NEET PG Exam > NEET PG Notes > Microbiology > Chapter Notes: Flagellates
Flagellates Chapter Notes | Microbiology - NEET PG PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Giardia Lamblia (Intestinal Flagellates) |

|
| Trichomonas Vaginalis (Genital Flagellates) |

|
| Hemoflagellates (Leishmania and Trypanosoma) |

|
| Leishmania |

|
| Trypanosoma Cruzi |

|
| Trypanosoma Brucei |

|
Giardia Lamblia (Intestinal Flagellates)
Habitat
- Resides in the mucosa of the duodenum and upper ileum in humans.
Morphology
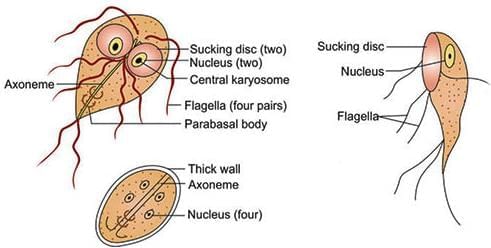
- Exists in two forms: Trophozoites and Cysts.
- Trophozoites:
- Front view: Tear-drop, racket, or piriform shaped.
- Lateral view: Sickle or spoon shaped.
- Exhibits falling leaf-like motility.
- Size: 15–20 µm.
- Contains 2 nuclei, 4 pairs of flagella, 2 axostyles, 2 parabasal bodies, and 2 ventral sucking disks.
- Cysts:
- Mature cyst is oval, size: 10–14 µm.
- Contains 4 nuclei and an axostyle.
- Passed in feces.
Life Cycle
- Infective stage: Cyst.
- Infective dose: As few as 10 to 25 cysts can cause infection.
- Route of infection: Feco-oral route.
- Cysts transform into trophozoites in the duodenum, where they multiply.
- Trophozoites attach to gastrointestinal tract mucosa using adhesive disks.
- Trophozoites shed into the lumen, transform back into cysts, and are passed in feces.
- Cysts are the diagnostic form of the parasite.
- Susceptible populations: Children, HIV-positive individuals, and those with achlorhydria or hypochlorhydria.
Pathogenesis
- Causes abnormalities in villous structure, leading to malabsorption of lipids and lipid-soluble vitamins.
- Types of malabsorption:
- Fat malabsorption (steatorrhea): Results in foul-smelling, profuse, frothy diarrhea.
- Disaccharidase deficiencies (lactate, xylose): Causes lactose intolerance.
- Malabsorption of vitamin B12 and folic acid.
- Protein-losing enteropathy.
- Antigenic variation in variant surface protein: Leads to chronic and persistent infection.
Laboratory Diagnosis
- Samples: Stool and duodenal contents.
- Microscopy: Detects trophozoites (indicating active infection) or cysts (indicating carrier state).
- String test/Entero test: Collects bile-stained mucus to examine for trophozoites.
- Antigen detection in stool (coproantigen): Performed using ELISA or immunochromatographic test (ICT), indicates active infection.
- Serum antibody detection: Performed using ELISA or indirect fluorescent antibody (IFA) test, indicates past infection.
Treatment: Metronidazole, Tinidazole, Nitazoxanide, or Furazolidone.
Trichomonas Vaginalis (Genital Flagellates)
Overview
- Most common parasitic cause of sexually transmitted diseases (STD) and nongonococcal urethritis (NGU).
- Habitat: Urethra, vagina, and prostate.
Morphology
- Only form: Trophozoite (no cystic stage).
- Trophozoite characteristics:
- Exhibits twitching or jerky motility.
- Pear-shaped.
- Contains 5 flagella (4 anterior + 1 recurrent flagellum) supported by an undulating membrane and a fibrillary structure called costa.
Life Cycle
- Mode of transmission: Sexual route.
- Reservoir of infection: Women.
- Infective and diagnostic stage: Trophozoites.
- Trophozoites divide by longitudinal binary fission.
Clinical Disease
- Incubation period: 4–28 days.
- In men: Can be asymptomatic or cause urethritis, prostatitis, or cystitis.
- In women: Can be asymptomatic or cause vulvo-vaginitis, characterized by:
- Profuse vaginal discharge with an offensive smell, high pH (>4.5).
- Smell accentuated by adding 10% KOH (whiff test).
- Strawberry appearance of vaginal mucosa (Colpitis macularis), seen in 2% of cases.
Laboratory Diagnosis
- Samples: Vaginal and urethral discharges, prostatic secretions, or urine sediment.
- Microscopy: Detects actively motile (jerky motility) trophozoites in vaginal or urethral discharges.
- Staining: Giemsa, Papanicolaou, or direct fluorescent antibody (DAF) test.
- Culture: Most sensitive, considered the gold standard, using media like Lash’s cysteine hydrolysate serum media.
- Antigen detection in vaginal smear: Performed using ICT or ELISA, more sensitive than microscopy, indicates recent infection.
- Serology by ELISA: Detects antibodies, indicating past infection.
- PCR: Used for detection.
Treatment
- Drug of choice: Metronidazole or Tinidazole (2 grams, single dose) for both sexual partners.
- Resistance: Rare but reported.
Hemoflagellates (Leishmania and Trypanosoma)
Exist in four morphological forms: Promastigote, Amastigote, Trypomastigote, and Epimastigote.
 Various morphological forms of hemoflagellates
Various morphological forms of hemoflagellates
Leishmania
- Infective form: Promastigote.
- Mode of transmission: Bite of female sandfly during late evening or night.
- Infective dose: 10–1000 promastigotes per bite required to initiate infection.
- Promastigotes enter skin macrophages, transform into amastigotes, and are carried to organs like liver, spleen, and bone marrow.
- Diagnostic form in humans: Amastigote inside macrophages, known as LD body.
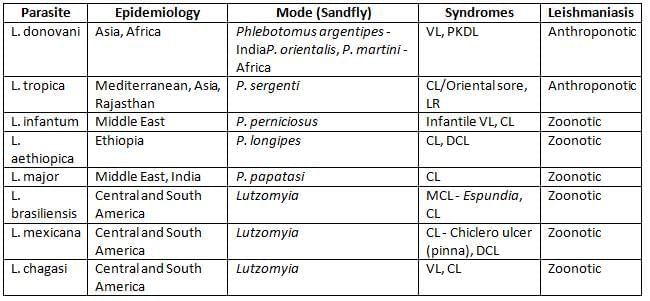
- VL: Stands for Visceral Leishmaniasis, a severe form of leishmaniasis that affects internal organs.
- CL: Refers to Cutaneous Leishmaniasis, which causes skin sores and lesions.
- LR: This denotes Leishmaniasis Recidivans, a type where the disease reappears after treatment.
- MCL: Represents Mucocutaneous Leishmaniasis, which affects the mucous membranes and can lead to significant tissue damage.
- DCL: Stands for Diffuse Cutaneous Leishmaniasis, characterized by widespread skin lesions that may not have the usual ulcers.
- PKDL: Refers to Post Kala-azar Dermal Leishmaniasis, a skin condition that can develop after successful treatment of visceral leishmaniasis.
Kala-Azar (Visceral Leishmaniasis)
- Bone marrow involvement causes:
- Anemia, leucopenia, thrombocytopenia.
- Hypergammaglobulinemia.
- Enlarged spleen and liver.
- Symptoms: Fever, hyperpigmentation (common in Indian cases).
- Lymphadenopathy: Common in African cases, not in Indian cases.
- Kala-azar with HIV:
- Absence of hepatosplenomegaly.
- Gastrointestinal and respiratory symptoms.
- Reported in Southern Europe (France, Italy, Spain, Portugal) and in India (Bihar, sub-Himalayan region, other North Indian states).
- Diagnosis: Amastigotes detected in bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) and buffy coat region of blood; antibodies are negative.
Post Kala-azar Dermal Leishmaniasis (PKDL)
- Occurs 2–10 years after VL treatment (within 6 months in Sudan).
- Incidence: 50% in Sudan, 2–20% in India.
- Features: Nonulcerative hypopigmented macular lesions, later becoming nodular.
- Duration: Persists for 20 years (few months in Sudan).
- Treatment: Longer courses of antimonials, resolves slowly.
Virulence Factors
- Glycoprotein (gp-63), Lipophosphoglycan (LPG), Glycosylphosphatidylinositol.
Host Immune Response
- T helper 1 (Th1) Response:
- Protective response.
- Leishmanin skin test positive.
- T helper 2 (Th2) Response:
- Indicates disease progression.
- Leishmanin skin test negative.
Laboratory Diagnosis
- Samples:
- Spleen aspirate (most sensitive).
- Bone marrow aspirate (commonly preferred).
- Lymph node aspirate (not useful in Indian cases).
- Blood: Buffy coat region and BAL (for HIV-infected).
- Microscopy: Stained peripheral blood smear shows LD bodies (amastigotes).
- Culture: NNN medium (McNeal, Novy, and Nicolle) and Schneider’s Liquid medium (amastigotes transform to promastigotes).
- Serological tests:
- Hypergammaglobulinemia: Detected by Napier’s aldehyde and Chopra’s antimony test.
- Complement fixation test (CFT): Uses tubercle bacilli antigen like WKK antigen.
- Immunochromatographic test (ICT): Detects antibodies to rK39 antigen.
- Direct agglutination test (DAT), ELISA, IFA.
- Leishmanin (Montenegro) skin test:
- Indicates delayed hypersensitivity reaction.
- Positive in patients with good cell-mediated immunity (CL, LR, recovered VL).
- Negative in patients with low cell-mediated immunity (active VL, DCL).
- PCR: Detects kinetoplast DNA.
- Animal inoculation: Chinese and golden hamsters.
Treatment
- Pentavalent antimonials: Drug of choice in most endemic regions except Bihar.
- Sodium stibogluconate.
- Meglumine antimoniate.
- Amphotericin B: Drug of choice in Bihar.
- Paromomycin: Used for diffuse CL caused by L. aethiopica.
- Miltefosine.
- Pentamidine: Drug of choice for CL caused by L. guyanensis.
- Prevention: Insect control, sleeping on top floors.
Trypanosoma Cruzi
Life Cycle
- Mode of transmission: Rubbing of reduviid bugs (Triatomine).
- Infective form: Metacyclic trypomastigotes.
- Invades macrophages, transforms into amastigotes, which multiply to form pseudocysts.
- Amastigotes transform back into trypomastigotes:
- Slender, highly motile forms: Invade various organs.
- Broader, less motile forms: Infective to reduviid bugs.
Acute Chagas’ Disease
- Chagoma: Subcutaneous nodule.
- Romana’s sign: Periorbital edema.
- Lymphadenopathy and hepatosplenomegaly.
Chronic Chagas’ Disease
- Caused by autoimmune hypothesis due to molecular mimicry.
- Parasite multiplication in muscles (skeletal, cardiac, GIT) and CNS leads to:
- Cardiac form: Myocarditis, dilated cardiomyopathy.
- Gastrointestinal form: Megaesophagus, megacolon.
- Meningoencephalitis: Increased in HIV-infected individuals.
Diagnosis and Treatment
- Diagnostic form: C-shaped trypomastigotes in blood smear (may be confused with non-pathogenic T. rangeli).
- Culture: Blood inoculated in NNN media.
- Radioimmune precipitation assay (Chagas’ RIPA): Highly sensitive and specific.
- PCR: Detects kinetoplast DNA, useful in chronic disease.
- Xenodiagnosis.
- Animal inoculation in mice.
Treatment: Benznidazole (drug of choice), Nifurtimox.
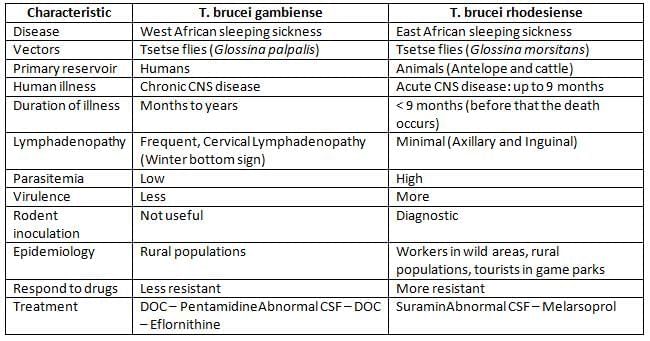
Trypanosoma Brucei
Life Cycle
- Infective form: Metacyclic trypomastigotes.
- Mode of transmission: Bite of tsetse fly.
- Transforms into long slender trypomastigotes, then short stumpy forms (infective to tsetse fly).
- Undergoes periodic antigenic variation of surface glycoprotein (VSG).
Clinical Features
- Trypanosomal chancre.
- Stage I disease: Systemic febrile illness, lymphadenopathy.
- Stage II disease: African sleeping sickness, characterized by progressive daytime somnolence, restlessness, and insomnia at night.
Diagnosis
- Diagnostic form: Trypomastigotes seen in blood smear.
- CSF examination: Shows Mott cells (abnormal plasma cells containing IgM).
- Antigen detection: From serum and CSF using ELISA, useful for clinical staging and monitoring.
- Antibody detection: Card agglutination test for trypanosomes (CATT), ELISA, IFA.
The document Flagellates Chapter Notes | Microbiology - NEET PG is a part of the NEET PG Course Microbiology.
All you need of NEET PG at this link: NEET PG
|
75 docs|5 tests
|
FAQs on Flagellates Chapter Notes - Microbiology - NEET PG
| 1. What are the two main morphological forms of flagellates? |  |
Ans. The two main morphological forms of flagellates are the trophozoite and the cyst. The trophozoite is the active, motile form that feeds and reproduces, while the cyst is a dormant, resistant form that can survive in unfavorable conditions.
| 2. What is the life cycle of flagellates, and how do they reproduce? |  |
Ans. The life cycle of flagellates typically includes both asexual and sexual reproduction. Asexual reproduction occurs through binary fission, where one organism divides into two identical daughter cells. In some cases, flagellates can undergo sexual reproduction that involves the exchange of genetic material, resulting in genetic diversity.
| 3. How do flagellates cause disease in humans? |  |
Ans. Flagellates cause disease through various mechanisms, including tissue invasion, immune evasion, and toxin production. For instance, species like Leishmania can invade macrophages, leading to diseases such as kala-azar. The symptoms often arise from the host's immune response to the parasites.
| 4. What methods are used for the laboratory diagnosis of flagellate infections? |  |
Ans. Laboratory diagnosis of flagellate infections typically involves microscopic examination of blood, bone marrow, or tissue samples to identify the parasites. Serological tests and molecular techniques, such as PCR, can also be used to detect specific flagellate species.
| 5. What are the treatment options for kala-azar and post kala-azar dermal leishmaniasis (PKDL)? |  |
Ans. Treatment options for kala-azar include antimonial compounds like sodium stibogluconate and amphotericin B, which are effective against Leishmania parasites. For post kala-azar dermal leishmaniasis (PKDL), treatment may involve the same antileishmanial drugs, but the management can be more challenging due to the condition's persistence and potential for recurrence.
Related Searches