Earth and Universe Chapter Notes - Class 4 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Universe and Solar System |

|
| Sun |

|
| Planets |

|
| Mercury |

|
| Venus |

|
| Earth |

|
| Mars |

|
| Jupiter |

|
| Saturn |

|
| Uranus |

|
| Neptune |

|
| Moon |

|
| Meteors, Meteorites, and Meteoroids |

|
Universe and Solar System
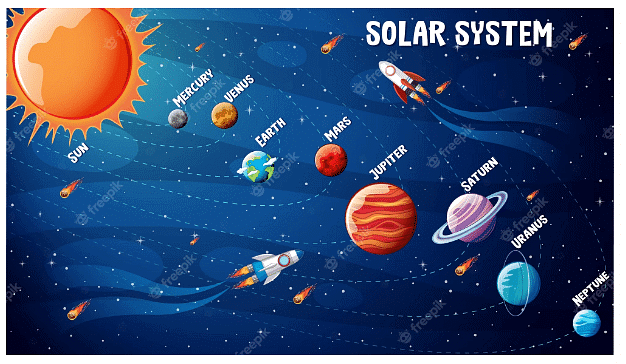
The universe consists of various celestial bodies, including galaxies, stars, planets, and other objects. Within the universe, our solar system is a specific arrangement of celestial bodies centered around the sun. The solar system is located within a galaxy known as the Milky Way and consists of the sun, eight planets, and their accompanying satellites.
Sun
The sun is a massive ball of hot and burning gases. It is primarily composed of hydrogen and helium. Positioned at the center of the solar system, the sun serves as the nearest star to Earth and acts as the primary source of energy for all life on our planet.
Planets
Planets are heavenly bodies that orbit around the sun in elliptical paths. They can be categorized into two main groups: inner planets and outer planets. The inner planets, which include Mercury, Venus, Mars, and Earth, are rocky in nature. On the other hand, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune belong to the outer planets, which are primarily composed of gases. Additionally, there exists a ring of small rocky and metallic bodies called asteroids between the inner and outer planets, forming the asteroid belt.
Mercury
Mercury is a planet with significant temperature variations between day and night. It does not possess any natural satellites and lacks both water and atmosphere. Due to its proximity to the sun, Mercury has the shortest year among all the planets, taking approximately 88 days to complete one orbit. Despite its small size, Mercury can be observed with the naked eye, and it does not experience distinct seasons on its surface.
Venus
Venus, often referred to as the Veiled planet, completes one orbit around the sun in about 225 Earth days. It lacks oceans and has an atmosphere predominantly composed of carbon dioxide, with minimal water vapor content. The planet is entirely shrouded in thick clouds, which contribute to its high reflectivity, making it the brightest planet in our solar system. Venus is also the hottest planet, featuring a slow rotation and reaching its maximum brightness shortly before sunrise or after sunset. It is sometimes referred to as the Morningstar or the Evening star.
Earth
Earth is the largest of the four inner planets and is commonly known as the Water Planet due to its abundant liquid water on the surface. With approximately 71% of its surface covered by water, Earth appears blue from space due to the combined effect of oceans and the atmosphere. The planet possesses a protective layer of gases held by gravity, which helps regulate temperature and filters harmful UV rays from the sun. The Earth has a natural satellite called the Moon, which revolves around it, causing the creation of seasons and the cycle of day and night. It takes approximately 365 Earth days for Earth to complete one orbit around the sun.
Mars
Mars, also known as the red planet, has a diameter approximately half that of Earth. It possesses two natural satellites and is named after the Roman God of War. Mars experiences the largest dust storms in the solar system but currently lacks active volcanoes.
Jupiter
Jupiter, the largest planet in our solar system, is named after the Roman God Jupiter. Its immense size allows it to encompass all the other planets within its volume. Jupiter exhibits a great red spot, which is a rotating storm system within its atmosphere. With the fastest rotation period of all the planets, Jupiter completes one rotation in approximately 10 hours. It also possesses a faint ring system comprising dust particles and is characterized by high winds due to its rapid rotation.
Saturn
Saturn is the sixth planet from the sun and the second largest planet in our solar system after Jupiter. It derives its name from the Roman god Saturn and is classified as a gas giant planet. Saturn boasts a complex ring system composed of numerous rock and ice fragments. Additionally, it possesses the highest number of known moons among all planets in the solar system.
Uranus
Uranus, named after the Roman god of the sky, stands out due to its unique orientation, appearing to lie on its side. It is the only planet in the solar system that rotates on its axis from east to west. Uranus features 27 known satellites and possesses ten thin, uniform black rings composed of dust particles. It is known for its extremely low temperatures, receiving significantly less sunlight compared to Earth due to its greater distance from the sun. A season on Uranus lasts for approximately 20 Earth years.
Neptune
Neptune, the farthest planet from the sun, takes an average of 164.79 Earth years to complete one orbit. It is considered the coldest planet in the solar system and has the slowest revolution speed. Unlike some of the other planets, Neptune cannot be seen with the naked eye.
Moon
The Moon is Earth's only natural satellite and shares similar characteristics with other celestial bodies in the solar system. It does not emit its own light but rather reflects sunlight, resulting in its varying phases. The Moon lacks water and atmosphere, causing extreme temperature differences between day and night. Its diameter is approximately one-fourth that of Earth, and its close proximity to our planet makes it appear relatively large in the night sky.
Meteors, Meteorites, and Meteoroids
Meteors are small celestial objects that enter the Earth's atmosphere, often referred to as shooting stars when they are visible during their burning path. If a meteor survives its journey through the atmosphere and lands on Earth's surface, it becomes a meteorite. Meteoroids are similar to meteors but are smaller in size and have not yet entered Earth's atmosphere.
Asteroids
Asteroids are large rocky objects found in outer space. While scientists have discovered 26 significant asteroids, most of them being large in size, there are still countless smaller asteroids yet to be observed due to their tiny dimensions.
Comets
Comets are celestial bodies that orbit the sun and consist of a central mass surrounded by a dust and gas envelope. As comets approach the sun, they often develop a visible coma and, at times, a tail composed of emitted materials influenced by solar radiation.



















