Class 10 Economics Chapter 1 Notes - Development
What Development Promises- Different People, Different Goals
- Development has many aspects. People have different perspectives on development and there are ways by which we can arrive at common indicators for development.
- Different persons have different notions of development. They seek different things. They seek things that are most important to them.
- For example, a girl may seek equal opportunities and responsibilities compared to her brother, who might not share the same viewpoint.
- Similarly, industrialists aiming for increased electricity supply may clash with the interests of tribals who prioritize land preservation and sustainable irrigation methods.
 Different People Have Different Goals
Different People Have Different Goals - Development is subjective and varies among individuals based on their priorities and circumstances.
- What one person perceives as progress may not align with another's definition and could potentially harm their interests.
- Understanding diverse perspectives is crucial in crafting inclusive and sustainable development policies.
Income and Other Goals
- People's desires often revolve around aspects like regular work, improved wages, and fair prices for their produce, aiming for increased income.
- Alongside the pursuit of higher income, individuals also strive for equal treatment, freedom, security, and respect from others, while strongly opposing discrimination.
- Non-material factors such as friendship, dignity, security, and freedom significantly contribute to one's quality of life, surpassing the sole importance of material possessions or wealth.
- When considering job opportunities, factors beyond monetary rewards play a crucial role, including family amenities, work environment, learning prospects, and job security.
- Developmental aspirations encompass a blend of objectives, where women's involvement in unpaid work not only enhances their status but also promotes a culture of shared responsibilities and support for women in the workforce.
National Development
- It's crucial to recognize that individuals can hold conflicting views on what constitutes a nation's progress.
- Not all ideas are of equal significance.
- When there are conflicting opinions, it's essential to determine a fair and just path forward. Consider whether an idea benefits a large population or just a small segment.
- National development involves contemplating the impact of ideas on a broad spectrum of people and assessing whether there are better approaches to achieve progress.
How to Compare Different Countries or States
- Development can have various interpretations, leading to the classification of some countries as developed and others as underdeveloped.
- When comparing entities, it's essential to consider both similarities and differences.
- For instance, income is a crucial criterion for comparing countries.
- Higher income levels are often associated with more developed nations, as increased income enables access to essential resources and amenities.
- Total income alone is not a sufficient measure for comparing countries, as populations vary.
- To address this, the average income, also known as per capita income, is calculated by dividing the total income by the population.
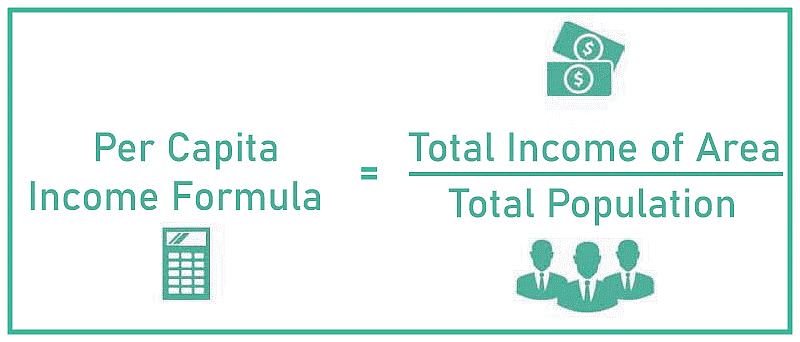
- The World Bank classifies countries in its World Development Reports based on per capita income. In 2019, high-income countries had per capita incomes of $49,300 or more, while low-income countries had $2,500 or less. India, with a per capita income of $6,700, is considered a low-middle-income country. Rich countries are typically termed developed countries.
- Countries with higher incomes are more developed than others with less income.
- As different countries have different populations, comparing total income will not tell us what an average person earns. So, we compare the average income of countries.
Income and Other Criteria
When we think of a nation or a region, besides average income, public facilities and other criteria are equally significant attributes.
- Individual Aspirations and Goals: People aspire for better income along with goals like security, respect, equal treatment, and freedom.
- National or Regional Attributes: Besides average income, other important attributes define the development of a region or nation. When comparing per capita income, Haryana emerges as the most developed state, while Bihar appears least developed.
- Infant Mortality Rate: Kerala has lower infant mortality compared to Haryana, highlighting significant differences in child welfare.
- Educational Disparities: In Bihar, around half of children aged 14-15 do not attend school beyond Class 8, indicating educational challenges.
- The data reflects disparities in healthcare and education across different states, impacting the well-being and future opportunities of their populations.
Public Facilities
These are the services provided by the government to its citizens. Some of the important public facilities include:
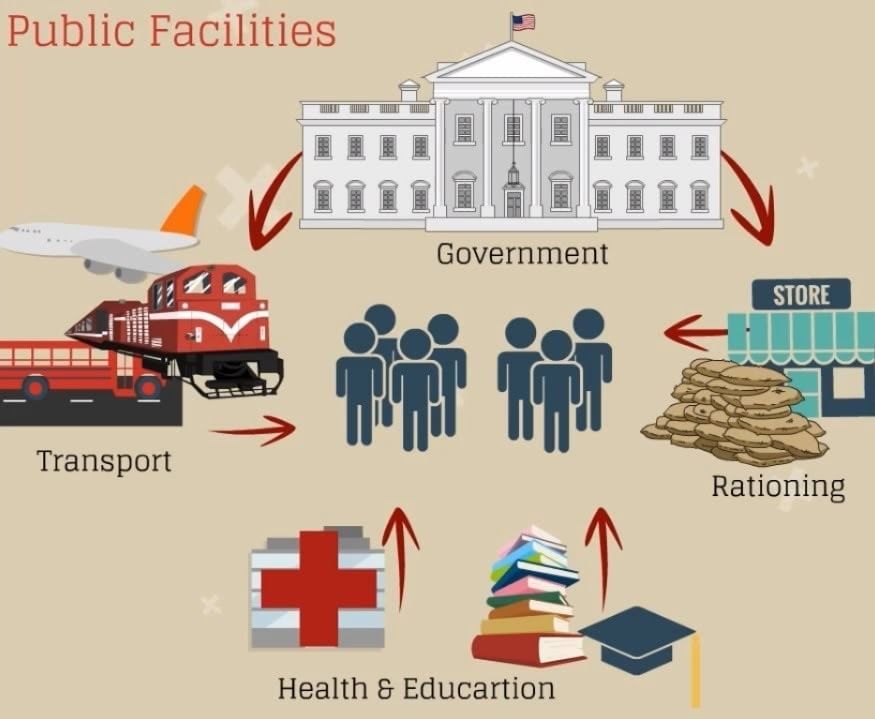
- Public Education
- Hospitals
- Public Distribution System
- UNDP on the basis of educational level, health status and per capita income
- Comparison with neighbouring countries - Sri Lanka much better in per capita income, life expectancy, HDI rank etc.
Income Limitations: Higher income doesn't guarantee access to essential services like clean environment, unadulterated medicines, or protection from diseases.
Collective Provision: Essential services such as security and education are best provided collectively. This is more cost-effective and ensures broader access.
Kerala vs. Haryana
- Kerala: Lower infant mortality rate, higher literacy rate, and better school attendance despite lower per capita income.
- Haryana: Higher income but poorer health and education indicators.
Public Distribution System (PDS): States with efficient PDS have better health and nutrition outcomes.
International Comparisons
- Sri Lanka: Higher human development indicators than India.
- Nepal and Bangladesh: Better life expectancy despite lower per capita income.
Human Development Index (HDI): Measures health, education, and standard of living, emphasizing overall well-being rather than just income.
The Human Development Report (HDR) is an annual publication by the United Nations Development Programme (UNDP). It provides insights into global development issues and trends, focusing on improving human wellbeing.
Key Features:
- Human Development Index (HDI): A ranking of countries based on health, education, and income.
- Thematic Focus: Each report explores a specific theme like inequality, sustainability, gender equity, or climate change.
- Data & Analysis: Offers global and regional trends in human development, comparing progress across countries.
- Goal: To promote policies for sustainable development, equity, and human rights.
Significance: The HDR helps shape global and national policies to improve human development outcomes.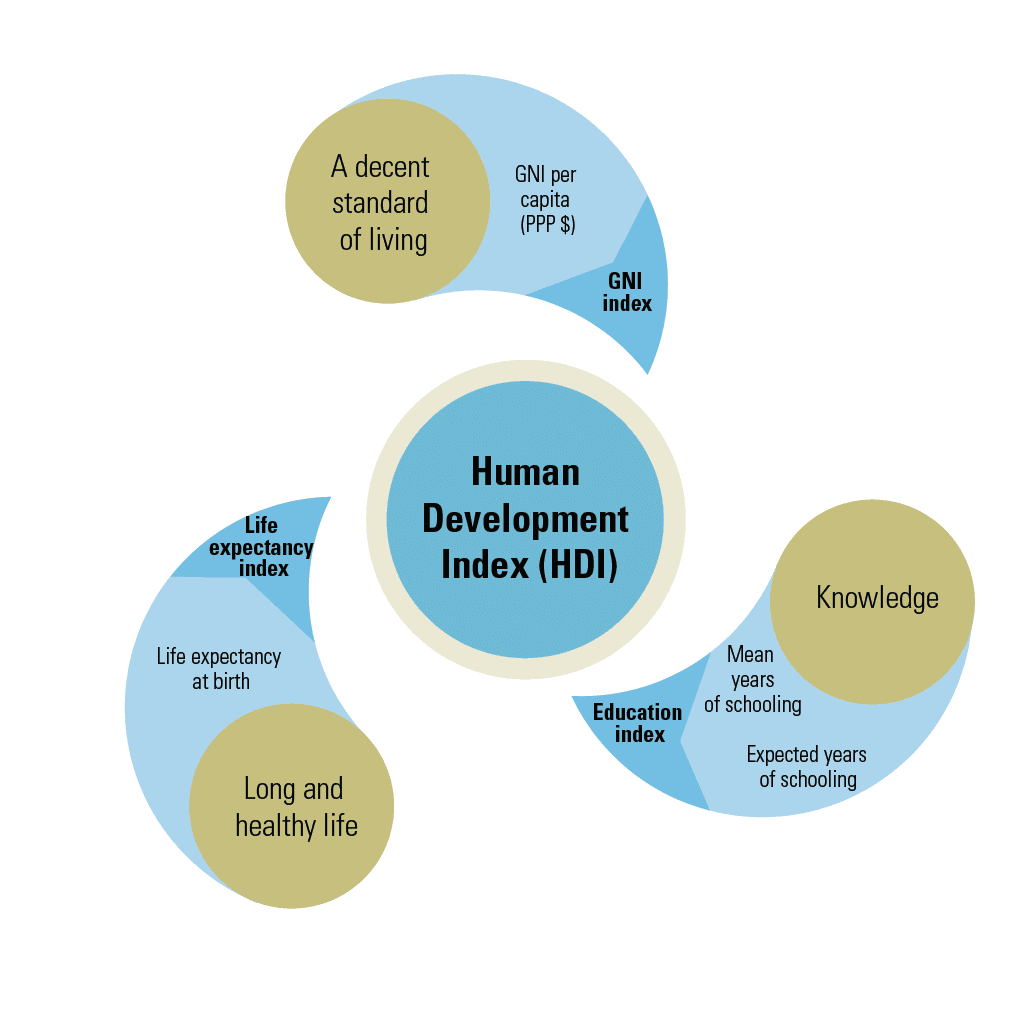
Sustainability of Development
Sustainable development is defined as development that meets the needs of the present, without compromising the ability of future generations. Scientists have been warning that the present type and levels of development are not sustainable.
Types of Resources
- Renewable Resources: Renewable resources like groundwater are naturally replenished, similar to crops and plants. However, if these resources are consumed at a faster rate than they are replenished, overuse occurs.
- Non-Renewable Resources: Non-renewable resources, such as fossil fuels, are finite and will eventually be depleted after continuous use. While new resources may be discovered, the stock is limited and will diminish over time.
- Example 1: Groundwater in India is overused, especially in agricultural regions, urban areas, and hard rock zones, leading to rapid depletion. If unchecked, 60% of the country will face this issue in 25 years. Sustainable practices like water conservation and efficient irrigation can prevent overuse.
- Example 2: Global crude oil reserves may last 50 years, with the Middle East having 70 years of reserves. Oil-importing nations like India face price risks, while countries with fewer reserves, like the U.S., seek control through military or economic means. Sustainable energy is essential to reduce dependency.
|
66 videos|614 docs|79 tests
|
FAQs on Class 10 Economics Chapter 1 Notes - Development
| 1. What are the different goals of development for various individuals and communities? |  |
| 2. How can we measure national development across different countries? |  |
| 3. What role does sustainability play in development? |  |
| 4. How do income levels influence development goals? |  |
| 5. What methods can be used to compare the development of different states or regions? |  |

















