Clothes—How Things are Made Chapter Notes | Our Wondrous World Class 5 - New NCERT PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Patterns with Threads |

|
| Traditions of Weaving |

|
| Thread |

|
| Crafting with Needle and Thread |

|
| Stitch and Decorate |

|
| Recycle |

|
| Exhibition |

|

Patterns with Threads
Nature’s artists inspire us to weave beautiful patterns. Let’s explore their creativity!
- Nature is full of hidden artists:
Birds build nests.
Spiders spin webs. - Animals, birds, and insects weave, stitch, and design things in nature.
- Birds like the male baya weaver build pouch-shaped nests from grass.

- Weaving strands over and under to make a pouch-like structure.
- Expert weaverbirds make fine nests, while young ones make rough ones.
- Weaving: Combines strips or threads to make patterns.
- One set of threads is placed vertically, the other horizontally and when crossed over and under each other, they make mats, baskets, and cloth.
Many natural materials like coconut fibre, bamboo, grass, jute, and cotton have been woven for a long time.
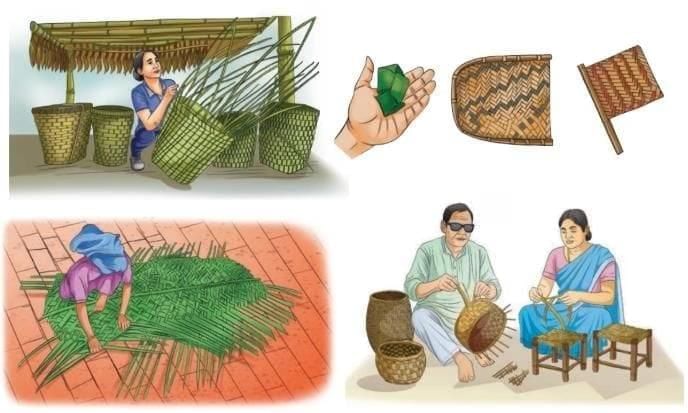

Do you know?
Indian muslin was so fine it was called “woven air,” and a saree could pass through a ring.
Traditions of Weaving
India’s weaving history is ancient and special. Let’s discover its story!

- People in India wove fabrics 4,000 years ago using a tool called a loom.
- Handloom fabrics are made by expert weavers using their hands.
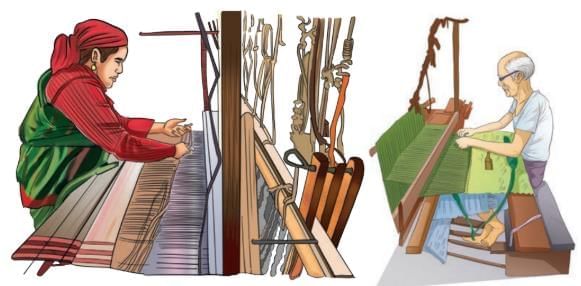
- Weaving keeps traditional skills and designs alive in India.
- Weaving provides work for many families across India.
- It’s special because it supports culture and people’s livelihoods.
- Textile mills use modern machines to weave cloth in large amounts.
Do you know?
Different regions have unique handloom traditions:
Kanjeevaram (Tamil Nadu)
Pashmina (Kashmir)
Ikat (Odisha and Gujarat).
Thread
Threads start as tiny fibres and become strong yarn. Let’s see how they’re made!
- Spinning twists cotton fibres into thread or yarn using a charkha.
- A charkha or spinning wheel helps to spin the thread from cotton like a pencil.
Do you know?
Gandhi Ji promoted making our own cloth (khadi) to become self-sufficient during the freedom struggle.
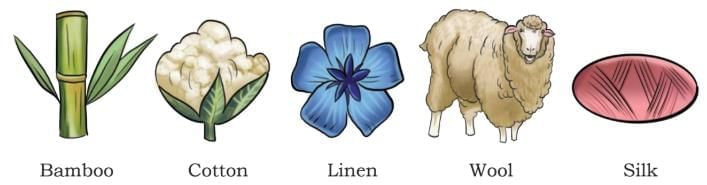
- The thin, hair-like strands from cotton are called fibres.
- Many natural sources of fibres like bamboo, cotton, linen, wool, and silk.
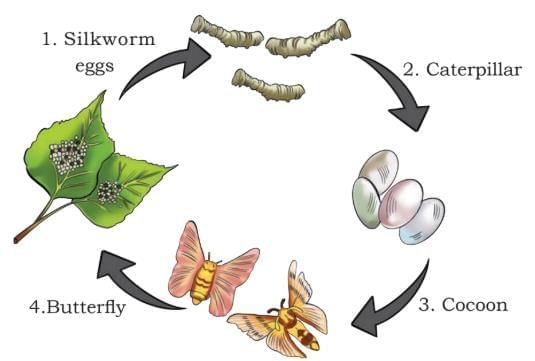
- Silk threads come from cocoons of the silk moth, put in hot water and then pulled gently to make thread.
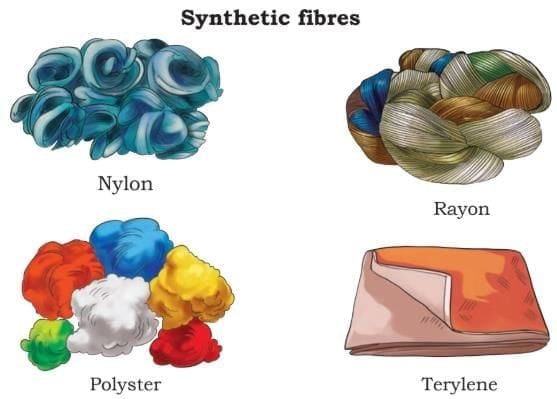
- Synthetic fibres are made by humans using artificial materials.
- Both natural and synthetic fibres are used in things we wear and use.
Do you know?
India is the largest producer of jute in the world.
Crafting with Needle and Thread
Nature is full of amazing things.Let's explore!
- The tailorbird, a tiny green bird, stitches big leaves to make a nest.
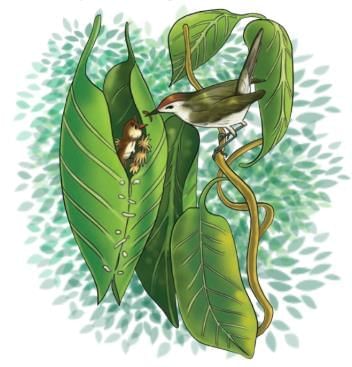
- It uses plant fibres or spider silk, poking holes with its beak like a needle.
- The bird sews leaf edges to form a soft, safe sleeve for its eggs.
- This green nest protects the tailorbird’s babies.
Do you know?
Pashmina wool comes from Changthangi goats of Ladakh. It is hand-spun and woven into very soft shawls.
You can use running stitches in daily life for:
- Mending or hemming clothes (like fixing a tear or shortening trousers)
- Basic hand sewing for joining pieces of fabric
- Embroidery on items such as pillow covers, scarves, table mats, and bags
- Temporary basting to hold fabric pieces in place before final sewing
- Creative crafts, homemade decorations, or simple repairs around the house.
If one thread breaks in your running stitch, the rest of the stitches can start to come undone because the running stitch is a continuous line. Once the tension is lost in one area, other stitches may loosen or unravel easily. This is why it’s important to secure the ends of your stitching well.
Stitch and Decorate
India’s stitches make clothes beautiful and tell stories. Let’s see how!
- Different parts of India use unique stitches to decorate clothes.
- Each stitch shows the traditions and stories of a place and its people.


Do you know?
Bandhani is a tie-dye style made by tying and dyeing parts of cloth to make patterns.
Recycle
Old clothes get a new life in India. Let’s learn how people reuse them!
- People rarely throw away clothes in our country; they pass them to younger siblings or others.
- An elder may turn old clothes into something new, like quilts.
- Beautiful quilts are made by joining small cloth pieces together.
- This tradition keeps clothes useful and reduces waste.
Do you know?
Handloom weaving supports thousands of families and is eco-friendly as it uses no electricity.
Exhibition
Show off your creations in a fun display. Let’s see how it’s done!

- Display mats, stitched cloth pieces, and leaf cutlery they made.
- Add name tags and short notes explaining how each item was created.
- Invite classmates or parents to visit the exhibition.
To get help with Activities, refer to the NCERT Solutions: Clothes-How Things are Made.
|
11 videos|234 docs|10 tests
|
FAQs on Clothes—How Things are Made Chapter Notes - Our Wondrous World Class 5 - New NCERT
| 1. What are the traditional methods of weaving in different cultures? |  |
| 2. How can I start crafting with needle and thread as a beginner? |  |
| 3. What are some creative ways to recycle old clothes into new items? |  |
| 4. What types of stitches can be used for decorating fabric? |  |
| 5. Why is understanding the history of weaving important in today's context? |  |




















