Class 5 Exam > Class 5 Notes > Year 5 Mathematics IGCSE (Cambridge) > Chapter Notes: Calculation, Positive and Negative Numbers
Calculation, Positive and Negative Numbers Chapter Notes | Year 5 Mathematics IGCSE (Cambridge) - Class 5 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Calculating with Positive and Negative Numbers |

|
| Addition and Subtraction |

|
| Missing Number Problems |

|
| Simplifying Multiplications |

|
| Multiplying Numbers up to 1,000 |

|
Calculating with Positive and Negative Numbers
- Positive numbers are greater than zero, while negative numbers are less than zero.
- The difference between two temperatures can involve positive and negative numbers, depending on whether the temperature increases or decreases.
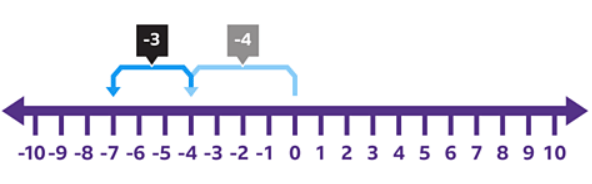
- A number line is used to perform additions and subtractions with negative numbers, especially when crossing zero.
- Bridging zero is necessary when the calculation moves from positive to negative numbers or vice versa.
- Example calculations using number facts for 9 to bridge zero:
- 4 - 5 = 4 + 4 - 4 - 5 = 9 - 5 = -1.
- 5 - 9 = 5 - 5 - 4 = 0 - 4 = -4.
Addition and Subtraction
- Estimation involves approximating the result of a calculation before performing it exactly.
- Example: Estimating the distance left to row or the total mass of a team requires rounding numbers to make quick approximations.
- Regrouping or reordering numbers can simplify addition:
- Example: 346 + 1,750 + 250 = (346 + 250) + 1,750 = 596 + 1,750 = 2,346.
- Subtraction does not always need to follow the given order; regrouping can help simplify calculations.
- Example sequence of operations starting with 4,653:
- Add 3,000: 4,653 + 3,000 = 7,653.
- Subtract 499:7,653 - 499 = 7,154.
- Subtract 2,486: 7,154 - 2,486 = 4,668.
- Add 32: 4,668 + 32 = 4,700.
- Mental calculations are suitable for simpler operations, while written methods (e.g., column method) are used for more complex ones.
Missing Number Problems
- Inverse operations (e.g., addition as the inverse of subtraction) are used to find unknown quantities.
- Symbols represent unknown quantities in number sentences.
- Example: For shopping bag problems:
- $20 - $2 = $18 (total for three trucks).
- $18 ÷ 3 = $6 (cost of one truck).
- $15 - $6 = $9 (cost of the model airplane).
- Related facts help solve problems with multiple unknowns by using known values to deduce others.
Simplifying Multiplications
- The distributive law regroups numbers to simplify multiplication:
- Example: 19 × 5 = (20 - 1) × 5 = (20 × 5) - (1 × 5) = 100 - 5 = 95.
- Example: 21 × 5 = (20 + 1) × 5 = (20 × 5) + (1 × 5) = 100 + 5 = 105.
- The commutative law allows reordering of factors:
- Example: 46 × 2 × 5 = 46 × (2 × 5) = 46 × 10 = 460.
- The associative law groups factors to simplify calculations:
- Example: 46 × 2 × 5 = (46 × 2) × 5 = 92 × 5 = 460.
- Using factors simplifies large multiplications:
- Example: 90 × 40 = (9 × 10) × (4 × 10) = (9 × 4) × (10 × 10) = 36 × 100 = 3,600.
Multiplying Numbers up to 1,000
Estimation is used to approximate products before calculating exactly.
Place value representation for multiplication:
Example: 234 × 3can be broken into:
- 200 × 3 = 600.
- 30 × 3 = 90.
- 4 × 3 = 12.
- Total: 600 + 90 + 12 = 702.
Example: 34 × 13 can be represented as:
- 30 × 10 = 300.
- 30 × 3 = 90.
- 4 × 10 = 40.
- 4 × 3 = 12.
- Total: 300 + 90 + 40 + 12 = 442.
Patterns in multiplication:
- Example: 27 × 10 = 270, 27 × 12 = 27 × (10 + 2) = 270 + 54 = 324.
Estimating before multiplying helps predict whether the actual product will be larger or smaller than the estimate:
- Example: For 597 × 4, estimate 600 × 4 = 2,400. The actual answer is slightly less.
Relationship between products:
- (234 × 4) + (345 × 4) = (234 + 345) × 4 = 579 × 4.
The document Calculation, Positive and Negative Numbers Chapter Notes | Year 5 Mathematics IGCSE (Cambridge) - Class 5 is a part of the Class 5 Course Year 5 Mathematics IGCSE (Cambridge).
All you need of Class 5 at this link: Class 5
|
43 docs|21 tests
|
FAQs on Calculation, Positive and Negative Numbers Chapter Notes - Year 5 Mathematics IGCSE (Cambridge) - Class 5
| 1. What are positive and negative numbers? |  |
Ans. Positive numbers are numbers greater than zero, while negative numbers are less than zero. For example, 5 is a positive number and -3 is a negative number. They are used to represent quantities, temperatures, and financial figures, among other things.
| 2. How do you add positive and negative numbers? |  |
Ans. When adding positive and negative numbers, you can think of it as combining two types of quantities. If you add a positive number to a negative number, you subtract the smaller absolute value from the larger absolute value and take the sign of the number with the larger absolute value. For example, 5 + (-3) equals 2, while -5 + 3 equals -2.
| 3. What is the rule for multiplying positive and negative numbers? |  |
Ans. The rule for multiplication is straightforward: when you multiply two positive numbers, the result is positive. When you multiply a positive number by a negative number, the result is negative. Conversely, multiplying two negative numbers results in a positive number. For example, 3 × (-2) equals -6, while (-3) × (-2) equals 6.
| 4. How do you subtract positive and negative numbers? |  |
Ans. To subtract a negative number, you add its positive counterpart. For example, subtracting -4 from 5 (5 - (-4)) is the same as adding 4 to 5, resulting in 9. Conversely, subtracting a positive number from a negative number requires you to move further into the negative range.
| 5. Why are positive and negative numbers important in real life? |  |
Ans. Positive and negative numbers are crucial in various real-life situations. They help in representing debts (negative values) and assets (positive values) in finance, temperatures below and above freezing in weather, and elevations above and below sea level in geography. Understanding these numbers allows for better decision-making and analysis in everyday life.
Related Searches














