Birds: Food and More Class 3 Notes Science
| Table of contents |

|
| What are Birds? |

|
| Special Features of Birds |

|
| Important Body Parts of a Birds |

|
| How Does A Bird Fly? |

|
| Nesting Habits Of Birds |

|
What are Birds?
Birds are animals that have feathers, wings, and beaks. They use their wings to fly and their beaks to eat different kinds of food, like seeds, insects, or fish.

Special Features of Birds
We all know birds can fly, but why? Well, birds have special stuff that other animals don't, which helps them fly through the sky.
- Light Body: Birds have lightweight bodies, which helps them stay in the air for a long time without getting tired.
- Hollow Bones: Their bones are hollow and filled with air, making them strong but light. This helps them fly without being weighed down.
- Boat-shaped Body: Their bodies are shaped like boats, which helps them slice through the air easily and move forward smoothly.
- Two Wings: Birds have two wings, kind of like their arms, but with feathers that help them catch the air and stay up in the sky.
- Strong Muscles: Birds have super strong muscles, called flight muscles, that help them move their wings in all directions – up, down, forward, and backward – so they can fly wherever they want to go.
- Tail as a Rudder: Their tail acts like a rudder on a boat, helping them steer and change direction while they're flying.
These special features all work together to make birds awesome flyers!

Birds such as hens, turkeys and peacocks can fly only short distances because their bodies are heavy for flying long distances. Birds such as pigeons, swallows and crows can fly long distances. Birds such as sparrows and mynah fly at very low heights. Eagles, vultures and kites fly at a great height. They have sharp eyesight to see their prey on the ground and are called preying birds or birds of prey.
Would you be able to fly if you had a pair of wings?
No, because along with wings, birds have some other special features which help them to fly.
Important Body Parts of a Birds
Like human body-parts birds also have different body-parts as:
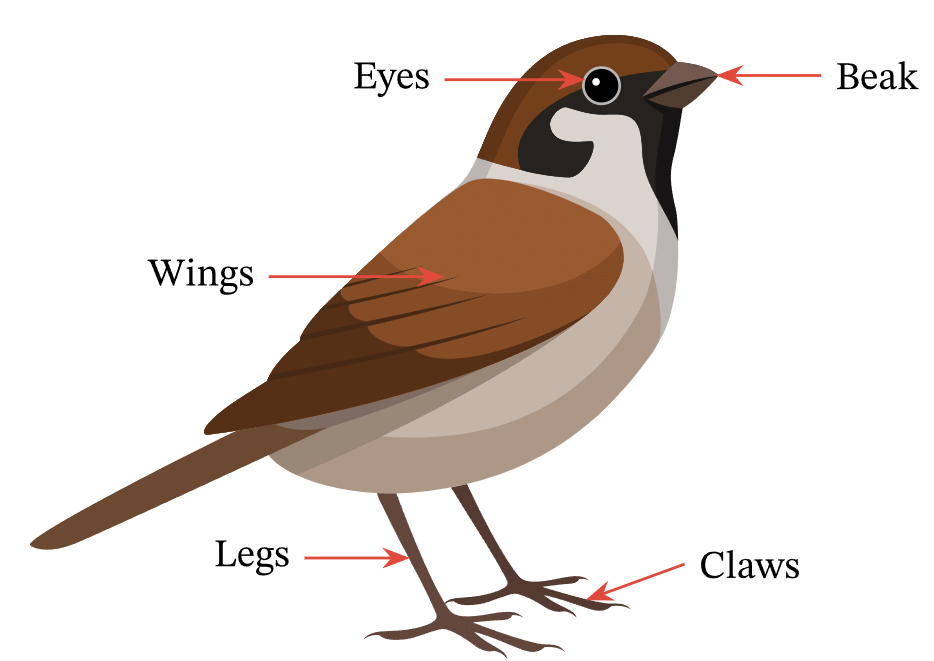 Body parts of a bird
Body parts of a bird
1. Feathers
Birds have these tiny, soft feathers covering their bodies. These feathers help keep them warm when it's cold and cool when it's hot and they're crucial for flying. There are two main types of feathers: down feathers, which are super soft and fluffy, and flight feathers, which are sturdier and help birds soar through the air.

2. Feet and Claws
Birds use their claws, also known as talons, for lots of stuff. They grab onto branches with them, catch their dinner, and defend themselves from other animals. Their claws are like their hands, helping them do all sorts of things in their birdy world.
1. Swimming Birds
Water birds such as ducks and swan have three toes in front and one toe at the back. The front toes are joined together by skin called a web. Such feet are called webbed feet. They help the bird to swim by pushing the water backwards.

2. Climbing Birds
Birds such as parrot and woodpecker have two toes that point forward and two toes that point backwards. Such toes help them climb trees.

3. Perching Birds
The feet of birds such as crow, sparrow and mynah have three toes in front and one at the back. They use their toes to perch or sit on high branches without falling even while sleeping.

4. Wading Birds
Water birds such as cranes and herons have long and thin legs. The spread out toes prevent the birds from sinking into the muddy water. These help them to walk through water in search of food. This movement is called wading.
 Crane
Crane
5. Scratching Birds
Hen, rooster and peacock have hard and sharp claws. Their hard claws help them to scratch and dig the ground and pull out insects and worms.
 Peacock
Peacock
6. Preying Birds (Flesh-Eating Birds)
Eagles, hawks and vultures are flesh-eating birds. They have strong and sharp claws called talons. They use their talons to catch live rats, toads and other small animals and hold their prey between their talons while flying.

3. Beak
Do you know how we use forks and spoons to eat? Well, birds use their beaks kinda like that. They use them to grab, hold, and munch on their food. Some beaks are pointy for poking into things, while others are hooked for tearing up food.

Beaks of Different Birds
The size and shape of beaks depend on the type of food they eat.
- A flesh-eating bird such as eagle or vulture has a strong, sharp beak, which is shaped like a hook. It helps to tear the flesh.
- Birds like kingfishers and pelicans have long, scissor-like beak for catching small fish.
- A woodpecker has a long, sharp beak which helps it to tap the bark of trees and pull out insects.
- An insect-eating bird such as swallow has a short and broad beak used to trap insects while flying.
- A parrot eats seeds, nuts and fruits. It has a strong, cur ved beak, which it uses to crack nuts and seeds.
- A duck has a beak with holes on its sides. It takes muddy water in its beak. Mud and water flow out through the holes. Plants and insects remain in the mouth and are eaten.
- A sparrow has a short, pointed, strong beak to crack seeds and eat insects.
 Different types of beaks
Different types of beaks
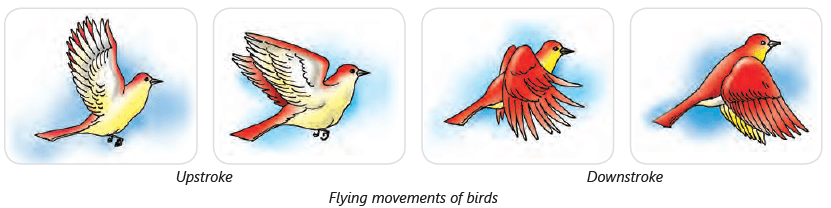
How Does A Bird Fly?
How Does A Bird Fly?
The bird first flaps its wings up and down to rise up in the air. When it reaches the desired height, it stops flapping its wings and simply glides through the air. The two types of flapping movements that birds show are:
- Upstroke: When the wings move upward and backward.
- Downstroke: When the wings move downward and forward.
Nesting Habits Of Birds
Birds build nests. They use twigs, grass, feathers, cotton, wool, leaves and sometimes even mud to build their nests. The nest acts as the shelter for the birds.
- It keeps them safe from bad weather.
- It protects them from their enemies.
- Birds lay their eggs in nests.
They take care of their young ones in the nests till they are ready to fly. Different birds make different kinds of nests. Once their young ones grow and fly away, birds do not use their nests. Most birds make a new nest every year.
- Nests in holes: A woodpecker makes a hole in a tree trunk with its beak. The hole is used as a nest.
- Nests in rocks: Eagles make their nests on the higher branches of tall trees or on rocks.
- A woven nest: A weaver bird uses grass, twigs, and leaves to weave a nest on a tree with its beak. The nest hangs from the branch of a tree. It pulls the grass in and out with its beak as it weaves the nest. There is a tunnel-shaped opening for the bird to enter.
- A stitched nest: A tailor bird makes its nest out of large-sized leaves. It uses its beak like a needle to stitch the leaves together using cotton threads or threads from a spider’s web. That is why it is called a tailor bird.
- Nests on open ground: Penguins and partridges make their nests on the ground with a few stones or pebbles. This prevents the eggs from rolling away.

How Do Birds Help Us?
Birds are our feathered friends. They are very useful to us in many ways:
- Birds eat insects, controlling their populations and reducing pests.
- Some birds pollinate flowers, helping plants grow fruits and seeds.
- Birds spread seeds by eating fruits and dispersing seeds in different areas.
- They indicate environmental health; diverse bird populations mean a healthy ecosystem.
- Birds inspire us with their beauty, songs, and amazing abilities.
|
19 videos|48 docs|30 tests
|
FAQs on Birds: Food and More Class 3 Notes Science
| 1. What are some special features of birds? |  |
| 2. What are some important body parts of birds? |  |
| 3. How does a bird fly? |  |
| 4. What are the nesting habits of birds? |  |
| 5. What do birds eat? |  |

|
Explore Courses for Class 3 exam
|

|




















