Physical and Chemical Changes Class 7 Notes Science Chapter 5
| Table of contents |

|
| 1. Physical Change |

|
| 2. Chemical Change |

|
| Rusting of Iron |

|
| Crystallisation |

|

Every day, we notice many changes in our surroundings. These changes can involve one or more substances. For instance, when you dissolve sugar in water to make a cold drink, a change occurs. Setting curd from milk is another example of a change, as is the souring of milk. Even stretching a rubber band represents a change.
These everyday changes can be grouped into two main types: physical changes and chemical changes. In this chapter, we will explore these changes through various activities to understand their nature better.
1. Physical Change
In a physical change, a substance undergoes changes only in its physical properties such as shape, size, colour and state, and no new substance is formed.
Examples: Heating of water, melting of butter, cutting of paper etc.
 Physical Changes
Physical Changes
Properties of Physical Changes
- A physical change is temporary.
- No new substance is formed when a physical change takes place.
- Forms of energy, such as heat, light and electricity, are neither emitted nor absorbed in a physical change.
- A physical change can usually be reversed.

2. Chemical Change
Chemical changes are also called chemical reactions. A chemical change occurs when two substances react chemically to form a new substance with different chemical properties.
Examples: Food digestion, fruit ripening, and grape fermentation, Medicine results from a series of chemical reactions, creating beneficial materials such as plastics and detergents.
Properties of Chemical Changes
- A chemical change is permanent.
- A new substance is formed.
- Forms of energy, such as heat, light or electricity, may be emitted or absorbed during a chemical reaction.
- A chemical change is generally irreversible.
- Sound can be made (Explosion of a firework).
- A smell might change, or a new smell could be released (food gets spoiled).
- A color alteration might occur (slice of an apple acquires a brown color if it is not consumed immediately).
- A gas could be created (explosion produces heat, light, sound and unpleasant gases).
 Chemical Changes
Chemical Changes
A common change you might be familiar with is the rusting of iron. When you leave an iron object exposed for a while, it develops a layer of brownish material known as rust, called rusting.
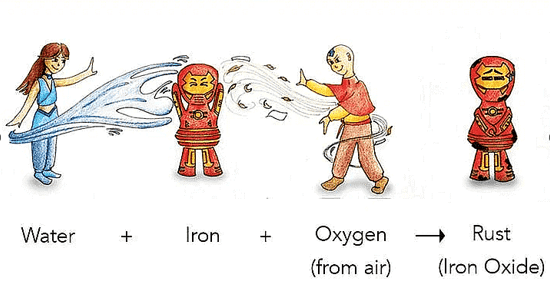 Rusting of Iron
Rusting of Iron
Example of Rusting: A wet iron pan (tawa) can rust in the kitchen if not properly dried, Iron gates of parks or farmlands, iron benches when kept in gardens. At home, you may have seen shovels and spades getting rusty after being exposed to the air for some time.
Rust is not the same as iron; it forms on the iron surface but is a different substance.
Let's understand more about Chemical Reaction with the help of Activities:
1. Burning of Magnesium Strip
- Obtain a small piece of a thin magnesium strip or ribbon.
- Clean its tip with sandpaper. Bring the tip close to a candle flame.
- It will burn with a bright white light.
- When it is fully burnt, it leaves behind a powdery ash.
- The following equation can represent the change:
Magnesium (Mg) + Oxygen (O2) → Magnesium oxide (MgO)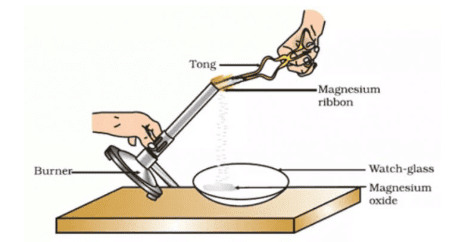 Burning of Magnesium Strip
Burning of Magnesium Strip - Gather the ash and mix it with a small amount of water.
- Stir the mixture (aqueous solution) well.
- Upon dissolving the ash in water, it forms a new substance. This change can be written in the form of the following equation:
Magnesium oxide (MgO) + Water (H2O) → Magnesium hydroxide (Mg(OH)2) - So, magnesium oxide is a new substance formed when magnesium is burnt.
- Magnesium hydroxide is another new substance formed by mixing magnesium oxide with water.
- When tested with litmus paper, Magnesium hydroxide turns red litmus to blue. Hence, it is a base.
2. Reaction Between Copper Sulphate with Iron
- Mix a teaspoon of copper sulphate (blue vitriol or neela thotha) in about half a cup of water in a test tube.
- Add a few drops of dilute sulphuric acid to the mixture. You should get a blue coloured solution.
- Put a nail into the mixture. Leave for half an hour or so and observe the colour of the mixture.
- Remove the nail and notice the changes due to a reaction between copper sulphate and iron.
- The change in colour of the solution from blue to green is because of the formation of iron sulphate, a new substance.
- The brown deposit on the iron nail is copper, another new substance.
- We can write the reaction as:
Copper sulphate solution (blue) + Iron → Iron sulphate solution (green) + Copper (brown deposit)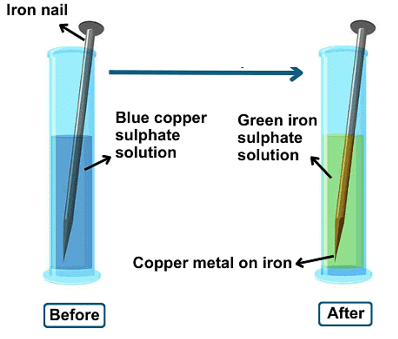
3. Reaction Between Vinegar and Baking Soda
- Take vinegar (acetic acid) in a glass beaker and add a pinch of baking soda (sodium hydrogen carbonate) to it.
- We will observe gas bubbles coming out of the beaker.
- This is due to the release of carbon dioxide.
- This can be confirmed by making the gas produced pass through freshly prepared lime water.
- The lime water turns milky when carbon dioxide is passed through it due to the formation of calcium carbonate.
- This reaction is a standard test for carbon dioxide presence.
- We can write the reaction as:
Carbon dioxide (CO2) + Lime water [Ca(OH)2 ] → Calcium Carbonate (CaCO3) + Water (H2O)
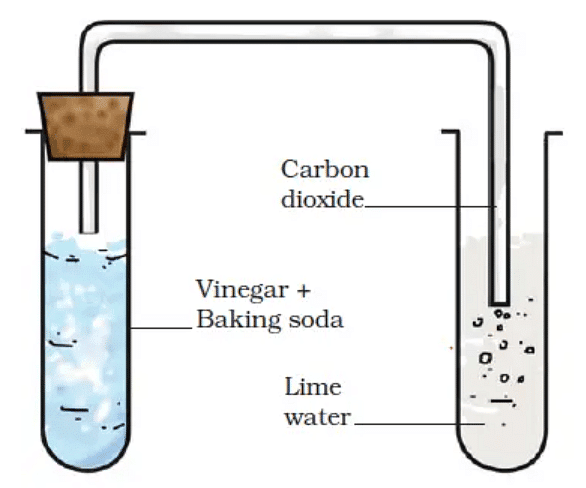 Set up to pass gas through lime water
Set up to pass gas through lime water
A protective shield:
- Ozone layer in our atmosphere serves as a protection against harmful ultraviolet radiation from the sun.
- The ozone absorbs this radiation and changes into oxygen. It is important to note that oxygen is different from ozone.
- The process of ozone breaking down can be considered a chemical change.
- If the ozone did not absorb ultraviolet radiation, this radiation would reach the Earth's surface. The presence of this radiation could harm us and other living creatures.
Rusting of Iron
When the iron comes in contact with oxygen and water it reacts and forms a red colored substance over it. It is called Rust, and the process is called Rusting of Iron.
 Rusting of Iron
Rusting of Iron
The chemical equation for the rusting of iron is 4Fe + 3O2 + xH2O → 2Fe2O3.xH2O
 |
Download the notes
Chapter Notes: Physical & Chemical Changes
|
Download as PDF |
Factors Essential for Rusting Process
- Rusting requires both oxygen and water or water vapour.
- Higher moisture content in air increases rusting speed.
Preventing Rusting
- Oiling and greasing: A thin layer of oil or grease on an iron object prevents it from coming in contact with moist air. Thus, rusting can be stopped.
- Painting: If iron articles like gates, chairs, bodies of cars, trucks, ships, etc. are painted, then it prevents moist air from coming in contact with iron. Ships made of iron rust easily because they are always in contact with seawater, which speeds up the rusting, even if they are painted.
- Coating with other metals: When iron sheets are dipped in molten zinc, a thin layer of zinc gets coated over the sheets. The process is called galvanization. This zinc layer prevents iron from coming in contact with moist air and stops rusting.
- Converting iron into stainless steel: Molten iron is mixed with a certain amount of carbon, chromium and nickel to form an alloy called stainless steel. This doesn't rust in moist air. So, it is used for making household utensils and surgical instruments.
Crystallisation
Salt can be obtained from seawater through evaporation, but this salt is impure, and its crystals are difficult to observe. Thus, large crystals of pure substances can be created from their solutions through a process known as crystallization, which is an example of a physical change.
Crystallization of Copper Sulphate
Let's understand this with an Activity:
- Take a glass of water and pour it into a beaker.
- Add a small amount of diluted sulphuric acid and heat the mixture.
- As the water starts to boil, gradually add copper sulphate powder while stirring it constantly.
- Keep adding the powder until it no longer dissolves.
- Next, filter the solution and let it cool down without disturbing it.
- After a while, you will see copper sulphate crystals forming.
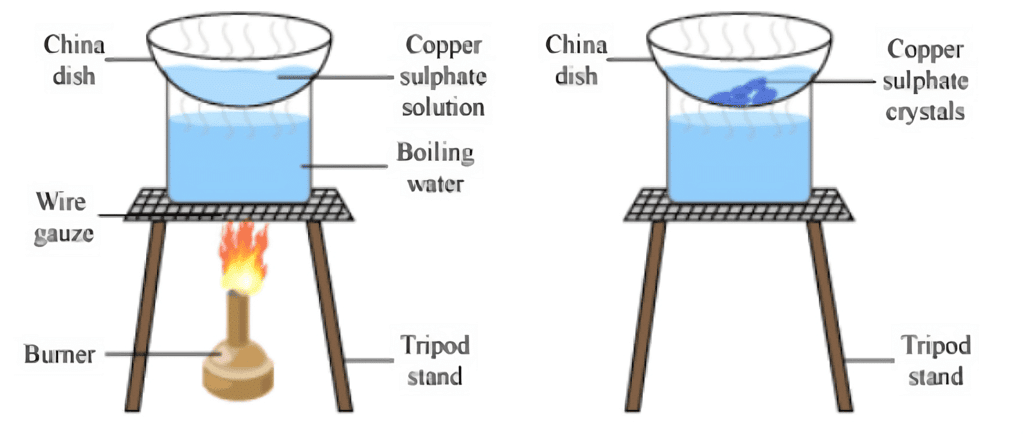 Crystallization of Copper Sulphate
Crystallization of Copper Sulphate
Now that you’ve learned about physical and chemical changes, observe the changes around you and classify them. For example, ice melting is a physical change, while rusting is a chemical change. This helps you understand everyday processes better.
|
112 videos|252 docs|28 tests
|
FAQs on Physical and Chemical Changes Class 7 Notes Science Chapter 5
| 1. What is the difference between a physical change and a chemical change? |  |
| 2. What is rusting of iron and how does it occur? |  |
| 3. Can crystallization be considered a physical change? |  |
| 4. What are some examples of physical changes? |  |
| 5. How can you identify a chemical change? |  |



































