Dissolving Chapter Notes | Natural Science and Technology (Grade 6-A) PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| What is Dissolving? |

|
| Rates of Dissolving |

|
| Points to Remember |

|
| Difficult Words |

|
| Summary |

|
What is Dissolving?
Dissolving is the process where a solute (a substance, usually a solid) mixes completely with a solvent (usually a liquid, like water) to form a solution, a special type of mixture. In a solution, the solute’s particles spread evenly among the solvent’s particles, making the solute invisible, though it is still present. This process is distinct from melting, which involves a state change due to heat.
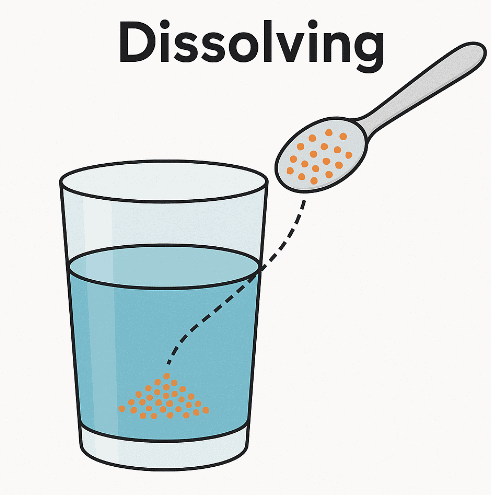
Dissolving vs. Melting
- Dissolving: Occurs when a solute, like sugar, mixes with a solvent, like water, to form a solution. The sugar particles disperse among water particles, creating a uniform mixture without changing state (sugar remains a solid at the particle level). For example, in a sugar-water solution, the sugar is no longer visible but can be recovered by evaporating the water.
- Melting: A state change where a solid becomes a liquid due to heat, e.g., ice melting into water. The particles in a solid (with fixed positions) gain energy to move freely as a liquid, where they are close but mobile. Melting does not involve mixing with another substance, unlike dissolving.
- Key Difference: Dissolving involves mixing two substances (solute and solvent) to form a solution, while melting is a single substance changing from solid to liquid due to heat.
Characteristics of Dissolving
- In a solution, the solute appears to disappear because its particles are evenly distributed among the solvent’s particles, e.g., sugar in water looks like clear water.
- The solute is still present, as evidenced by taste (sweetness in sugar-water) or color (blue in copper sulfate solution).
- A solution is a mixture of two or more substances, distinct from a pure liquid, which contains only one substance.
Rates of Dissolving
The rate of dissolving, or how quickly a solute dissolves in a solvent, is influenced by several factors: the temperature of the solvent, whether the solution is stirred, and the grain size of the solute. These factors affect how fast the solute’s particles spread among the solvent’s particles.
Factors Affecting the Rate of Dissolving
Temperature of the Solvent:- Warmer solvents increase the rate of dissolving. For example, salt dissolves faster in hot water than in cold water because higher temperatures provide more energy, causing solvent particles to move faster and interact more effectively with solute particles.
- In cold water, the rate of dissolving is slower due to less particle movement.
Stirring or Shaking:
- Stirring a solution speeds up dissolving by mixing the solute and solvent particles more quickly, ensuring the solute spreads evenly. For example, stirring salt in water makes it dissolve faster than leaving it unstirred.
- Without stirring, dissolving relies on the slow natural movement of particles, taking longer.
Grain Size of the Solute:
- Smaller solute grains dissolve faster than larger ones. For example, fine table salt dissolves quicker than coarse rock salt in water because smaller grains have a larger surface area exposed to the solvent, allowing more particles to interact at once.
- Larger grains have less surface area relative to their volume, slowing the dissolving process.
Practical Example: In a cup of coffee, sugar (solute) dissolves in the coffee (solvent) to form a solution. The coffee is a mixture containing water, coffee grounds, and sugar, with water as the primary solvent. To make the sugar dissolve faster, one could use hot coffee (higher temperature), stir the mixture, or use finer sugar grains.
Points to Remember
- The rate of dissolving is how quickly a solute dissolves in a solvent, influenced by temperature, stirring, and grain size.
- Warmer solvents, like hot water, make solutes dissolve faster due to increased particle energy.
- Stirring or shaking a solution speeds up dissolving by mixing particles more effectively.
- Smaller solute grains, like fine salt, dissolve faster than larger grains, like rock salt, due to greater surface area.
- Dissolving is different from melting; dissolving forms a mixture of solute and solvent, while melting changes a solid to a liquid without mixing.
Difficult Words
- Dissolving: The process where a solute mixes completely with a solvent to form a solution, with solute particles spreading evenly among solvent particles.
- Solute: The substance that dissolves in a solvent, e.g., sugar in water.
- Solvent: The substance that dissolves the solute, e.g., water in a sugar-water solution.
- Solution: A uniform mixture of solute and solvent, where the solute appears invisible.
- Melting: The process where a solid turns into a liquid due to heat, e.g., ice to water.
- Rate of Dissolving: How quickly a solute dissolves in a solvent, measured by time.
- Temperature: The degree of heat in a solvent, affecting how fast a solute dissolves.
- Stirring: Mixing a solution to speed up the dissolving process by spreading solute particles.
- Grain Size: The size of solute particles, with smaller grains dissolving faster due to larger surface area.
Summary
Dissolving is the process where a solute, like sugar, mixes completely with a solvent, like water, to form a solution, distinct from melting, which is a state change from solid to liquid due to heat. In dissolving, solute particles spread evenly among solvent particles, making the solute invisible but still present. The rate of dissolving is affected by the solvent’s temperature (warmer is faster), stirring (speeds up mixing), and solute grain size (smaller grains dissolve faster). Understanding these factors helps explain how to make solutions more efficiently, as seen in everyday examples like sweetening coffee.
FAQs on Dissolving Chapter Notes - Natural Science and Technology (Grade 6-A)
| 1. What is dissolving in simple terms? |  |
| 2. What factors affect the rate of dissolving? |  |
| 3. How can I demonstrate dissolving at home? |  |
| 4. What are some common examples of dissolving? |  |
| 5. Why is understanding dissolving important? |  |














