Class 8 Geography Chapter 4 Notes - Agriculture
| Table of contents |

|
| Farm System |

|
| Types Of Farming |

|
| (a) Subsistence Farming |

|
| (b) Commercial Farming |

|
| Major Crops |

|
| Agricultural Development |

|
| (a) A Farm in India |

|
| (b) A Farm in USA |

|
Introduction
Four children walked through the village, they noticed a farmer working in his field. Curious, they asked him what he was doing. The farmer smiled and explained that he was planting wheat and had just added manure to the soil to help the plants grow better.
He told them that once the wheat was ready, he would sell it at the local market, where it would be sent to factories to be made into bread and biscuits. The children were excited to realize that the wheat from this very field could end up as the bread and biscuits they loved to eat at home.

This transformation from a plant to a finished product involves three types of economic activities.
Economic Activities
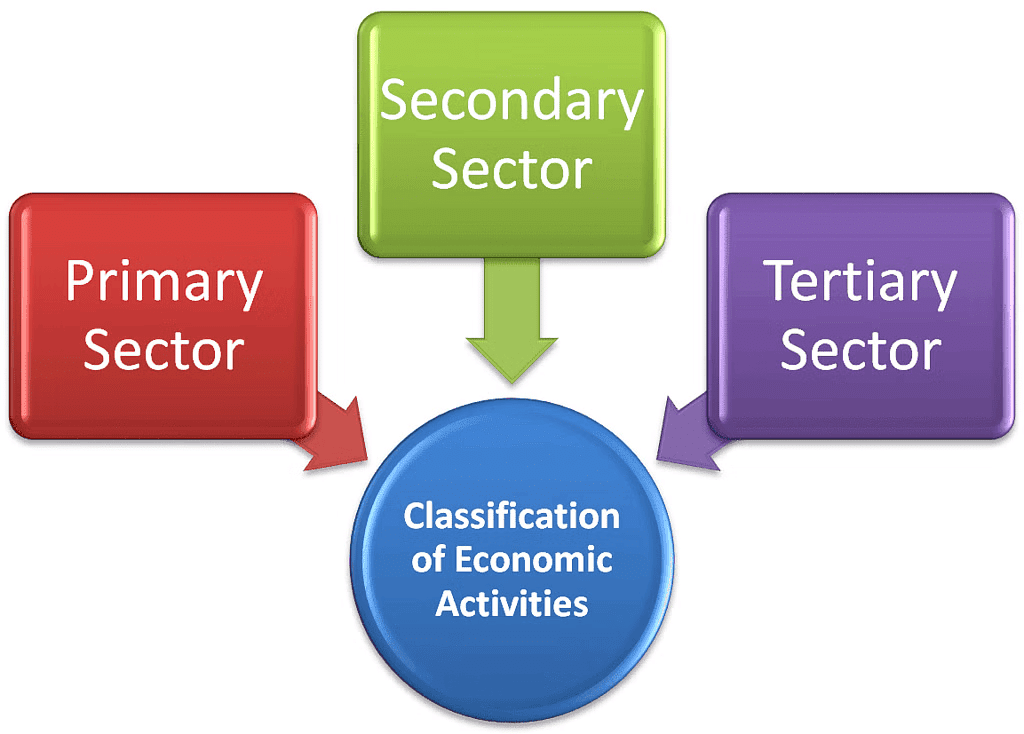 Economic activities are of three types:
Economic activities are of three types:
- Primary activities involve the extraction and production of natural resources, such as farming, fishing, and agriculture.
- Secondary activities focus on processing these natural resources into products, like baking bread or weaving cloth.
- Tertiary activities provide services support to primary and secondary sectors including transportation, trade, banking, insurance, and advertising.
Agriculture
- The term "agriculture" comes from the Latin wordsager or agri, meaning soil, and culture, meaning cultivation.
- Agriculture is a primary activity that involves growing crops, fruits, vegetables, and flowers, and raising livestock.
- Globally, 50 percent of people are engaged in agriculture, and in India, two-thirds of the population still relies on it for their livelihood.
- Favourable soil conditions and climate are essential for agricultural activities.
- The land used for growing crops is calledarable land.
- As shown in the map below, farming is mainly concentrated in areas of the world where the conditions for crop growth are suitable.
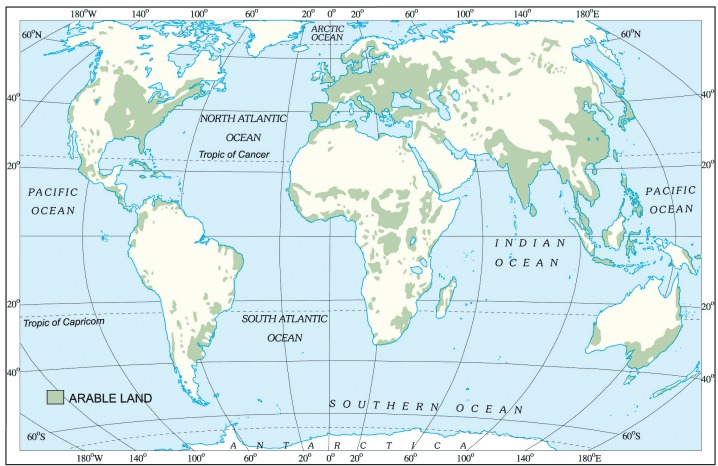 World Distribution of Arable Land
World Distribution of Arable Land
Some important terms you should know
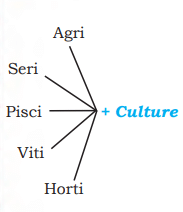
- Agriculture -The science and art of cultivation on the soil, raising crops, and rearing livestock. It is also called farming.
- Sericulture -Commercial rearing of silkworms. It may supplement the income of the farmer.
- Pisciculture -Breeding of fish in specially constructed tanks and ponds.
- Viticulture -Cultivation of grapes.
- Horticulture -Growing vegetables, flowers, and fruits for commercial use.
Farm System
Agriculture or farming can be viewed as a system with key components:-
- The main inputs include seeds, fertilizers, machinery, and labor. Essential operations in this system are ploughing, sowing, irrigation, weeding, and harvesting.
- The outputs of this system are products such as crops, wool, dairy, and poultry.
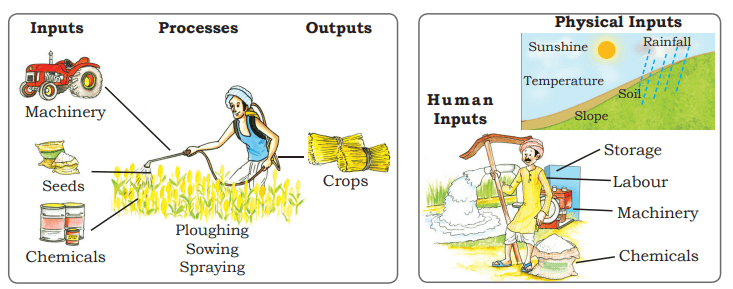 The farm system of an arable farm and physical & human farm inputs
The farm system of an arable farm and physical & human farm inputs
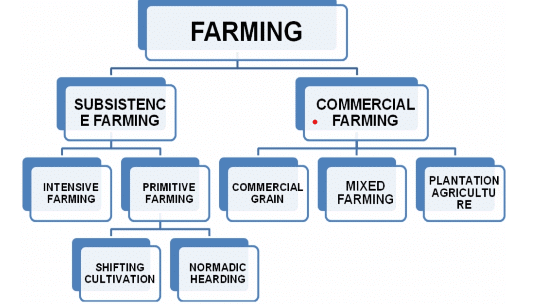
Types Of Farming
- Depending upon the geographical conditions, demand to produce, labor, and level of technology, farming can be classified into two main types.
- These are subsistence farming and commercial farming.
Organic Farming
In this type of farming, organic manure and natural pesticides are used instead of chemicals. No genetic modification is done to increase the yield of the crop.
(a) Subsistence Farming
- This type of farming is practised to fulfil the needs of the farmer's family. It typically involves low levels of technology and household labour to produce a small output.
- Subsistence farming can be divided into two categories :intensive subsistence farming and primitive subsistence farming.

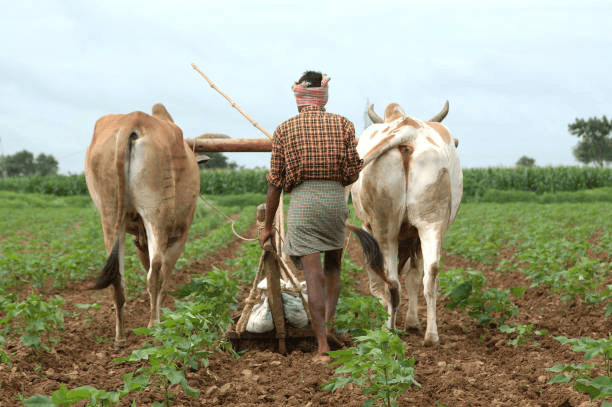
(i) Intensive Subsistence
- In intensive subsistence agriculture, farmers work a small plot of land with simple tools and a lot of labour.
- Favourable climates with plenty of sunshine and fertile soil allow for the cultivation of multiple crops per year on the same plot.
- Rice is the primary crop, but other crops like wheat, maize, pulses, and oilseeds are also grown.
- This type of farming is common in the densely populated monsoon regions of South, Southeast, and East Asia.
 (ii) Primitive Subsistence
(ii) Primitive Subsistence
- Primitive subsistence agriculture includes shifting cultivation and nomadic herding.
Shifting Cultivation:
- Shifting cultivation is practiced in the densely forested regions of the Amazon basin, tropical Africa, parts of Southeast Asia, and Northeast India.
- These areas experience heavy rainfall and rapid vegetation regrowth.
- To start, a plot of land is cleared by cutting down trees and burning them.
- The ashes are mixed into the soil, and crops such as maize, yam, potatoes, and cassava are planted.
- Once the soil's fertility declines, the land is abandoned, and the farmer moves to a new plot. This method is also known as ‘slash and burn’agriculture.
Note:- Shifting cultivation is known by different names in different parts of the world Jhumming - North-East India, Milpa-Mexico, Roca- Brazil, Ladang - Malaysia
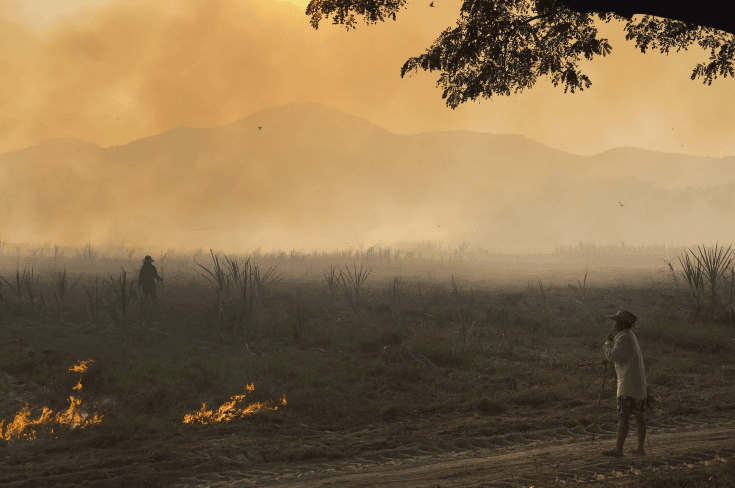 Slash and Burn Agriculture
Slash and Burn Agriculture
Nomadic Herding:
- Nomadic herding is practiced in the semi-arid and arid regions of the Sahara, Central Asia, and parts of India, such as Rajasthan and Jammu and Kashmir.
- In this system, herders move with their animals along established routes to find fodder and water.
- This movement is driven by climatic conditions and the terrain.
- Commonly reared animals include sheep, camels, yaks, and goats, which provide milk, meat, wool, hides, and other products for the herders and their families.
 Nomadic Herding
Nomadic Herding
(b) Commercial Farming
- In commercial farming, crops grown and animals are produced primarily for sale in the market.
- This type of farming involves large areas of cultivation and substantial capital investment, with most of the work being done bymachines.
- Commercial farming encompasses several types, including commercial grain farming, mixed farming, and plantation agriculture.
- In commercial grain farming, crops are grown specifically for sale, with wheat and maize being common examples.
- This farming method is typically found in the temperate grasslands of North America, Europe, and Asia. These regions have large, sparsely populated farms coveringhundreds of hectares.
- Due to severe winters, the growing season is limited, allowing for the cultivation of only one crop per year.
 Commercial Farming
Commercial Farming
(i) Mixed Farming
- In mixed farming, the land is utilized for both growing food and fodder crops as well as raising livestock. This approach combines crop cultivation with animal husbandry, providing a diverse range of products.
- It is commonly practised in regions such as Europe, the eastern USA, Argentina, southeast Australia, New Zealand, and South Africa.
- Mixed farming helps optimize the use of land by allowing farmers to produce a variety of goods and reduce reliance on any single crop or livestock product.
This system also contributes to soil fertility and reduces the risk of crop failure by balancing crop and animal production.
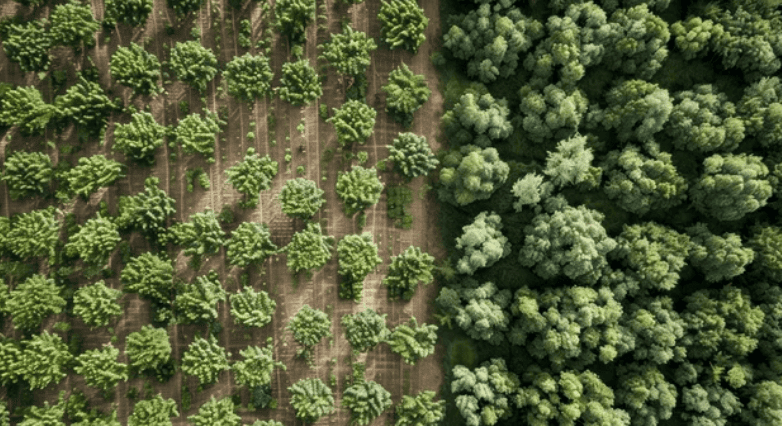 Mixed Farming
Mixed Farming
(ii) Plantations
- Plantations are a form of commercial farming where large-scale cultivation focuses on single crops such as tea, coffee, sugarcane, cashew, rubber, bananas, or cotton.
- These operations require substantial labor and capital investment. The harvested produce may be processed directly on the plantation or in nearby factories, making an efficient transport network essential for moving goods to processing facilities and markets.
- Plantations are primarily found in tropical regions with the right climate conditions.
- For instance, rubber is extensively cultivated in Malaysia, coffee thrives in Brazil, and tea is a major crop in India and Sri Lanka.
- The success of these plantations relies on the consistent weather patterns and specialized care needed for each crop, often leading to large, well-organized estates dedicated to a single type of product.
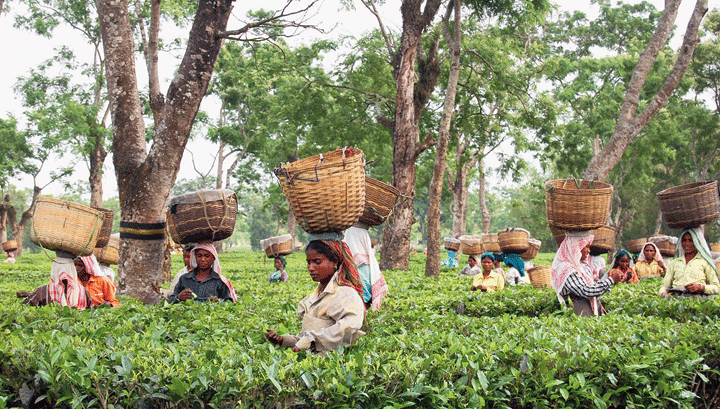 Assam land for tea and rubber plantation
Assam land for tea and rubber plantation
Major Crops
- A wide range of crops is grown to feed the increasing population and provide raw materials for industries that rely on agriculture.
- Major food crops include wheat, rice, maize, and millet.
- Jute and cotton are important for making fibres.
- Tea and coffee are key beverage crops.
 1. Rice
1. Rice
Rice is the world's most important food crop and is a staple food in tropical and subtropical regions.
- It thrives in hot, humid conditions with plenty of rainfall. Rice grows best in alluvial clayey soil that holds water well.
- China is the top producer of rice, followed by India, Japan, Sri Lanka, and Egypt.
In places with ideal weather, like West Bengal and Bangladesh, farmers can grow two to three rice crops each year. Rice Cultivation
Rice Cultivation
2. Wheat
- Wheat needs moderate temperatures and rainfall during its growing season, and plenty of sunshine at harvest time.
- It grows best in well-drained loamy soil. Major wheat-producing countries include the USA, Canada, Argentina, Russia, Ukraine, Australia, and India.
- In India, wheat is primarily cultivated during the winter months.
- Wheat farming is essential for food security and is a key crop in many of the world's most important agricultural regions.

3. Millets
- These crops, known as coarse grains, grow well in less fertile, sandy soils and are very tough.
- They don’t need much rain and can survive in warm to moderate temperatures with just enough moisture.
- In India, jowar, bajra, and ragi are common coarse grains.
- Other countries that grow these crops include Nigeria, China, and Niger.
- These grains are important for food in areas with dry conditions and are also used as animal feed.
 Millet cultivation
Millet cultivation
4. Maize
- Maize needs a moderate temperature, sufficient rainfall, and plenty of sunshine to grow well. It thrives in well-drained, fertile soils.
- Major maize-producing countries include North America, Brazil, China, Russia, Canada, India, and Mexico.
- Maize is also known as corn. Various colourful varieties of maize are found across the world.
 Maize cultivation
Maize cultivation
5. Cotton
- Cotton needs high temperatures, light rainfall, at least 210 frost-free days, and bright sunshine to grow well.
- It thrives best in black and alluvial soils.
- The leading cotton-producing countries are China, the USA, India, Pakistan, Brazil, and Egypt. Cotton is a key raw material for the cotton textile industry.
 Cotton cultivation
Cotton cultivation
6. Jute
- Jute, often called the ‘Golden Fibre,’ grows best in alluvial soil and thrives in high temperatures, heavy rainfall, and a humid climate.
- This crop is mainly cultivated in tropical regions, with India and Bangladesh being the leading producers of jute.
 Jute cultivation
Jute cultivation
7. Coffee
- Coffee needs a warm and wet climate, along with well-drained loamy soil. It grows best on hill slopes.
- Brazil is the top producer of coffee, with Colombia and India also being major producers.
 Coffee Plantation
Coffee Plantation
Who discovered the Coffee Plant? There are different versions about the discovery of coffee. In about AD 850, Kaldi, an Arab goat-herder, who was puzzled by the queer antics of his flock, tasted the berries of the evergreen bush on which the goats were feeding. On experiencing a sense of exhilaration, he proclaimed his discovery to the world.
8. Tea
- Tea is grown on large plantations and needs a cool climate with plenty of rain all year to help its leaves grow.
- It grows best in well-drained, loamy soil on gentle slopes. Many workers are needed to pick the tea leaves.
- The best tea in the world comes from Kenya, India, China, and Sri Lanka.
 Tea Plantation
Tea Plantation
Agricultural Development
- Agricultural development involves efforts to boost farm production to meet the needs of a growing population.
- This can be done in various ways, such as expanding the area under cultivation, growing more crops, improving irrigation, using fertilizers, and planting high-yielding seeds.
- Another key aspect is the mechanization of farming. The main goal of agricultural development is to enhance food security.
- Food security exists when all people, at all times, have access to sufficient, safe and nutritious food to meet their dietary needs and food preferences for an active and healthy life.
- In developing countries with large populations, intensive farming is common, where small plots of land are used to grow crops mainly for the farmer's own needs.
- In contrast, larger farms in countries like the USA, Canada, and Australia are more suited to commercial farming.
- To better understand agriculture in both developing and developed countries, let's look at two case studies—one from India and one from the USA.
(a) A Farm in India
- Small-size farmland.
- Use HYV seeds purchased from markets.
- Take advice from friends, elders or the government.
- Use tractors or bullock carts for ploughing the field.
- Use tubewell for irrigational activities.
- Also, rear livestock to earn more income.
- All the members of the family help him in various farm activities.
- The farmers take credit from a bank or the agricultural co-operative society to buy HYV seeds and implement them.
- Lack of storage facilities, so they are forced to sell the produce even when the market is not favorable to them.
- In recent years, the government has taken some steps to develop storage facilities.
 An Agricultural Field in India
An Agricultural Field in India
(b) A Farm in USA
- Large-sized farmland.
- The farmer generally resides in the farm.
- Some of the major crops grown are corn, soybean, wheat, cotton and sugarbeet.
- Adequate measures are taken to control pests that can damage the crop.
- From time to time, Soil samples are checked in the laboratory to check whether the nutrients are sufficient or not.
- The Farmer's computer is linked to the satellite, which gives him a precise picture of his field.
- This helps farmers to use chemical fertilisers and pesticides wherever they are required.
- Farmers use tractors, seed drills, levellers, combined harvesters and threshers to perform various agricultural operations.
- Grains are stored in automated grain storage or despatched to market agencies.
 Spray of Pesticides
Spray of Pesticides
|
69 videos|431 docs|46 tests
|
FAQs on Class 8 Geography Chapter 4 Notes - Agriculture
| 1. What is the difference between subsistence farming and commercial farming? |  |
| 2. What are the major crops grown in India? |  |
| 3. How does agricultural development differ between a farm in India and a farm in the USA? |  |
| 4. What factors influence the choice of farming type in different regions? |  |
| 5. What role does agricultural development play in improving food security? |  |
















