Grade 9 Exam > Grade 9 Notes > AP Computer Science Principles > Chapter Notes: Crowdsourcing
Crowdsourcing Chapter Notes | AP Computer Science Principles - Grade 9 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| Citizen Science |

|
| Crowdsourcing |

|
| Key Terms |

|
Introduction
The internet has transformed how data and resources are shared, enabling collaboration on a global scale. This chapter explores crowdsourcing, a method that leverages the internet to gather input, data, or solutions from large groups of people, and citizen science, a specific type of crowdsourcing where non-scientists contribute to research. It highlights how these approaches make problem-solving easier, provide diverse data, and reduce costs for organizations.
The Internet’s Role in Collaboration
- The Internet has transformed access to information and human resources, enabling researchers to tap into vast pools of data and collective effort.
- This connectivity simplifies problem identification and resolution, making solutions widely accessible.
- For instance, a quick online search can now replace consulting manuals or experts, and scientific discoveries are shared globally through digital journals and news, unlike the past when physical copies or word-of-mouth were required.
- This collaborative environment has fueled innovations like citizen science and crowdsourcing.
Citizen Science
- Definition: Citizen science involves ordinary people, often non-scientists, helping with scientific research by collecting data using devices like smartphones.
- Examples of tasks: Activities include counting birds at local feeders or observing the sky to identify new galaxies.
- Benefits: Allows a wide range of people to contribute to science, providing researchers with more diverse and extensive data.
- Impact: Enables scientists to conduct larger-scale research compared to working alone or in small lab groups.
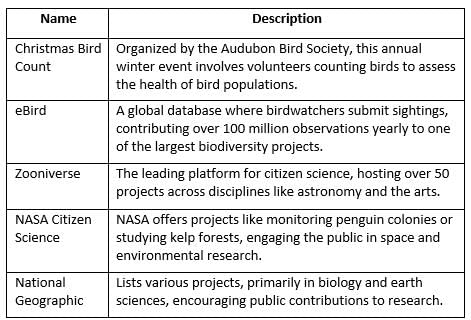
Examples of Citizen Science Projects
Below are notable citizen science initiatives:
Question for Chapter Notes: CrowdsourcingTry yourself: What does citizen science involve?View Solution
Crowdsourcing
- Definition: Crowdsourcing involves collecting large amounts of input, information, or solutions from people via the internet.
- Relation to citizen science: Citizen science is a form of crowdsourcing, but crowdsourcing extends to non-scientific areas as well.
- Benefits for organizations: Provides diverse data, reduces the need for manual data collection, and often eliminates costs for labor or information.
- Applications: Used for gathering feedback, finding workers or volunteers, solving problems, or obtaining content.
Examples of Crowdsourcing
Crowdsourcing takes many forms across industries:- Feedback Collection: Businesses gather public input through online reviews (e.g., for restaurants or products) or surveys (e.g., College Board questionnaires).
- Labor and Volunteering: Platforms like Uber and Airbnb rely on crowdsourced drivers and hosts, while Wikipedia depends on volunteer editors to create and maintain its content.
- Problem Solving and Content Creation: Innovation contests encourage people to submit solutions or designs for challenges, such as new products or global issues, often with prizes as incentives.
- Crowdfunding: Platforms like GoFundMe, Kickstarter, and Patreon enable individuals to raise funds for projects, from artistic endeavors to medical expenses, by collecting small contributions from many supporters.
Key Terms
- Citizen Science: The participation of non-scientists in research, contributing data to scientific projects using digital tools.
- Crowdfunding: Raising funds for projects by collecting small contributions from many people via online platforms.
- GoFundMe: A crowdfunding platform for raising money for personal causes, emergencies, or specific needs like medical or educational expenses.
- Kickstarter: A crowdfunding site supporting creative projects through small contributions from a large audience.
- Patreon: A platform enabling creators to receive recurring payments from supporters in exchange for exclusive content or rewards.
- Zooniverse: An online hub for citizen science, allowing users to assist in research tasks like data analysis or image classification across various fields.
The document Crowdsourcing Chapter Notes | AP Computer Science Principles - Grade 9 is a part of the Grade 9 Course AP Computer Science Principles.
All you need of Grade 9 at this link: Grade 9
FAQs on Crowdsourcing Chapter Notes - AP Computer Science Principles - Grade 9
| 1. What is citizen science and how does it involve the public in research? |  |
Ans.Citizen science is a collaborative approach to scientific research where members of the public contribute to scientific projects. This participation can include collecting data, analyzing results, or contributing knowledge and insights. By involving the public, citizen science enhances research efforts and promotes scientific literacy.
| 2. Can you provide examples of successful citizen science projects? |  |
Ans.Some notable examples of citizen science projects include the Audubon Society's Christmas Bird Count, where volunteers count bird species, and Zooniverse, which allows the public to help classify galaxies, transcribe historical documents, and more. These projects showcase how citizens can significantly contribute to scientific knowledge.
| 3. What is crowdsourcing and how does it differ from citizen science? |  |
Ans.Crowdsourcing is a method of obtaining input, ideas, or services from a large group of people, typically through the internet. Unlike citizen science, which focuses on scientific research, crowdsourcing can be applied to various fields, such as business, art, and technology, to gather diverse perspectives and solutions.
| 4. What are some popular applications of crowdsourcing? |  |
Ans.Popular applications of crowdsourcing include platforms like Wikipedia, where users collaboratively create and edit articles, and platforms like Kickstarter, which allow individuals to fund creative projects through collective financial contributions. These applications highlight the power of collective input in generating content and resources.
| 5. What key terms should one understand when learning about citizen science and crowdsourcing? |  |
Ans.Key terms include "volunteer," which refers to individuals who contribute their time and effort; "data collection," the process of gathering information; "collaborative," which emphasizes working together; and "platform," which refers to the online tools that facilitate these interactions. Understanding these terms is crucial for grasping the concepts of citizen science and crowdsourcing.
Related Searches














