Electrical Conductors and Insulators Chapter Notes | Natural Science and Technology (Grade 6-B) PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| What are Conductors and Insulators? |

|
| Good Electrical Conductors and Insulators |

|
| Applications in Everyday Life |

|
| Points to Remember |

|
| Difficult Words |

|
| Summary |

|
What are Conductors and Insulators?
Electricity flows through some materials but not others, which is why electric wires are made of two different materials: a conductive core and an insulating cover. Understanding the difference between conductors and insulators is key to building safe and effective electric circuits.
Defining Conductors and Insulators
- Conductor: A material that allows electric current to flow easily through it, completing a circuit. When a conductor is placed in a closed circuit with a bulb, the bulb lights up, indicating current flow.
- Insulator: A material that does not allow electric current to flow easily, breaking the circuit. When an insulator is placed in a closed circuit, the bulb does not light up, showing no current flow.
- Conductivity: The ability of a material to conduct electricity. Conductors have high conductivity, while insulators have low or no conductivity.
Testing Conductivity
- To determine if a material is a conductor or insulator, it can be placed in a simple closed circuit with a battery, wires, and a bulb. If the bulb lights up, the material is a conductor; if it does not, the material is an insulator.
- Common materials tested include metals (e.g., copper, steel), non-metals (e.g., plastic, rubber), and others like glass, wood, or ceramic.
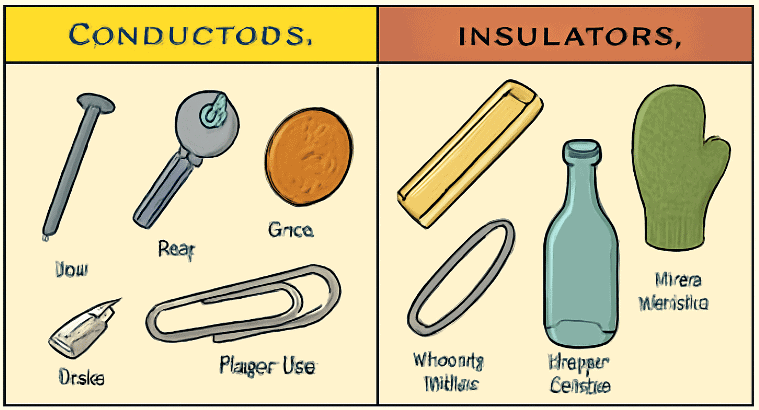
Good Electrical Conductors and Insulators
Materials are classified as good conductors or insulators based on their ability to allow electric current to pass through. This property determines their use in electrical systems, ensuring both functionality and safety.
Characteristics of Conductors
- Materials: Most metals are good conductors, with copper being one of the best due to its high conductivity. Gold and silver are even better but are expensive and less commonly used.
- Examples: Copper wires, steel wool, aluminum foil, brass coins, silver coins, metal spoons, and nails.
- Use in Circuits: Conductors form the pathways in circuits, such as the copper core of electric wires, allowing current to flow to devices like bulbs.
- Human Body: The human body is a good conductor, which is why contact with live wires can result in an electric shock as current flows through the body to the ground.
Characteristics of Insulators
- Materials: Non-metals are typically insulators, including plastic, rubber, wood, glass, ceramic, paper, cardboard, leather, and styrofoam. Air is also generally an insulator, though lightning can force current through it.
- Examples: Plastic coating on wires, rubber gloves, wooden poles, ceramic caps, glass in bulbs.
- Behavior in Circuits: Insulators prevent current flow, so they do not allow a bulb to light up in a circuit. However, under extreme conditions (e.g., lightning), some insulators like air may conduct.
Importance of Insulators
- Safety: Insulators protect against electric shocks by preventing unwanted current flow. For example, plastic coatings on wires stop current from reaching the user, and rubber gloves or boots shield electricians from shocks.
- Preventing Unwanted Flow: Insulators separate conductors to avoid short circuits or unintended current paths. For instance, ceramic caps on power lines prevent current from flowing between wires or into wooden poles.
- Component Design: In devices like bulbs, insulators (e.g., glass separating metal pins) ensure current flows only through intended paths, maintaining circuit integrity.
Applications in Everyday Life
- Wires: Electric wires have a copper core (conductor) for current flow and a plastic coating (insulator) for safety.
- Power Lines: Wooden poles (insulators) support wires, and ceramic caps (insulators) separate conducting wires to prevent current leakage.
- Bulbs: Glass (insulator) separates metal pins (conductors) to direct current through the filament, ensuring the bulb functions correctly.
- Safety Gear: Rubber gloves and boots (insulators) are worn by electricians to prevent shocks when handling live circuits.
Points to Remember
- Metals like copper, used in South African wiring, are excellent conductors, while non-metals like plastic and rubber are insulators, critical for safe circuit design.
- Conductors allow electric current to flow, lighting a bulb in a closed circuit, while insulators block current, keeping the bulb off.
- Insulators like plastic on wires and rubber gloves protect users from electric shocks by preventing current from reaching the body.
- Ceramic and wood in power lines ensure current stays in the wires, avoiding leakage or short circuits.
- The human body conducts electricity, making insulators essential for safety in electrical systems.
Difficult Words
- Conductor: A material, usually metal, that allows electric current to flow easily, completing a circuit.
- Insulator: A material, usually non-metal, that does not allow electric current to flow, breaking a circuit.
- Conductivity: The ability of a material to let electric current pass through it; high in conductors, low in insulators.
- Electric Current: The flow of energy through a circuit, enabling devices to work.
- Shock: The harmful effect of electric current passing through the body, which can occur because the body is a conductor.
Summary
Electrical conductors, like copper and other metals, allow electric current to flow easily, forming the pathways in circuits, while insulators, such as plastic, rubber, and ceramic, block current to ensure safety and proper function. Conductors like copper wires power devices, but insulators like plastic coatings and rubber gloves prevent shocks by stopping unwanted current flow. In everyday applications, from household wiring to power lines, insulators like wood and ceramic separate conductors to avoid short circuits, while the human body’s conductivity underscores the need for insulating materials in electrical systems.
FAQs on Electrical Conductors and Insulators Chapter Notes - Natural Science and Technology (Grade 6-B)
| 1. What are the main differences between conductors and insulators? |  |
| 2. Can you give examples of good electrical conductors and insulators? |  |
| 3. How are conductors and insulators used in everyday life? |  |
| 4. Why is it important to understand conductors and insulators? |  |
| 5. What are some common applications of conductors and insulators in household items? |  |















