Introduction
The chapter "The Age of Industrialisation" explores the significant transformation that industrialisation brought to societies, economies, and cultures around the world. It begins by challenging the common belief that industrialisation is synonymous with the rise of factories, revealing that large-scale production existed even before factories through a system known as proto-industrialisation. The chapter traces the evolution of industries, starting from the early proto-industrial phase to the establishment of factories, and examines the impact of industrialisation on workers, society, and economies, especially focusing on India and Britain. It delves into how technology, changes in production methods, and global trade shaped the modern world, while also highlighting the resistance to industrialisation and its uneven impact across different regions and industries.
- E.T. Paull’s 1900 Music Book: Featured a cover image celebrating the "Dawn of the Century," symbolizing progress and the future.
- Angel of Progress: Central figure holding a flag, representing time and the future, surrounded by symbols of technological progress like railways, cameras, machines, and factories.
- Glorification of Technology: The image represents the early 20th-century belief that technological advancements equated to progress and development.
- Contrast Between East and West: Another image from a trade magazine compares Aladdin from the East (representing the past) with a modern mechanic from the West (representing modernity and technological innovation).
- Historical Focus: The chapter will explore the history of industrialization, starting with Britain and then examining India, particularly how colonial rule influenced industrial change.
- Impact on Society: The text encourages reflection on the true impact of industrialization on people's lives and whether continuous mechanization should still be celebrated today.
Before the Industrial Revolution
- Industrialisation is often associated with the rise of factory production and factory workers. Histories of industrialisation typically start with the establishment of factories. However, this view overlooks an earlier phase known as proto-industrialisation.
- For example: Before factories were widespread in England and Europe, there was already a lot of industrial production for global markets. This early stage of industrialisation, called proto-industrialisation, didn’t use factories but involved large-scale production in various ways.
- In the 17th and 18th centuries, European merchants moved to the countryside to supply money to peasants and artisans, encouraging them to produce goods for international markets. With expanding world trade and growing demand, merchants faced challenges in towns due to powerful urban associations that controlled production, competition, and prices. These associations had monopolies granted by rulers, making it hard for new merchants to start businesses in towns. As a result, merchants turned to the countryside to meet the increasing demand.
- In the countryside, poor peasants and artisans started working for merchants during a time when open fields were disappearing and common lands were being enclosed. With limited land and resources, they eagerly took advances from merchants to produce goods, which provided extra income and allowed them to stay on their small farms and earn additional income from proto-industrial production.
- In the proto-industrial system, a close relationship developed between towns and the countryside. Merchants, based in towns, managed production done primarily in the countryside.
- For example, a merchant clothier in England sourced wool, which was processed through spinning, weaving, fulling, and dyeing, with final finishing in London. This system, a network of commercial exchanges, was controlled by merchants who oversaw production by numerous producers working from their homes. Each merchant employed 20 to 25 workers at different stages, effectively managing hundreds of workers in total.

The Coming Up of the Factory
- Early Factories: The earliest factories in England appeared around the 1730s, but their numbers only began to grow significantly in the late 18th century.
Boom in Cotton Production: By the late 18th century, cotton production surged. In 1760, Britain imported 2.5 million pounds of raw cotton, which increased to 22 million pounds by 1787.
Technological Advancements: The 18th century saw a series of inventions that improved the production process for cotton. These innovations increased worker output and enabled the production of stronger threads and yarn.
Creation of the Cotton Mill: Richard Arkwright's invention of the cotton mill revolutionized production by consolidating all production processes—carding, twisting, spinning, and rolling—under one roof. This allowed for better supervision, quality control, and labor regulation.
Factories and English Landscape: By the early 19th century, factories became a prominent feature of the English landscape. The new mills and technologies were highly visible and impressive, overshadowing the traditional production methods still used in village workshops.

The Pace of Industrial Change
How rapid was the process of industrialisation?
Dynamic Sectors:
Leading Industries: In Britain, the most dynamic industries were cotton and metals. Cotton was the primary industry during the first phase of industrialisation up to the 1840s.
Shift in Dominance: After the 1840s, the iron and steel industry became the leading sector. The expansion of railways in England and its colonies from the 1840s and 1860s significantly increased the demand for iron and steel.
Export Growth: By 1873, Britain was exporting iron and steel worth about £77 million, which was double the value of its cotton exports.
Persistence of Traditional Industries:
Challenge of Displacement: New industries faced difficulty in displacing traditional industries.
Workforce Distribution: By the end of the 19th century, fewer than 20% of workers were employed in technologically advanced industrial sectors.
Textiles Production: Despite being a dynamic sector, much of the textile output was still produced outside factories, within domestic units.
Innovations in Traditional Sectors:
- Change in Traditional Industries: Traditional industries were not driven by the rapid changes in steam-powered cotton or metal industries, but they did experience growth.
Small Innovations: Growth in non-mechanised sectors like food processing, building, pottery, glass work, tanning, furniture making, and tool production was driven by seemingly small and ordinary innovations.
Slow Spread of Technology:
- Slow Technological Change: Technological advancements spread gradually and did not dramatically transform the industrial landscape.
- High Costs and Caution: New technology was expensive, leading merchants and industrialists to be cautious about adopting it.
- Maintenance Issues: Machines often broke down, and repairs were costly. Additionally, the technology did not always meet the claims made by its inventors and manufacturers.
These points reflect both the progress and limitations of industrialization, highlighting the persistence of traditional industries and the challenges in adopting new technologies.
Consider the case of the steam engine.
- James Watt improved the steam engine produced by Newcomen and patented the new engine in 1781.
- His industrialist friend Mathew Boulton manufactured the new model. But for years he could find no buyers.
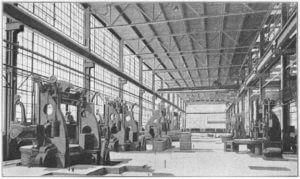
 A spinning factory in 1830
A spinning factory in 1830
- By the early 19th century, only 321 steam engines were in use in England.
- Most steam engines were used in cotton, wool, mining, canal works, and iron industries.
- Steam engines were not widely adopted in other industries until much later in the century.
- Industrialists were cautious about adopting the new technology due to its high cost and maintenance issues.
- Typical Worker: Historians now recognize that in the mid-19th century, most workers were still traditional craftspeople and laborers, not machine operators.
Question for Chapter Notes: Age of Industrialisation
Try yourself:
What was the key industry that led early industrialization in Britain?Explanation
- Textiles, particularly the cotton industry, were the key industry that led early industrialization in Britain.
- The growth of cotton production and the development of cotton mills revolutionized the industrial landscape.
- Cotton became a symbol of industrial progress due to significant advancements in production processes and technology.
Report a problem
Hand Labour and Steam Power
Abundant Labour in Victorian Britain: There was no shortage of workers, as poor peasants and vagrants flocked to cities for jobs. This kept wages low, discouraging industrialists from investing in machines that could replace human labor.
Skilled Hand Labour in 19th Century Britain: In the mid-19th century, hand labour was vital for producing specialized goods with intricate designs. Machines focused on mass production, but demand for custom products, example 500 types of hammers and 45 kinds of axes in Britain, relied on human skill, highlighting the continued importance of manual craftsmanship.
Seasonal Demand for Labor: Some industries, like gas works and breweries, needed more workers during certain seasons, so they preferred to hire hand labor temporarily rather than investing in machines.
Preference for Handmade Goods: The upper classes in Britain valued handmade products for their quality and craftsmanship, while machine-made goods were primarily exported to colonies. Handmade products came to symbolise refinement and class because of better finish and careful and unique design .
Different Contexts Abroad: In contrast, countries with labor shortages, like 19th-century America, favored mechanization to reduce the need for human labor.
Life of the Workers
1. Labour Migration:
- Urban Shift: Workers flocked to cities seeking jobs, often relying on social networks for quicker employment.
- Struggles: Those without connections faced long waits and stayed in temporary shelters.
2. Seasonal and Job Insecurity:
- Work Cycles: Seasonal work led to periods of unemployment, with some returning to rural areas during off-seasons.
- Odd Jobs: Finding alternative work was tough until the mid-nineteenth century.
3. Wages and Economic Variability:
- Wage Impact: Wages increased but did not always reflect real income due to inflation and economic fluctuations.
- Unemployment: High unemployment rates during economic slumps, with significant poverty in urban areas.
4. Resistance to Technology:
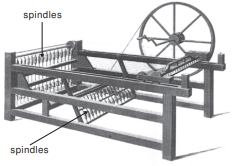
- Job Loss Fear: Workers resisted new technologies like the Spinning Jenny due to fears of losing their jobs.
5. Increased Employment Opportunities Post-1840s:
- Building Boom: Urban construction and infrastructure projects created new job opportunities.
- Transport Industry Growth: Employment in the transport sector doubled in the 1840s and again in the following decades.

A Spinning Jenny
Question for Chapter Notes: Age of Industrialisation
Try yourself:
What was a major concern of workers during the Industrial Revolution?Explanation
- Workers during the Industrial Revolution were afraid of being replaced by machines.
- The fear of losing job opportunities to automation was a significant concern among workers.
- This led to resistance towards adopting new technologies that could potentially replace human labor.
Report a problem
Industrialisation in the Colonies
The Age of Indian Textiles
Decline of Traditional Trade Networks:
- Disruption: The collapse of the traditional trade network, controlled by Indian merchants, led to the breakdown of established supply chains.
- Financial Impact: Weavers and artisans lost their access to advances and financial support previously provided by local merchants and bankers.
Shift to European-Controlled Ports:
- Port Decline: Major old ports like Surat and Hoogly experienced a dramatic fall in trade volume.
- New Ports Rise: The rise of new ports such as Bombay and Calcutta, controlled by European companies, meant that traditional trade routes were marginalized.
Economic Challenges:
- Credit Crisis: The drying up of credit from local bankers who had financed the textile trade led to economic hardships for weavers and artisans.
- Bankruptcies: The financial strain contributed to the bankruptcy of local bankers and further exacerbated the difficulties faced by producers.
Control by European Companies:
- European Monopoly: European trading companies gained monopoly rights, controlling trade and using European ships, which disrupted the traditional trade practices.
- New Dynamics: Weavers and artisans had to adapt to a new trading environment dominated by European interests, often leading to reduced autonomy and lower bargaining power.
Economic and Social Impact:
- Reduced Income: The decline in traditional markets and the shift to European-dominated trade affected the income and livelihood of weavers and artisans.
- Unemployment and Poverty: The collapse of old trading systems contributed to unemployment and poverty among artisans who struggled to find new markets or adapt to the changing economic landscape.
What Happened to Weavers?
Initial Demand: Increased Textile Exports: Post-1760s, despite consolidation, the demand for Indian textiles remained high in Europe, with the Company keen to expand exports.
Monopoly Establishment: Control Over Trade: The Company replaced local traders with Gomasthas, eliminating competition and imposing direct control over the weavers.
Control Measures: Gomasthas were appointed to supervise weavers, collect supplies, and enforce exclusive sales to the Company. Advance System: Weavers received loans but were tied to selling only to the Company, reducing their market options.
Economic Impact: Dependency: Weavers had to focus solely on weaving, often abandoning farming, leading to increased reliance on the Company.
Social Impact: Conflicts: Harsh treatment by gomasthas led to clashes and revolts; many weavers migrated or shifted to agricultural labor.
Long-Term Effects: Decline: Many weavers closed their workshops and faced economic hardship as traditional practices were undermined by Company policies.

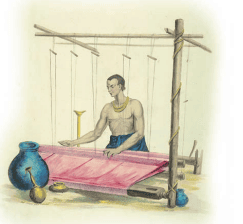
A weaver at work, Gujarat
Manchester Comes to India
Initial Optimism: Henry Patullo’s Prediction: In 1772, Patullo predicted that the demand for Indian textiles would remain high due to their unmatched quality.
Decline in Textile Exports: Export Decline: By the early 19th century, Indian textile exports plummeted. Piece-goods exports dropped from 33% of India’s total exports in 1811-12 to just 3% by 1850-51.
Factors Contributing to Decline: British Cotton Industry Growth: As England’s cotton industries advanced, there was increasing pressure to restrict imports and promote British goods. The British government imposed duties on imported cotton textiles to protect domestic industries. The East India Company facilitated the entry of British textiles into Indian markets, further damaging local industries.
Impact on Indian Weavers: Market Contraction: Indian weavers faced a dual challenge: a collapse in their export market and a local market overwhelmed by cheap British imports. Increased Competition: Manchester-made goods, produced more cheaply due to mechanization, made it difficult for Indian weavers to compete.
Raw Material Issues: Cotton Supply Disruptions: The American Civil War disrupted cotton supplies, leading to a rise in raw cotton prices. Indian weavers struggled to afford the high costs of raw materials.
Further Challenges: Domestic Industrialization: By the late 19th century, Indian factories began producing machine-made textiles, flooding the local market and exacerbating the difficulties for traditional weavers.
Consequences: The decline led to widespread economic hardship among weavers. Many faced unemployment or had to migrate for survival. Craft Decline - Traditional weaving industries struggled to survive amidst these changing conditions, leading to a significant decline in the handloom sector.
Question for Chapter Notes: Age of Industrialisation
Try yourself:
What was one of the main challenges faced by cotton weavers in India as a result of the industrialization in Britain?Explanation
- The collapse of the export market due to Manchester imports overwhelmed the market with machine-made goods, causing a problem for cotton weavers in India.
Report a problem
|
|
Download the notes
Chapter Notes: Age of Industrialisation
|
Download as PDF
|
Factories Come Up
• In 1854, the first cotton mill in Bombay came up.
• In 1855, first jute mill in Bengal came up.
• By 1862, four cotton mills came up.
• In 1862, another jute mill came up.
• In 1860s, the Elgin mill was started in Kanpur
• In 1861, the first cotton mill of Ahmadabad was set up.
• In 1874, the first spinning and weaving mill of Madras began production.
The Early Entrepreneurs
Business Origins: Many Indian business groups trace their roots back to trade with China, especially in opium and tea.
- Dwarkanath Tagore: Made a fortune in the China trade, later invested in industries.
- Parsis in Bombay: Dinshaw Petit and Jamsetjee Tata built industrial empires using wealth from China trade and cotton exports.
- Hukumchand: Founded India’s first jute mill in Calcutta in 1917, also involved in China trade.
Trade Networks: Merchants from Madras traded with Burma and had links to the Middle East and East Africa.
Local Merchants: Some operated within India, transporting goods and providing banking services. They later set up factories when investment opportunities arose.
Colonial Challenges: British colonial control limited Indian merchants, forcing them to export raw materials and pushing them out of shipping.
European Dominance: Before WWI, European agencies controlled much of Indian industry, making investment and business decisions while Indian financiers provided capital.
Where Did the Workers Come From?
• In most industrial regions workers came from the districts around.
• Industrialists usually employed a jobber to get new recruits.
→ He got people from his village, ensured them jobs, helped them settle in the city. Young workers of a Bombay mill, early twentieth century
Young workers of a Bombay mill, early twentieth century
Question for Chapter Notes: Age of Industrialisation
Try yourself:
Where did most of the workers in the early Indian factories come from?Explanation
- Most of the workers in the early Indian factories came from the districts around the industrial regions.
- Jobbers were employed to get new recruits, who usually brought people from their villages to the city for jobs.
Report a problem
The Peculiarities of Industrial Growth
European Managing Agencies: Dominated Indian industrial production, focusing on products for export, like tea, coffee, mining, indigo, and jute.
Indian Industry Beginnings: In the late nineteenth century, Indian entrepreneurs avoided competing directly with British imports, producing coarse cotton yarn instead of fabric.
Shifts in Production: By the early 1900s, the swadeshi movement encouraged boycotting foreign cloth, leading to increased domestic production of cotton piece-goods, which doubled between 1900 and 1912.
Impact of World War I:
- Before World War I, industrial growth was relatively slow. However, the war brought a dramatic shift.
- With British mills focused on war production, imports from Manchester to India declined, leaving a large gap in the market. Indian mills quickly seized this opportunity to supply the domestic market with essential war-related items such as jute bags, cloth for uniforms, tents, leather boots, and saddles.
- This surge in demand led to the establishment of new factories, extended hours for existing ones, and increased employment.
- As a result, industrial production in India experienced significant growth during the war years.
Post-War Changes:
- After World War I, Manchester was unable to regain its former status in the Indian market due to its failure to modernize and compete with emerging industrial powers like the US, Germany, and Japan.
- This led to a significant decline in Britain's economy, causing a collapse in cotton production and a dramatic drop in cotton cloth exports.
- Meanwhile, local industrialists in the colonies, such as India, consolidated their positions by replacing foreign imports with locally produced goods, gradually capturing the domestic market.

|
|
Take a Practice Test
Test yourself on topics from Class 10 exam
|
Practice Now
|
Small-scale Industries Predominate
Post-War Industrial Expansion: After World War I, factory industries grew, but they remained a small part of the economy. Major industrial centers were Bengal and Bombay, with about 67% of industries located there.
Small-Scale Production: Most industrial labor (95% in 1911 and 90% in 1931) was employed in small workshops and household units, often in less visible areas like alleys and bylanes.
Persistence of Handicrafts: Despite the rise of factory industries, small-scale and handicraft production continued to thrive. For instance, handloom cloth production grew nearly threefold from 1900 to 1940.
Technological Adoption: Handicraft workers adopted new technologies to improve productivity. By the 1940s, over 35% of handlooms used fly shuttles, which increased efficiency and production speed.
Survival of Specialized Weavers: Weavers who produced finer cloths for wealthier customers, such as Banarasi and Baluchari saris, fared better than those making coarser cloths. High-quality, specialized weaves could not be easily replicated by mills.
Challenges and Hardships: Weavers and craftspeople often faced difficult conditions, working long hours, and involving entire households in production. Despite their integral role in industrialization, their lives were marked by struggle and limited prosperity.
Market for Goods
- British Manufacturers and Indian Market: British manufacturers tried to dominate the Indian market, while Indian weavers, craftsmen, traders, and industrialists resisted colonial control and demanded tariff protection to safeguard their products.
Creation of New Consumers: To sell new products, manufacturers needed to create demand. Advertisements were used to make products appear desirable and necessary, shaping consumer preferences and creating new needs.
Role of Advertisements in Industrial Age: From the start of the industrial age, advertisements played a significant role in expanding markets and fostering a new consumer culture. Advertisements appeared in various media, such as newspapers, magazines, hoardings, and calendars.
Manchester Labels and Branding: Manchester industrialists labeled their cloth with "Made in Manchester" to establish brand recognition and signify quality. Labels were often beautifully illustrated and carried images, making the products more appealing to Indian buyers.
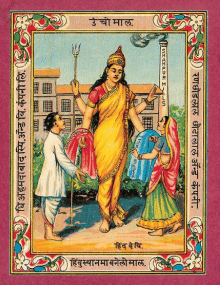
Use of Religious Imagery: Images of Indian gods and goddesses like Krishna and Saraswati were commonly featured on product labels. This created a sense of familiarity and divine approval, making foreign goods more acceptable to Indian consumers.
Calendars for Promotion: By the late 19th century, manufacturers began printing calendars to advertise their products. Calendars reached a wide audience, including illiterate people, as they were displayed in homes, shops, and offices. These calendars often featured gods and religious figures.
Royal Imagery in Advertisements: Advertisements frequently included images of emperors, nawabs, and royal figures, implying that products associated with royalty were of superior quality and worthy of respect.
Nationalist Advertisements and Swadeshi: Indian manufacturers promoted the nationalist message of Swadeshi through advertisements, urging people to support Indian-made goods. The advertisements emphasized the connection between supporting national industry and demonstrating patriotism.
 An Indian mill cloth label
An Indian mill cloth label
Question for Chapter Notes: Age of Industrialisation
Try yourself:
What was a key strategy used by Indian manufacturers to promote their products in the market?Explanation
- Advertisements played a crucial role in shaping consumer culture and making products seem desirable and necessary.
Report a problem
New Words
Proto – Indicating the first or early form of something
Stapler – A person who ‘staples or sorts of wool according to its fiber.
Fuller – A person who ‘Fulls’ – that is, gathers – cloth by pleating
Carding – The process in which fibers, such as cotton or wool, are prepared prior to spinning
Spinning Jenny – Devised by James Hargreaves in 1764, this machine speeded up the spinning process and reduced labour demand. By turning one single wheel a worker could set in motion a number of spindles and spin several threads at the same time.
Fly shuttle – It is a mechanical device used for weaving, moved by means of ropes and pullies. It places the horizontal threads (called the weft) into the verticle threads (called the warp).