Forms of Business Organisation Chapter Notes | Business Studies (BST) Class 11 - Commerce PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| Sole Proprietorship |

|
| Types of partnership |

|
| Formation of a Company |

|
| Question and Answers |

|
Introduction
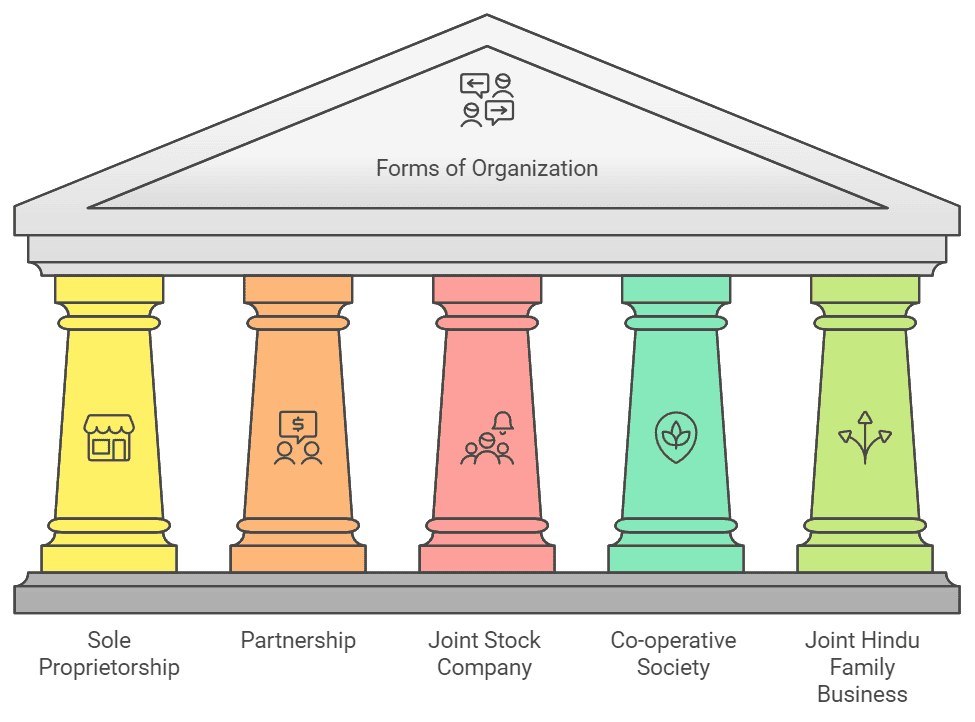
Decision relating to the form of organization plays an important role. If one has to start a business. The forms of organization are: (i) Sole proprietorship (ii) Partnership (iii) Joint Stock Company (iv) Co-operative society (v) Joint Hindu Family business
Sole Proprietorship
- A sole proprietorship is a common and suitable form of business for small ventures, especially in their early stages.
- It is owned, managed, and controlled by a single individual who keeps all the profits and bears all the risks.
- The term "sole" means "only," and "proprietor" means "owner," signifying a single owner.
- This type of business is common in personalized services like beauty parlours and salons or small-scale activities like local retail shops.
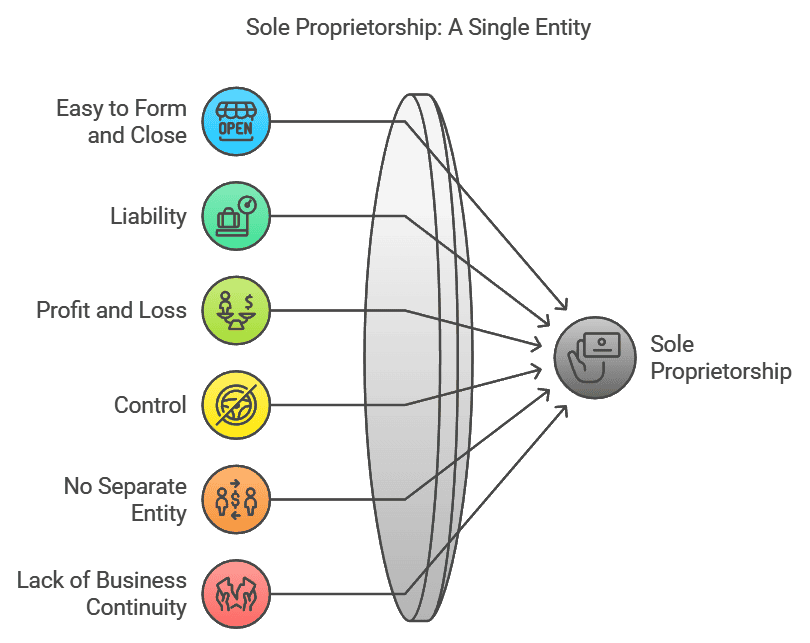
Features
(i) Easy to form and close
- There is no specific law that regulates a sole proprietorship.
- Starting a sole proprietorship requires very few legal steps.
- In some situations, you might need a license to operate.
- It is also simple to close down the business when needed.
- Overall, it is easy to both establish and shut down a sole proprietorship.
(ii) Liability
- Sole proprietors are responsible for all the debts of their business, meaning they have unlimited liability.
- This means that if the business owes money, the owner must pay it back, which can include using their personal funds.
- For example, an owner might need to take out Rs. 20,000 from their own savings or assets.
- In some cases, this could mean having to sell personal property to cover the debts of the business.
(iii) Sole risk bearer and profit recipient
- The risk of business failure is entirely shouldered by the sole proprietor.
- If the business succeeds, the proprietor gets to enjoy all the rewards.
- All the profits from the business go directly to the proprietor, serving as a direct reward for taking on the risks.
(iv) Control
- The right to run the business belongs entirely to the sole proprietor.
- The sole proprietor has the authority to make all decisions regarding the business.
- He can implement his plans without any interference from anyone else.
(v) No separate entity
- According to the law, there is no difference between a sole trader and their business.
- The business does not exist as a separate entity from the owner.
- This means that the owner is fully responsible for everything that happens in the business.
- All actions and decisions made in the business are attributed to the owner.
- If the business faces any legal issues, the owner is the one who will be held accountable.
(vi) Lack of business continuity
- A sole proprietorship is a type of business that is owned and managed by a single person.
- The business is directly affected by the personal circumstances of the owner.
- If the owner experiences death, mental illness, imprisonment, serious health issues, or bankruptcy, it can have a negative impact on the business.
- Such personal problems may even lead to the closure of the business.
Merits
1. Quick decision-making
- A sole proprietor has a significant amount of freedom when it comes to making business decisions.
- Decision-making is quick because there is no need to consult with others.
- This can result in timely opportunities to take advantage of market changes as they happen.
2. Confidentiality of information
- Sole decision-making authority allows the owner to keep all business operation details private.
- A sole trader is not required by law to publish the company's financial statements.
- This means the owner can maintain confidentiality regarding the business.
- The owner has full control over the business without needing to share financial information publicly.
- This level of secrecy can provide the owner with an advantage in managing business strategies.
3. Direct incentive
- A sole proprietor enjoys the full rewards of their work because they are the only one who receives the profits.
- Since there is no one else to share the earnings with, the sole proprietor is highly motivated to put in a lot of effort.
- This setup gives the sole trader a strong reason to work diligently and strive for success.
- Being the only owner means they have complete control over their business decisions.
4. Sense of accomplishment
- There is a personal satisfaction involved in working for oneself.
- The knowledge that one is responsible for the success of the business not only contributes to self-satisfaction but also instils in the individual a sense of accomplishment and confidence in one’s abilities.
5. Ease of formation and closure
- An important advantage of a sole proprietorship is the ability to start a business with very few legal requirements.
- There is no distinct law that specifically regulates sole proprietorships.
- Since a sole proprietorship is the least controlled type of business, it is simple for the owner to begin and end the business whenever they choose.
Demerits
1. Limited resources
- The resources available to a sole proprietor are mainly their own savings and any money they can borrow.
- Banks and other lending institutions often hesitate to provide long-term loans to sole proprietors.
- A lack of resources is a key reason why these businesses typically do not grow very large and often stay small.
2. Limited life of a business concern
- A sole proprietorship is a type of business that is owned and managed by a single individual.
- Because it is run by just one person, various issues such as death, mental health problems, imprisonment, serious illness, or bankruptcy of the owner can impact the business.
- These circumstances can potentially lead to the closure of the business.
3. Unlimited liability
- A major disadvantage of a sole proprietorship is that the owner has unlimited liability.
- If the business fails, the creditors can recover their dues not merely from the business assets, but also from the personal assets of the proprietor.
- A poor decision or an unfavourable circumstance can create a serious financial burden on the owner.
- That is why a sole proprietor is less inclined to take risks in the form of innovation or expansion.
4. Limited managerial ability
- The owner has to take on many different management tasks such as:
1. Purchasing goods and services
2. Selling products
3. Financing the business - It is uncommon to find one person who is skilled in all these areas.
- As a result, decision-making may not be even or fair in every situation.
- Additionally, because of limited resources, a sole proprietor might struggle to hire and keep talented and ambitious employees.
Joint Hindu Family Business
It's a business structure owned and operated by members of a Hindu undivided family, allowing for up to three consecutive generations to participate in the business.

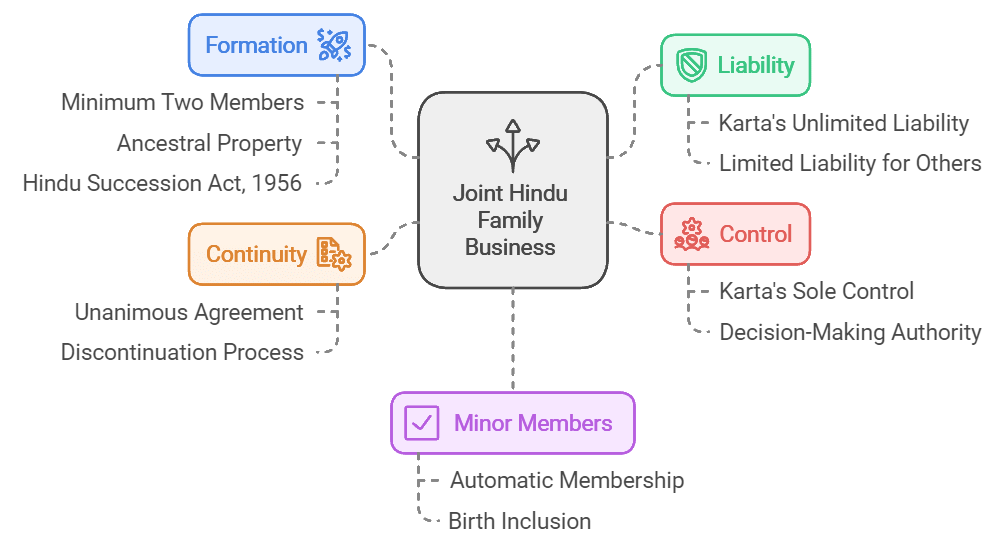
Features:
- Formation: A Hindu Undivided Family is established with a minimum of two family members possessing ancestral property, governed by the Hindu Succession Act, 1956.
- Liability: With the exception of the Karta, all family members have limited liability, extending only to their share in the business property.
- Control: The Karta has sole control over all activities within the business organization.
- Continuity: Discontinuation of the family business requires unanimous agreement from all family members.
- Minor members: Membership in the organization is automatic at birth for minor family members.
Merits:
- Effective control: The 'Karta' holds complete control over the business, facilitating effective decision-making.
- Continued business existence: The business persists as long as all members desire to continue, with control passing to the next elder member in the event of the 'Karta's' death.
- Limited liability of members: Family members are liable only to the extent of their share in the business, enjoying limited liability.
- Increased loyalty and cooperation: Family members' strong sense of belongingness and loyalty fosters a shared goal of growth, promoting increased cooperation among them.
Demerits:
Limited resources: Funding for the business is primarily derived from ancestral property, thereby restricting financial resources.
Unlimited liability of Karta: The 'Karta' bears unlimited liability, putting personal property at risk.
Dominance of Karta: Potential conflicts may arise among family members and the 'Karta' due to differences of opinion.
Limited managerial skills: The 'Karta' may lack the knowledge and expertise required for all functions performed in the business.
Meaning of Partnership
As per the Partnership Act 1932, a partnership is defined as the association between individuals who have consented to distribute the profits of a business conducted by any one of them, either on behalf of all partners or independently.

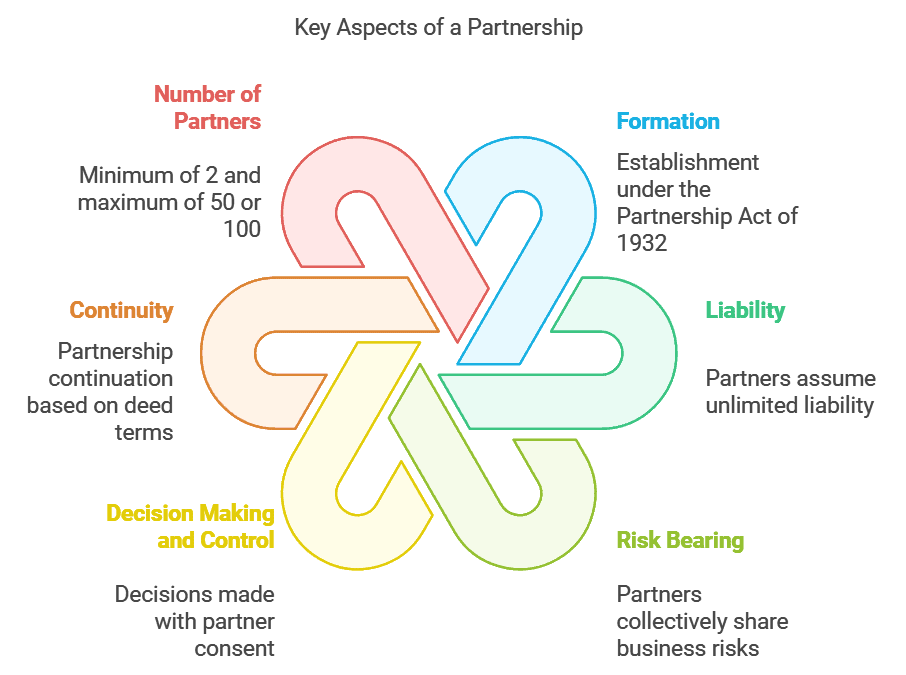
Features:
Formation: The business is established in accordance with the provisions outlined in the Partnership Act of 1932.
Liability: Each partner within the business assumes unlimited liability.
Risk bearing: All partners collectively share the risks associated with the business.
Decision making and control: Decisions are made with the consent of all partners, and each partner shares responsibility for the business's operation.
Continuity: The continuation of the partnership depends on the terms specified in the partnership deed agreed upon by the partners during formation.
Number of partners: The partnership must consist of a minimum of 2 and a maximum of 50 members (as per the Companies (Miscellaneous) Rules 2014), or up to 100 members (as per the Companies Act, 2013).
Mutual agency: Each partner serves as both the owner and agent of the firm, acting on behalf of the business and other partners.
Merits:
Ease of formation and closure: The establishment and closure of the business can be accomplished with the agreement of all partners, as registration is optional.
Balanced decision making: Decisions are made collectively by the partners, allowing each partner to contribute according to their expertise.
More funds: Business operations benefit from contributions made by all partners, enabling the pursuit of larger-scale ventures.
Sharing of risks: Risks and responsibilities associated with the business are distributed among all partners.
Secrecy: Maintaining confidentiality regarding business affairs is simplified as there is no requirement to disclose financial results.
Limitations:
Unlimited liability: Partners are personally liable for the business's debts, extending to their personal assets.
Limited resources: Financial resources are constrained due to the limitation on the number of partners involved.
Possibility of conflicts: Differing opinions among partners may lead to conflicts within the partnership.
Lack of continuity: Disputes between partners or the death of a partner could result in the cessation of business operations.
Lack of public confidence: Outsiders may struggle to assess the true financial status of the business due to limited access to financial reports.
Types :
Active partner: Contributes capital, shares profits and losses, participates in management, and bears unlimited liability.
Sleeping or dormant partner: Contributes capital, shares profits and losses, and bears unlimited liability but does not participate in management.
Secret partner: Participates in management operations covertly, and contributes to profits and losses.
Nominal partner: Does not contribute capital, share profits or losses, but allows the partnership to represent them as a partner.
Partner by estoppel: Not a partner but represented as one to an outsider, with unlimited liability.
Partner by holding out: Not a partner but projected as one by other partners, with unlimited liability.
Minor as partner: An individual under 18 years old may be admitted as a partner with the unanimous consent of all other partners, but legally they are not considered a partner.
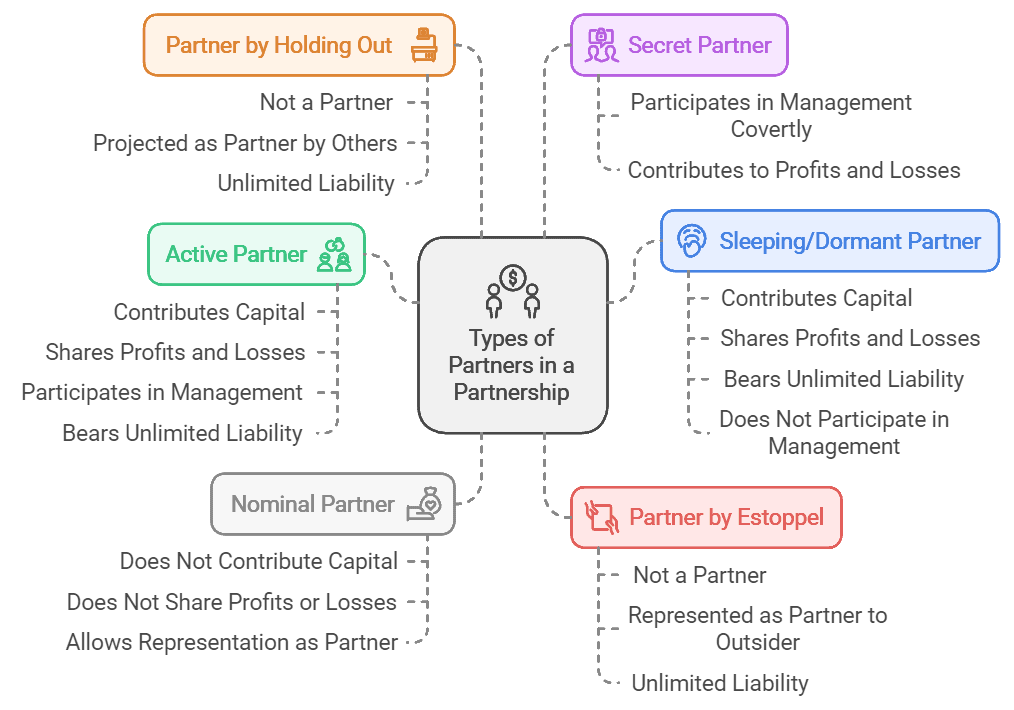
Types of partnership
Classification based on duration:
- Partnership at will: Continues until the partners mutually agree to dissolve it.
- Particular partnership: Formed for a specific project or period, ending upon completion of the task or expiration of the time frame.
Classification based on liability:
- General partnership: All partners have joint and unlimited liability.
- Limited partnership: All partners have limited liability, with at least one partner having unlimited liability.
Partnership deed:
Written document outlining all terms and conditions of the partnership, including:
- Name and nature of the firm
- Duration of partnership
- Duties and obligations of partners
- Valuation of assets
- Interest on capital and drawings
- Profit-loss sharing ratio
- Salaries and withdrawals of partners
- Preparation of accounts and auditing
- Procedure for dissolution of the firm
- Dispute resolution methods
Registration:
- Optional for partnership firms with the registrar of firms in the state where the firm is located.
Consequences of non-registration:
- Inability for a partner to file a case against other partners or the firm.
- Inability for the firm to sue third parties.
- Inability for the firm to file a case against one or more partners.
Procedure for registration:
- Submission of application in the prescribed form to the Registrar of Firms.
- Fee deposition with the Registrar.
- Receipt of registration certificate after satisfaction of the Registrar.
Meaning of Cooperative Society:
- An organization of voluntary individuals working towards a common purpose, registered under the Cooperative Societies Act, 1912.

Features:
- Voluntary membership: Individuals with common interests are free to join or leave the society as they wish.
- Legal status: The society has a separate legal identity from its members and must be registered.
- Limited liability: Members' liability is restricted to their capital contribution.
- Control: Decision-making power lies with an elected managing committee chosen by members.
- Service motive: The society aims to provide mutual assistance to its members.
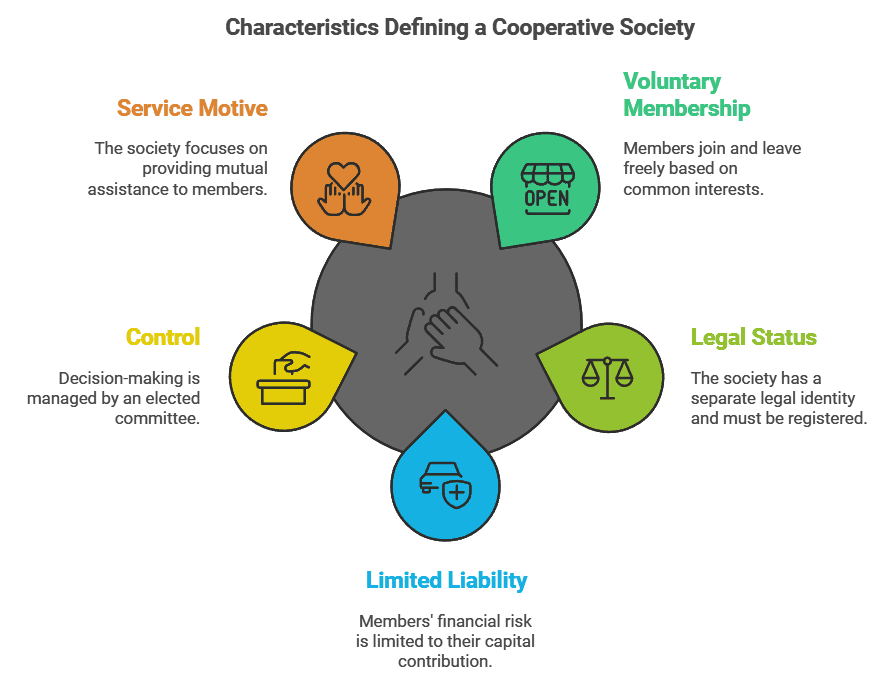
Merits:
- Equality in voting: Each member has an equal right to vote.
- Limited liability: Members are only liable for their capital contribution.
- Stable existence: Societies continue to operate despite changes in membership status.
- Economy in operations: Voluntary work reduces costs.
- Government support: Lower taxes, interest rates, and subsidies may be provided.
- Ease of formation: No legal formalities are required.
Limitations:
- Limited resources: Capital contribution is the primary source of finance.
- Inefficiency in management: Voluntary members may lack expertise.
- Lack of secrecy: Difficulty in maintaining confidentiality.
- Government control: Regulations may restrict freedom of operation.
- Differences of opinion: Conflicts may arise due to diverse interests.
Types of cooperative societies:
- Consumers, producers, marketing, farmers, credit, and housing cooperative societies.
Joint Stock Company
- A legal entity with perpetual succession, separate from its owners, created under the Companies Act, 2013.
Features:
- Artificial person: Created by law, operates through the board of directors.
- Separate legal entity: Distinct from its owners.
- Formation: Requires compliance with legal formalities.
- Perpetual succession: Continues regardless of changes in membership.
- Control: Managed by the board of directors.
- Limited liability: Shareholders' liability is restricted.
- Common seal: Acts as the official signature.
- Risk bearing: Shareholders bear risks in proportion to their investment.
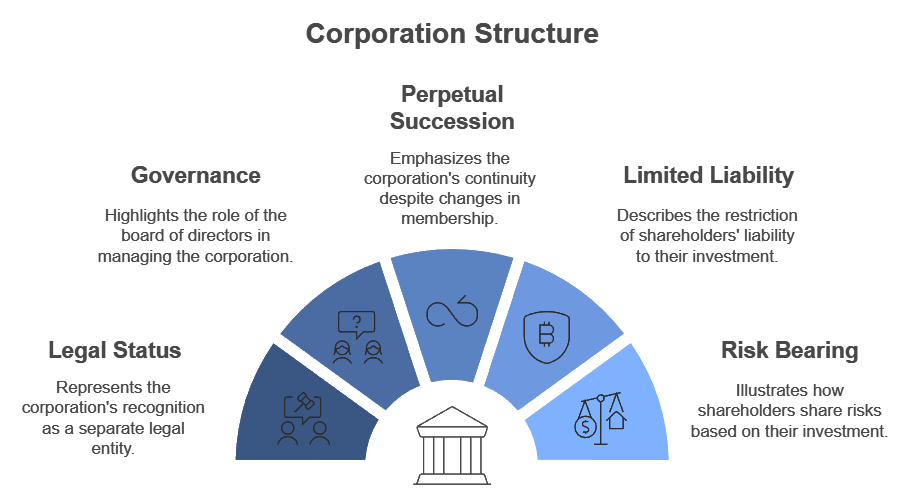
Merits:
- Limited liability: Personal assets are safeguarded.
- Transfer of interest: Shares can be easily sold.
- Perpetual existence: Continues irrespective of shareholder status.
- Scope for expansion: Can raise funds from the public.
- Professional management: Expertise is employed for operation.
Limitations:
- Complex formation: Involves lengthy legal procedures.
- Lack of secrecy: Financial information is public.
- Impersonal work environment: Lack of personal contact.
- Regulations: Involves strict rules.
- Delay in decision-making: Hierarchy may cause delays.
- Oligarchic management: Directors have significant control.
- Conflict in interests: Satisfying stakeholders can be challenging.
Types of Companies:
- Private Company: Limited to 200 members, restricted share transfer, 'Private Limited' in name.
- Public Company: Minimum 7 members, unrestricted share transfer, 'Public Limited' in name.
Formation of a Company
Functions of a Promoter:
(i) Finding out a business opportunity (ii) Conducting studies (iii) Getting the name approved. (iv) Fixing up persons to sign Memorandum of association (v) Appointment of professionals (vii) Preparation of necessary documents.
Documents
Memorandum of association:
(i) Name clause (ii) Registered office clause (iii) Objects clause (iv) Liability clause (v) Capital clause (vi) Association clause (vii) Articles of association (viii) Consent of directors (ix) Agreement with managing director or whole-time director (x) Statutory declaration
Incorporation:
(i) The memorandum of association must be duly stamped, signed and witnessed. (ii) The articles of association duly stamped and witnessed. (iii) Written permission of the directors. (iv) Agreement with the managing director/manager. (v)A copy of the registrar’s letter giving permission for the name. (vi) A declaration that all the legal requirements are followed. (vii) A notice about the exact office of the registered office. (viii) Documents showing the fees paid.
Capital subscription:
(i) SEBI approval (ii) Filing of prospectus. (iii) Appointment of brokers, bankers etc., (iv) Collection of minimum subscription (v) Application to stock exchange (vi) Allotment of shares.
Commencement of Business:
(i) A declaration about meeting minimum subscription requirement. (ii) A declaration regarding the application and allotment money paid by the directors as same as others. (iii) A declaration that no money is payable to the applicants because of the failure of the company.
(iv) A statutory declaration that the above particulars are followed. (v) The registrar shall examine the documents if these are found satisfactory a certificate of commencement of business will be issued.
Question and Answers
Very Short Answer type Questions: (1 Mark)
1. Varun is the only owner of his restaurant. Name the form of business organization.
Ans: Sole proprietorship.
2. Name the form of organization found only in India
Ans: Joint Hindu Family.
3. List two merits of Sole proprietorship.
Ans: (i) Single ownership (ii) Full control.
4. Name any one business in which sole proprietorship is most suitable.
Ans: Tailoring
5. Name the type of partnership which is formed to accomplish a specific project for a specific time.
Ans: Particular partnership
6. State any one consequence of non registration of a partnership firm.
Ans: An unregistered firm cannot file a case against third parties.
7. What is the minimum number of persons required to form a cooperative society?
Ans: Ten
8. Name the type of company which can invite the public to subscribe for the shares or debentures.
Ans: Public.
9. Name the process by which a joint stock company is registered.
Ans: Incorporation.
10. Name the document which defines the object and powers of the company.
Ans: Memorandum of Association.
Short Answer Type Questions: (3 or 4 Marks)
1. State three advantages of joint Hindu Family business.
Ans (i) Effective control (ii) Continuity of business (iii) limited liability of members (iv) Increased loyalty. (any three)
2. Explain the features of a Joint Hindu Family business.
Ans: (i) Formation (ii) Liability (iii) Control
3. List any three advantages of partnership.
Ans: (i) Easy to start and close (ii) proper decision making (iii) More money (iv) secrets are maintained.
4. State the important features of partnership.
Ans: (i) Formation (ii) Liability (iii) Risk bearing (iv) decision making (v) continuity (vi) Member .
5. What are the consequences of non registration of a partnership firm?
Ans: A Partner of an unregistered firm cannot file a case against the firm or other partners. The firm cannot file a case against third parties.
The firm cannot file a case against the partners.
6. Explain any three features of a company.
Ans: (i) Artificial person (ii) Formation is difficult (iii) Company has separate Identity.
7. Enumerate the various types of cooperative societies.
Ans: (i) Consumer (ii) Producer (iii) Marketing (iv) Farmer’s (v) Credit (vi) Cooperative housing societies
8. What are the functions of a promoter?
Ans: (i) Finding out a business opportunity (ii) Conducting studies (iii) Getting the name approved. (iv) Fixing up persons to sign Memorandum of Association. (v)Appointment of professionals.(vii) preparation of necessary Documents.
Long Answer Type Questions: (5 or 6 Marks)
1. Distinguish between Memorandum of Association and Articles of Association.
Ans : Memorandum of Association
- It defines the objects for which the company is formed.
- This is the main document of the company.
- This defines the relationship of the company with outsiders.
- Every company has to file Memorandum Of Association.
- Alteration of Memorandum of Association is difficult.
Articles of Association
- It defines the objectives of the company that are to be achieved.
- This is the subsidiary document of the company.
- Articles define the relationship of the members and the company.
- It is not necessary for the public limited company.
- It can be altered by passing a special resolution.
2. Distinguish between a private company and public company.
Ans:
PUBLIC COMPANY:
Members: Minimum 7, Maximum unlimited
Minimum number of directors: 3
Minimum paid up capital: 5lakhs.
Index of members: Compulsory.
Transfer of shares: Shares can be transferred easily from one person to another. Invitation to public: It can invite the public to purchase the share and debentures
PRIVATE COMPANY:
Members: Minimum 2, Maximum -50.
Minimum number of directors: 2
Minimum paid up capital: 1 lakh
Index of members: Not compulsory.
Transfer of shares: Shares cannot be transferred from one person to another. Invitation to public: It cannot invite the public to purchase the share and debentures.
3. Describe the various partners in a partnership firm.
Ans : TYPES OF PARTNERS
Active partner: An active partner is a partner who gives capital, participates in management, shares the profits and losses and has unlimited liability.
Sleeping partner: A Partner who do not take part in the business activities.
Secret partner: A partner who has association with the firm but unknown to the public.
Nominal partner: A partner who allows his name to be used by the firm
Partner by estoppel: A person who by behaviour sets an impression to others that he/she is a partner of the firm.
Partner by holding out: A person who is not a partner but allows himself to be represented as partner in a firm.
4. Why is company form of organization preferred than other forms of organization?
Ans : Merits: (i) Liability is limited (ii) Chances are there for expansion (iii) Managed by professional people (iv) Continuous existence (v) Shares can be easily transferred from one person to another person.
5. List and explain the factors which help in choosing an appropriate form of Organization.
Ans : Choice of form of Business organization: (i) less costly in setting up the Organization.(ii) Limited liability (iii) continuous existence (iv) Form of raising capital (v) Control to be made (vi) Nature of business.
HOTs
1. “One man control is the best in the world if that man is big enough to manage everything”. Explain.
Ans : Merits of sole proprietorship:
1. A sole proprietor can take decision quickly.
2. Information can be kept secretly without any leakage.
3. No need to share profits.
4. He gets self satisfaction for the work he has done.
5. Easy to start and to close because of less rules and regulations.
2. “A private company avoids many of the defects of a public company”. Explain.
Ans : Merits: (i) Liability is limited (ii) Chances are there for expansion (iii) Managed by professional people (iv) Continuous existence (v) Shares can
be easily transferred from one person to another person.
3. State the reasons for issuing prospectus:
Ans : 1. It serves as an invitation to the public to invest in the shares and debentures of the company.
2. It acts as an advertisement for inducing the investors to invest in the company.
3. It serves as an record of the terms and conditions on which shares and debentures are issued.
4. It helps to protect the interest of the investors.
4. “A company is said to be an artificial person created by law, having a separate entity with perpetual succession and a common seal”. Discuss the above statement.
Ans : Features: (i) Artificial person (ii) Formation is difficult (iii)Company has separate identity.(iv)Continuous existence (v) Control of the company is made by directors.(vi)liability is limited.(vii) Common seal.
5. Describe the steps involved in the flotation of the company.
Ans : Capital subscription:
1. SEBI Approval.
2. Filing of prospectus.
3. Appointment of bankers, brokers and underwriters.
4. Minimum subscription.
5. Application of stock exchange.
6. Allotment of shares.
Gist of the Lesson:
1. Sole proprietorship – one owner
2. Partnership – 2 or more partners.
3. Joint Hindu Family Business- at least 2 persons.
4. Cooperative society – At least 10 adults.
5. Company – Minimum 2 Maximum 50 (Private)
6. Company- Minimum 7 Maximum-unlimited.
7. Memorandum of Association- External rules and regulations.
8. Articles of Association – Internal rules and regulations.
|
37 videos|143 docs|38 tests
|
FAQs on Forms of Business Organisation Chapter Notes - Business Studies (BST) Class 11 - Commerce
| 1. What are the advantages of establishing a sole proprietorship? |  |
| 2. What are the different types of partnerships? |  |
| 3. What steps are involved in the formation of a company? |  |
| 4. What are the key concepts to understand in business organizations? |  |
| 5. How do the taxation processes differ among sole proprietorships, partnerships, and corporations? |  |

















