Class 5 Exam > Class 5 Notes > Year 5 Mathematics IGCSE (Cambridge) > Chapter Notes: Angles and Shapes, Symmetrical patterns
Angles and Shapes, Symmetrical patterns Chapter Notes | Year 5 Mathematics IGCSE (Cambridge) - Class 5 PDF Download
Symmetrical Patterns
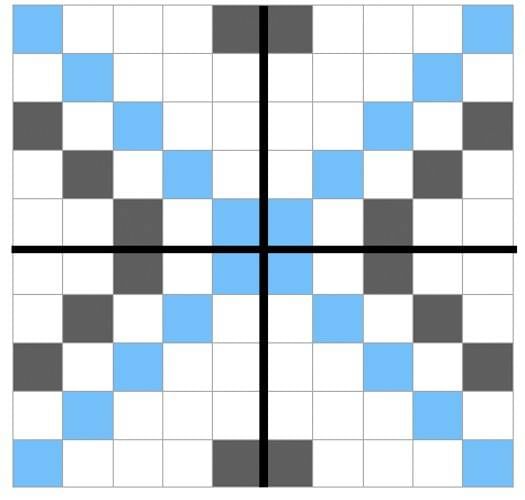
- Symmetry refers to a pattern or shape that can be divided into two or more identical parts.
- A symmetrical pattern may have multiple lines of symmetry, such as two or four, depending on how it is designed.
- Example: A completed symmetrical pattern can have two lines of symmetry, where reflecting across these lines produces identical halves.
Lines of symmetry can be:
- Horizontal: A line that runs left to right.
- Vertical: A line that runs up and down.
- Diagonal: A line that runs at an angle, neither horizontal nor vertical.
Identifying and Reasoning about Angles
An angle is formed by two rays or lines that share a common endpoint, measured in degrees.
Types of angles
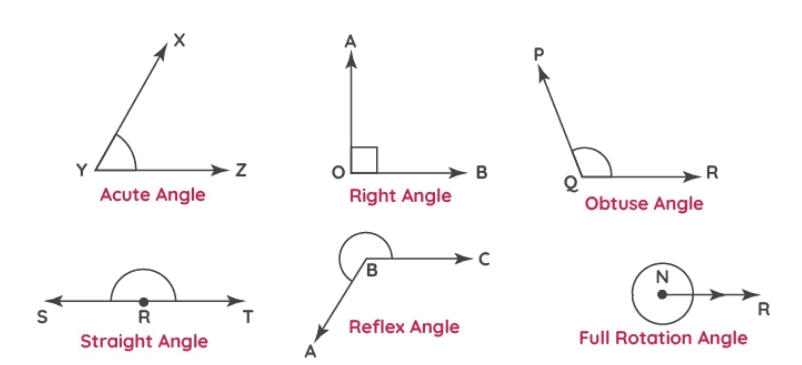
- Acute angle: Less than a quarter turn (less than 90°).
- Right angle: Exactly a quarter turn (90°), marked with a square symbol.
- Obtuse angle: Greater than a right angle but less than a half turn (between 90° and 180°).
- Reflex angle: Greater than a half turn but less than a whole turn (between 180° and 360°).
- Half turn: Exactly 180°, equivalent to a straight line.
- Whole turn: Exactly 360°, a complete rotation.
The angle on a straight line is always 180°, equivalent to a half turn (clockwise or anticlockwise).
Calculating missing angles on a straight line:
- Example: If one angle is 60°, the missing angle is 180° - 60° = 120°.
- Example: If one angle is 145°, the missing angle is 180° - 145° = 35°.
Triangles
Triangles are classified by their side lengths:
- Scalene triangle: All three sides are of different lengths.
- Isosceles triangle: Two sides are of equal length.
- Equilateral triangle: All three sides are of equal length.
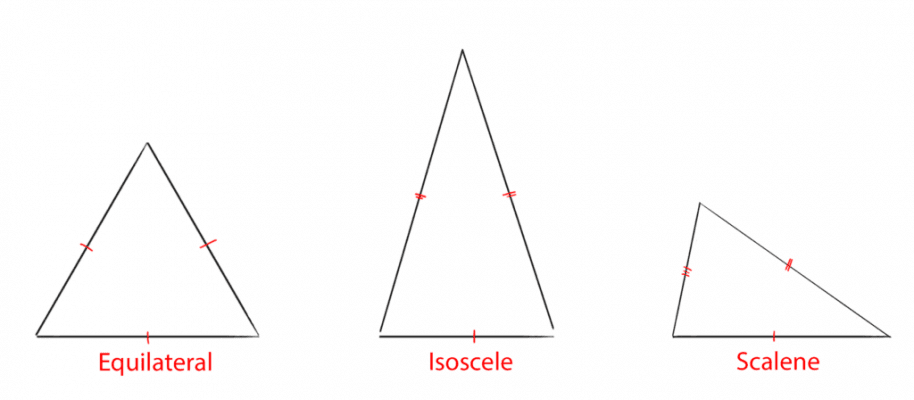
Markings are used to indicate equal side lengths:
- Equal sides are marked with identical symbols (e.g., a single hash mark or double hash mark).
Symmetry in triangles:
- Isosceles triangles have one line of symmetry, passing through the vertex between the equal sides and bisecting the base.
- Equilateral triangles have three lines of symmetry, each passing through a vertex and the midpoint of the opposite side.
Tessellation:
- Some triangles can tessellate, meaning they can cover a plane without gaps or overlaps.
- Equilateral triangles tessellate due to their equal sides and angles, fitting together perfectly.
Properties of isosceles triangles:
- Two sides are equal in length.
- The angles opposite the equal sides (base angles) are equal.
An isosceles triangle can have:
- Acute angles (all angles less than 90°).
- An obtuse angle (one angle greater than 90°).
- A right angle (one angle exactly 90°).
The document Angles and Shapes, Symmetrical patterns Chapter Notes | Year 5 Mathematics IGCSE (Cambridge) - Class 5 is a part of the Class 5 Course Year 5 Mathematics IGCSE (Cambridge).
All you need of Class 5 at this link: Class 5
|
43 docs|21 tests
|
FAQs on Angles and Shapes, Symmetrical patterns Chapter Notes - Year 5 Mathematics IGCSE (Cambridge) - Class 5
| 1. What is symmetry in shapes and how can it be identified? |  |
Ans.Symmetry in shapes refers to a balanced and proportionate similarity in the arrangement of parts on opposite sides of a dividing line or around a central point. A shape can be identified as symmetrical if it can be divided into two identical halves that are mirror images of each other. Common examples include circles, squares, and rectangles.
| 2. What are the different types of symmetry found in geometry? |  |
Ans.In geometry, there are several types of symmetry:
1. <b>Reflective Symmetry</b> (or Mirror Symmetry) - where one half of the shape is a mirror image of the other half.
2. <b>Rotational Symmetry</b> - where a shape looks the same after a certain amount of rotation.
3. <b>Translational Symmetry</b> - where a shape can be moved (translated) along a certain direction and still look the same.
4. <b>Glide Reflection Symmetry</b> - a combination of reflection and translation.
| 3. How are angles related to symmetrical patterns in shapes? |  |
Ans.Angles play a crucial role in creating symmetrical patterns. In symmetrical shapes, angles must be equal or match in specific ways. For instance, in a symmetrical triangle, the angles opposite equal sides are also equal. Understanding angles helps in recognizing and constructing symmetrical patterns effectively.
| 4. Can you give examples of everyday objects that exhibit symmetry? |  |
Ans.Yes, many everyday objects exhibit symmetry, including:
- A butterfly, which has reflective symmetry across its body.
- A human face, which typically demonstrates bilateral symmetry.
- Architectural structures like bridges and buildings that often use symmetrical designs for aesthetic appeal and structural integrity.
| 5. Why is understanding symmetrical patterns important in mathematics? |  |
Ans.Understanding symmetrical patterns is important in mathematics as it enhances spatial awareness and problem-solving skills. It helps students recognize patterns, which is a fundamental concept in geometry. Additionally, symmetry is used in various fields, including art, design, and science, making it a crucial aspect of mathematical education.
Related Searches
















