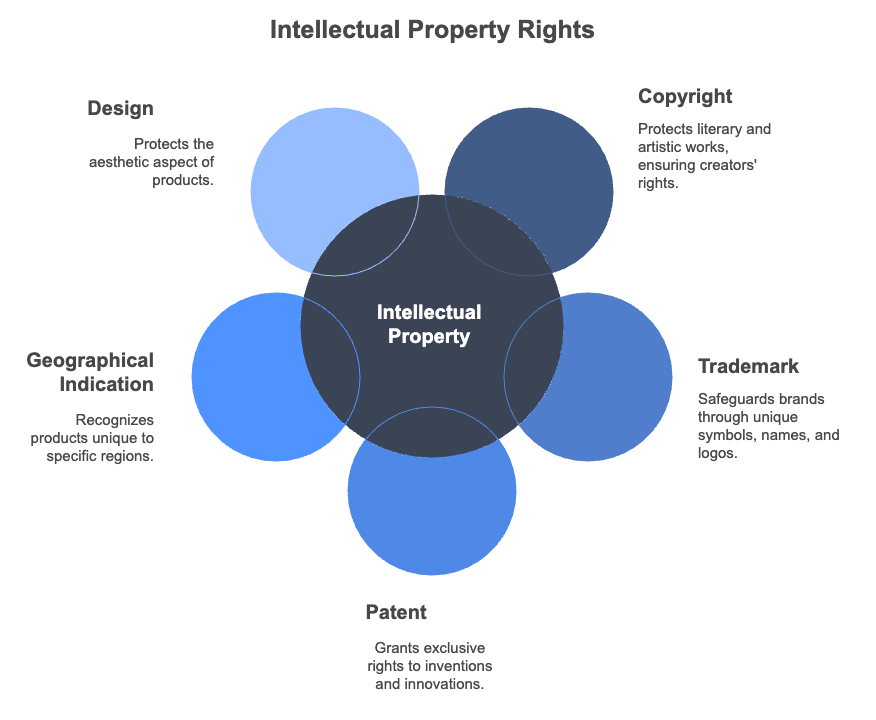
Why is IPR Important forEntrepreneurs?
- Encourages the creation of new and innovative inventions, like medicines for cancer.
- Rewards inventors, writers, and creators for their contributions.
- Ensures that a person's work can only be shared with others if they give their permission.
- Helps prevent loss of income for creators by protecting their work.
- Supports authors, creators, developers, and owners in gaining recognition for what they produce.
Types of IPs
IPRs are extremely essential forfostering creativity and contributetowards the economic growth of anation. Such rights allow creatorsand inventors to have control overtheir creations and inventions. Theserights create incentives for artists,entrepreneurs and inventors to furthercommit the necessary resourcesto research, develop, and marketnew technology and creative works.The changing global economy iscreating unprecedented challengesand opportunities for continuedprogress in human development. Thereare business opportunities to marketor sell IP worldwide. Geographicalborders present no impediments—consumers enjoy near immediateaccess to almost everything. At suchexciting times, it is critical that we areaware about the importance of IPRsand how it affects daily life
Copyright
- Copyright is the right to prevent copying of original work.
- This right is given when a creator or author shares their unique idea.
- It applies to creators of literary, artistic, musical, sound recordings, and films.
- Copyright gives the creator the exclusive power to stop others from using their content without permission.
- This includes the right to reproduce and distribute copies of the work.
- A key point about copyright is that it automatically protects a work as soon as it is created.
- While it is not required to register the work, doing so can help the creator enforce their rights if someone violates them.
Trademark
- A trademark is any word, name, or symbol (or a mix of these) that helps us recognize the products made by a person, company, or organization.
- Trademarks allow us to tell the difference between products from various companies.
- With a single brand or logo, trademarks can reveal a lot about a company's reputation, goodwill, products, and services.
- A trademark is essential for distinguishing similar products in the market from those of its competitors.
- A competitor is not allowed to use the same or similar trademark to sell their products because this would be considered deceptive similarity, which can be based on how the trademark sounds, looks, or is structured.
- Trademarks can be divided into two main categories:
- Conventional Trademark: This includes words, color combinations, labels, logos, packaging, and shapes of products.
- Non-Conventional Trademark: This category includes marks that were not originally seen as unique but have gained recognition over time, such as sound marks and dynamic marks. In some areas, smell and taste are also considered for trademark protection.
Geographical Indication
- A Geographical Indication (GI) is a sign that shows certain products come from a specific area. These can include agricultural products, natural goods, handicrafts, industrial items, and food products.
- The quality, reputation, or other important traits of these products are mainly linked to their geographical origin.
- GIs are part of our shared cultural and intellectual heritage, which need to be both protected and promoted.
- Products that are protected and officially recognized as GIs can be divided into several categories:
- Agricultural products
- Natural goods
- Handicrafts
- Manufactured items
- Food products
- The significance of GIs has grown more in recent years. A GI represents the collective goodwill of a region, developed over many years.
- Nowadays, many consumers are increasingly interested in where products come from and pay close attention to the special traits of the items they buy.
- It's important to note that there is a difference between “place of origin” and “geographical indications”. GIs suggest to consumers that a product has certain qualities or characteristics they might appreciate.
Patent
- A patent is a form of intellectual property rights (IPR) that protects scientific inventions, which can be either products or processes that demonstrate a technical advancement over what is already known.
- A patent gives an exclusive right from the Government to its holder, allowing them to exclude others from: making, using, offering for sale, selling and importing the invention.
- For an invention to be eligible for a patent, it must meet three criteria:
- It must be new, meaning it shouldn't already exist in the world.
- It must be non-obvious to someone skilled in the relevant technology field, which is known as the Inventive Step.
- It must be capable of industrial application, meaning it can be used or manufactured in an industry.
- A patent can only be applied for to secure rights over an invention, not a discovery.
- For example, Isaac Newton discovered gravity when he saw an apple fall, which is considered a discovery.
- In contrast, Alexander Graham Bell invented the telephone, which is an example of an invention.
- Thus, creating something new is called an invention, while identifying something that already exists is referred to as a discovery.
Design
- A design refers to the shape, pattern, and layout of lines or color combinations used in any item.
- It offers a protective layer for the visual appeal or attractive features of a product.
- The protection for a design lasts for 10 years.
- This period can be renewed for an additional 5 years after it expires.
- During the protection period, a registered design can only be used if a license is obtained from its owner.
- Once the validity period ends, the design enters the public domain.
Plant Variety
- Plant Variety refers to the classification of plants based on their botanical traits.
- This category of plants is developed and bred by farmers.
- Grouping plants this way is important for conserving, improving, and providing access to plant genetic resources.
- An example of this is hybrid potatoes, which are created through selective breeding.
- Such protective measures encourage investment in research and development.
- They also acknowledge Indian farmers as cultivators, conservers, and breeders.
- This process helps in the production of high-quality seeds and planting materials.
- As a result, it contributes to the growth of the seed industry.
Semiconductor Integrated Circuits Layout Design
- Have you ever seen a computer chip?
- Do you know about integrated circuits, also called ICs?
- A semiconductor is a key part of every computer chip.
- Any product that has transistors and other electronic parts is made using semiconductor material.
- This material is used for insulation or is embedded in the electronic parts to perform electronic functions.
- For businesses, whether they are just starting or already established, it is important to protect and manage their intellectual property (IP).
- This protection is essential for business growth and success.
- A business must keep innovating and planning for the future; otherwise, it risks becoming stagnant and failing.
- It is also important to respect the IP of others, not just for ethical reasons but also for legal ones.
- Recognizing and respecting other people's IP encourages them to respect your IP in return.
- A startup is a business that focuses on creating, improving, and innovating new products, processes, and services for its target market.
- Today, startups are responsible for many disruptive technologies that have changed how we think and live.
- With around 20,000 startups, India has the third-largest startup ecosystem in the world.
- The Startup India initiative aims to inspire entrepreneurship in India and create a nation of job creators rather than job seekers.
- Intellectual property rights can play a crucial role in helping new businesses monetize their ideas and gain a competitive edge by providing a protective framework.
|
38 videos|180 docs|28 tests
|
FAQs on Small Business Chapter Notes - Business Studies (BST) Class 11 - Commerce
| 1. What is the significance of small businesses in rural areas of India? |  |
| 2. What are some government schemes available for small-scale industries (SSI) in India? |  |
| 3. How do small businesses contribute to the economy of India? |  |
| 4. What challenges do small businesses in rural areas of India face? |  |
| 5. How can entrepreneurs in rural areas benefit from government support for small businesses? |  |






















