JSS 2 Exam > JSS 2 Notes > Information Technology for JSS 2 > Chapter Notes: Computer: Storage and Memory Device
Computer: Storage and Memory Device Chapter Notes | Information Technology for JSS 2 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| Data and Information |

|
| Data Storage Units |

|
| Computer Memory |

|
| Storage Devices |

|
Introduction
This chapter introduces the basic concepts of data, information, and how computers store and manage them. It explains the difference between data and information, various units used to measure data storage, and the types of memory in a computer. You will also learn about different storage devices used to keep data safe, both inside and outside the computer, and their purposes.Data and Information
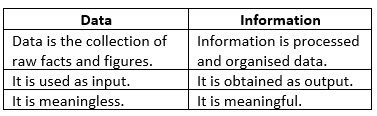
- Data includes text, numbers, special characters, facts, concepts, or instructions entered into a computer.
- Data represents unorganized facts and figures.
- Information is data that has been processed and organized.
- Information is meaningful and useful.
Let's understand the differences between data and information:
Let's get a better understanding about data and information with some examples from our everyday lives.
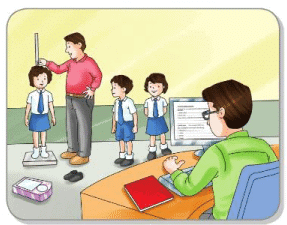
- Your sports teacher wants to make a list of height and weights of all the students. He collects the data from the students of your class and feeds it in the computer. After entering the raw data as input into the computer, he organises the data in ascending order. This processed data obtained as output is called information.
- When your mother purchases things from a grocery store, the grocer takes details from her about various food items purchased and feeds the data into the computer as input. After organising the data properly, the information is obtained as output and given to your mother in the form of a printed bill.

Data Storage Units
- All the data that we feed into a computer gets converted to a form that can be understood by the computer. This form is called the machine code.
- A computer takes the input in two forms: ON which is represented by 1 and OFF which is represented by 0.
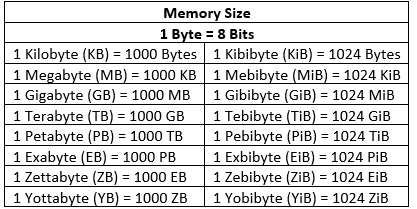
- Both 0 and 1 are called binary digits or bits. The data entered into a computer is stored in the form of bits and is measured in bytes.
- Bit is a single digit in binary number which can be either 0 or 1. It is the smallest unit of data in a computer.
- A group of 8 bits is called a byte. It is considered the smallest unit of memory.
Let's learn about a few more higher storage units.
Computer Memory
- Computers store data and instructions in memory.
- Two types of memory exist: primary memory and secondary memory.
Internal Memory
- Internal memory is the main memory, also called primary memory.
- It holds data and instructions while the computer is in use.
- Data in primary memory is lost when the computer is turned off.
- Two types of internal memory: Random Access Memory (RAM) and Read Only Memory (ROM).
Random Access Memory (RAM)
- RAM holds data and instructions during program use.
- It is temporary memory, erased when the computer is switched off.
- RAM allows reading and writing by the user.
- Data can be accessed randomly, hence the name Random Access Memory.
Read Only Memory (ROM)
- ROM is a key part of the computer’s memory unit.
- Computers need instructions to function, stored in ROM.
- When a computer starts, it looks for instructions in ROM.
- ROM is permanent memory, not erased when the computer is off.
- ROM is read-only, meaning users can only read, not write to it.
- It stores programs like the Basic Input/Output System (BIOS).
- BIOS helps hardware communicate with system and application software.
External Memory
- External memory, or secondary memory, stores data for a long time.
- Data remains safe even when the computer is off.
- Secondary memory is needed due to limited primary memory space.
- Accessing data from secondary memory is slower than from primary memory.
Storage Devices
Storage devices are used by a computer to store data and information. Let's learn about different storage devices.
Hard Disk
- Hard Disk Drive (HDD) is a common magnetic storage device.
- It is fixed inside the computer and not easily removable.
- Also called Winchester Disk, first made by IBM near Winchester, England.
- Contains disk platters for reading and writing data.
- Platters are sealed in a box.
- Available in capacities like 80 GB, 160 GB, 250 GB, 300 GB, and 500 GB.
Compact Disk (CD)
- CD is a round, shiny optical storage medium.
- Early CDs were read-only, but writable CDs exist now.
- Requires a CD Writer to write data.
- Stores nearly 640 MB of data.
- Used for large multimedia software, audio, and video files.
Digital Versatile Disk (DVD)
- DVD is an optical disk for multimedia applications.
- Storage capacity ranges from 4.7 GB to 17 GB.
- Removable media with high capacity.
Pen Drive/Flash Drive
- Pen drive, also called flash drive, is a portable USB device.
- Small, pen-like, and fits in a pocket.
- Stores data in capacities like 4 GB, 8 GB, and 16 GB.
- Used to transfer data between computers.
Blu-Ray Disk
- Blu-ray Disk (BD) is an optical disk, same size as CDs and DVDs.
- Single layer capacity is 25 GB, dual layer is 50 GB.
- Used for storing video data, like feature films.
- Named after the blue laser used to read it.
- Blue laser allows higher density storage than red laser for DVDs.
- Supports multimedia formats for high-definition video and audio.
Did You Know?
Blu-ray disk is called so because a blue laser is used to read the disk which allows information to be stored at a greater density than is possible with red laser used for DVDs.
Memory Stick
- Memory stick is a storage device for small digital products.
- Available in sizes: 4 MB, 8 MB, 16 MB, 32 MB, 64 MB, and 128 MB.
- Comes with a PC card adapter for use.
- 8 MB memory stick has over five times the capacity of a 3.5-inch floppy disk.
Glossary
- Computer: A smart machine.
- Bit: A single binary digit, either 0 or 1.
- Byte: A group of 8 bits.
- Primary memory: The main memory of a computer.
Points to Remember
- Data represents unorganized facts and figures.
- Information is processed and organized data.
- Data is converted to machine code for computers to understand.
- Computers take input as 0 (OFF) and 1 (ON).
- Data is stored in bits and measured in bytes.
- A byte is the smallest unit of memory.
- Two memory types: primary and secondary.
- Internal memory includes RAM and ROM.
- RAM allows reading and writing, erased when computer is off.
- ROM is read-only, permanent, and not erased when computer is off.
- Hard Disk Drive (HDD) is a common magnetic storage device.
- Compact Disk (CD) is an optical storage medium.
- DVDs are high-capacity removable media for multimedia.
- Blu-ray Disk (BD) is an optical disk, same size as CDs and DVDs.
- Memory stick is used for data transfer in small digital products.
The document Computer: Storage and Memory Device Chapter Notes | Information Technology for JSS 2 is a part of the JSS 2 Course Information Technology for JSS 2.
All you need of JSS 2 at this link: JSS 2
|
13 docs|11 tests
|
FAQs on Computer: Storage and Memory Device Chapter Notes - Information Technology for JSS 2
| 1. What is the difference between data and information? |  |
Ans.Data refers to raw facts and figures that have no context, while information is data that has been processed or organized in a way that makes it meaningful and useful.
| 2. What are the different types of data storage devices? |  |
Ans.The common types of data storage devices include Hard Disk Drives (HDD), Solid State Drives (SSD), USB flash drives, and optical discs such as CDs and DVDs. Each type has its own advantages and disadvantages in terms of speed, capacity, and portability.
| 3. How does computer memory work? |  |
Ans.Computer memory is used to store data temporarily or permanently. It works by using electronic circuits to hold data in the form of binary code. This data can be quickly accessed by the CPU for processing. Main types of memory include RAM (volatile memory) and ROM (non-volatile memory).
| 4. Why is it important to understand data storage units? |  |
Ans.Understanding data storage units is important because it helps users grasp how much data can be stored and how much space is available on their devices. Common units include bytes, kilobytes, megabytes, gigabytes, and terabytes, each representing increasing amounts of data.
| 5. What are the key points to remember about storage and memory devices? |  |
Ans.Key points to remember include the differences between storage (long-term data retention) and memory (temporary data access), the various types of storage devices available, their capacity and speed, and the importance of backing up data to prevent loss.
Related Searches




















