3-Digit Numbers Class 2 Notes Maths
| Table of contents |

|
| What are 3-Digit Numbers? |

|
| Counting 3-Digit Numbers |

|
| Place Value of a Number |

|
| Face Value of a Number |

|
| Expanded Form of Numbers |

|
| Ascending and Descending Order |

|
| Even and Odd Numbers |

|
What are 3-Digit Numbers?
- 3-digit numbers start from 100 and go up to 999.
- These numbers are made up of 3 digits. The first digit must be 1 or a higher number. The other two digits can be any number from 0 to 9.
- Understanding 3-digit numbers is crucial because it helps in learning about larger numbers.
- It is important to remember that the first digit of a three-digit number cannot be zero. If the first digit is zero, it would change the number into a 2-digit number. For example, the number 045 is actually 45 when the leading zero is removed.

Counting 3-Digit Numbers
Three-digit numbers in terms of hundreds can be written as:
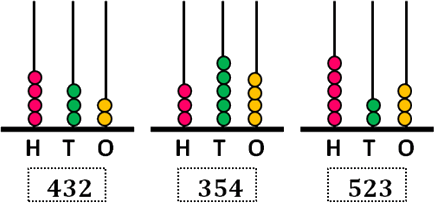
- 10 tens = 100 or 1 hundred
- 20 tens = 200 or 2 hundreds
- 30 tens = 300 or 3 hundreds
- 40 tens = 400 or 4 hundreds
- 50 tens = 500 or 5 hundreds
- 60 tens = 600 or 6 hundreds
- 70 tens = 700 or 7 hundreds
- 80 tens = 800 or 8 hundreds
- 90 tens = 900 or 9 hundreds
- 100 tens = 1000 or 10 hundreds = 1 thousand
Do you know?
- 1000 is the smallest 4-digit number.
- 999 is the largest 3-digit number.
- 100 is the smallest 3-digit number.
- 99 is the largest 2-digit number.
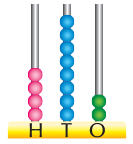
Place Value of a Number
The place value of a digit depends on the position of the digit in the place value chart.
- In a three-digit number, there are three positions: hundreds, tens, and units.
- The hundreds place tells us how many sets of one hundred are in the number.
- The tens place shows how many sets of ten are in the number.
- The units place indicates how many single ones are in the number.
- To better understand this, let’s use an example.
- The place value of 4 is 4 hundred or 400.
- The place value of 6 is 6 tens or 60.
- The place value of 9 is 9 ones or 9.
Face Value of a Number
In a numeral, the face value of a digit is the actual value of the digit, at whatever places it may be.
Thus, in the numeral 569,
- the face value of 5 is 5;
- the face value of 6 is 6;
- the face value of 9 is 9.
Expanded Form of Numbers
To express a number as a sum of place values of its digits is called expanded form.
In the numeral 29,

Q.1. Write 482 in expanded form.
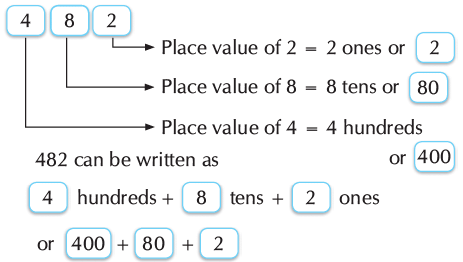
Comparison of Three-Digit Numbers
To compare 3-digit numbers, first we compare the digits at the hundreds place and then tens place and at last the ones place.
Let us compare the numbers 528 and 536.
Which one is lesser?
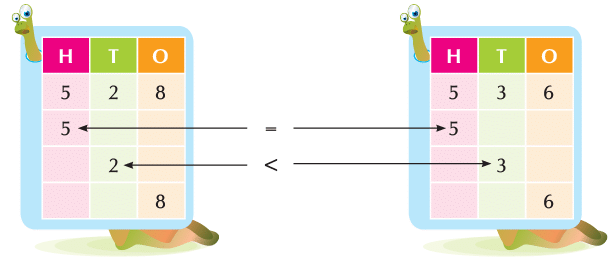
Here digits at the hundreds place in both the numbers are the same. So, we compare the tens place digits of both numbers.
Since 2 < 3
So, 528 < 536.
We say that 528 is less than 536.
Let us now compare 782 and 789. Which one is greater?
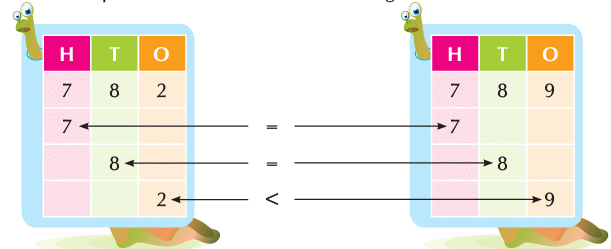
Digits at hundreds and tens places in both the numbers are same. So, we compare digits at ones place.
Since 9 > 2
So, 789 > 782.
We say that 789 is greater than 782.
Note: A one-digit number < a two-digit number < a three-digit number.
Ascending and Descending Order
Ascending order: Ascending is increasing (i.e., small → big).
Example: Arrange these numbers in ascending order (i.e., smallest to greatest).
498, 567, 834, 715
In the above numbers, the smallest number is 498 and the greatest number is 834.
Ascending order is: 498, 567, 715, 834
or
498 < 567 < 715 < 834
Descending order: Descending is decreasing (i.e., big → small).
Example: Arrange these numbers in descending order (i.e., biggest → smallest).
826, 736, 582, 914
In the above numbers, the largest number is 914 and the smallest number is 582.
Descending order is: 914, 826, 736, 582
or
914 > 826 > 736 > 582
Even and Odd Numbers
Even numbers
Let us take a collection of 6 apples.
Group these apples into pairs (i.e., set of 2 apples each).
Is there any apple left? No.
So, 6 can be fully grouped into pairs. Such numbers which can be fully grouped into pairs are called even numbers.
Note: Even numbers have 0, 2, 4, 6 or 8 at ones place. In other words, any 3-digit number with these digits at the ones place will be an even number. For example 122, 364, 678, 850, 936, etc.
Odd numbers
Let us take a collection of 7 oranges.
Group these oranges into pairs (i.e., set of 2 oranges each).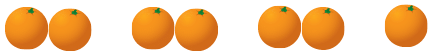 Is there any orange left? Yes, one.
Is there any orange left? Yes, one.
So, 7 cannot be fully grouped into pairs.
Such numbers which cannot be fully grouped into pairs are called odd numbers.
Note: Odd numbers have 1, 3, 5, 7 or 9 at ones place. In other words, any 3-digit number with these digits at the ones place will be an even number. For example 111, 237, 489, 865, 923, etc.
|
33 videos|87 docs|82 tests
|
FAQs on 3-Digit Numbers Class 2 Notes Maths
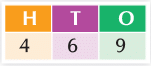
| 1. What is the place value of a number? |  |
| 2. What is the face value of a number? |  |
| 3. What is the expanded form of a number? |  |
| 4. How do you arrange three-digit numbers in ascending order? |  |
| 5. What are even and odd numbers? |  |
















