Governance Chapter Notes | Chapter Notes For Class 6 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| What Is a Government? |

|
| Three Organs of Government |

|
| Three Levels of Government |

|
| Dr. A.P.J. Abdul Kalam |

|
| Democracy |

|
What Is a Government?
A government is a group that makes important decisions for a country. Its job is to handle many different tasks to improve life for everyone.
The government is responsible for governance, which includes creating and enforcing rules (laws) and policies for the country.
Governance is a broader concept that involves more than just laws and policies. It includes how the government interacts with people and addresses their needs.

- A government is crucial for organizing and improving every aspect of life in a country. The government has many important jobs to ensure everything runs smoothly and people’s needs are met. Here’s how it handles its responsibilities:
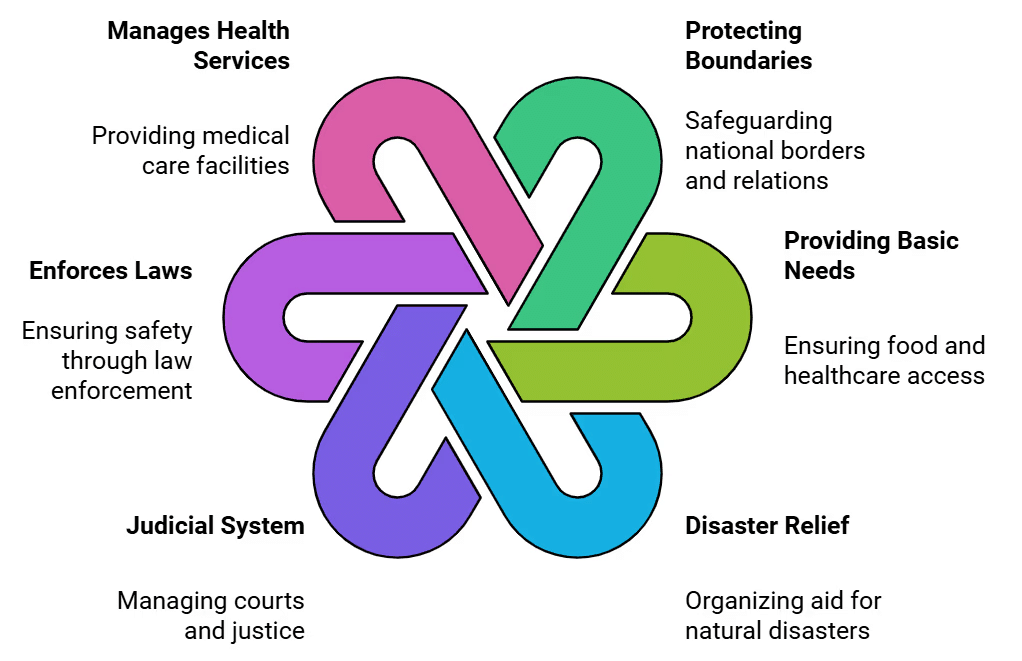
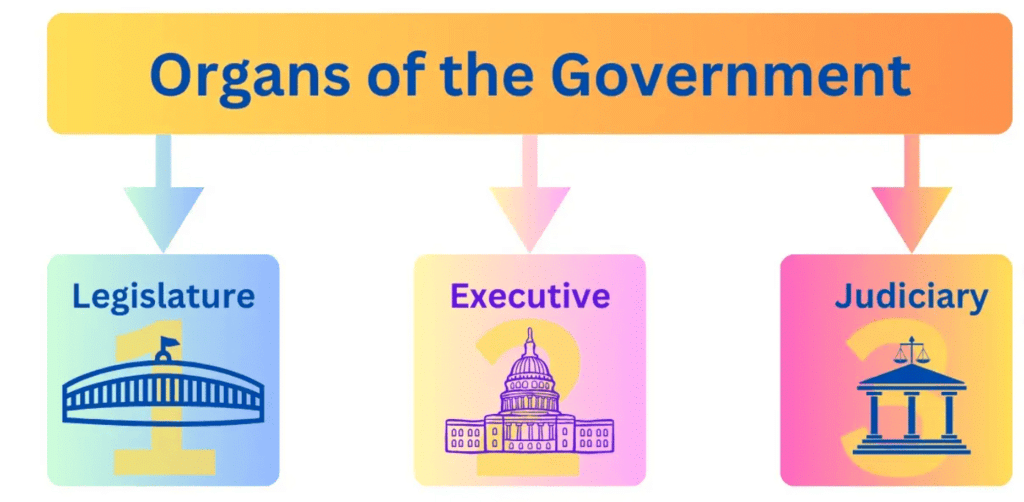
Three Organs of Government
- Legislature: This part of the government makes new laws. It is made up of representatives chosen by the people who discuss, change, and approve laws that control how society works.
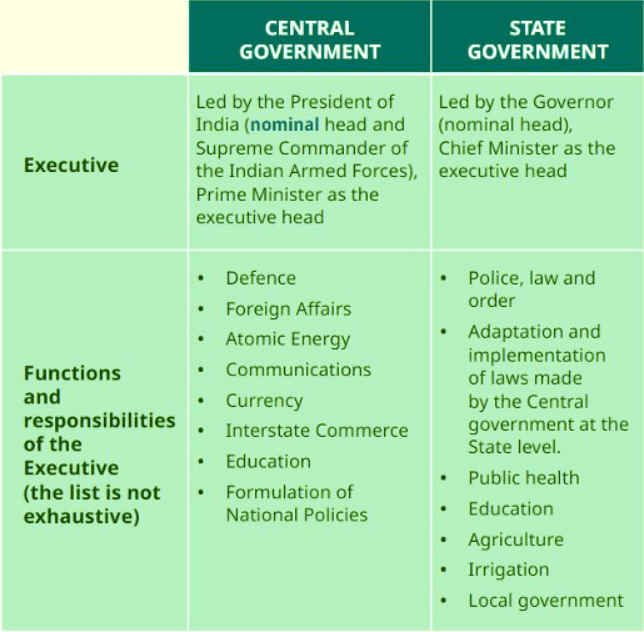
- Executive: The executive carries out the laws created by the legislature. This includes the head of state (like a president or prime minister), ministers, and various agencies that enforce laws and keep order.
- Judiciary: The judiciary is the court system that explains the laws and decides if someone has broken them. It also determines the right actions to take, including penalties if needed.
This separation of powers helps create a system of checks and balances. This means each part can keep an eye on the others to make sure no one oversteps their limits.
Three Levels of Government
In India, the government functions at three levels:
- Centre or National: Responsible for national issues.
- State: Handles state-specific matters.
- Local: Deals with local governance.
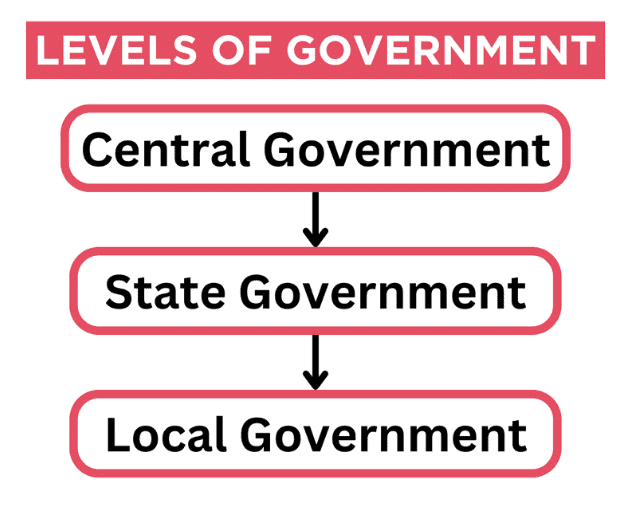
Each level has distinct responsibilities, contributing to overall governance.
Digital technology has transformed how societies function worldwide. In India, around 30 years ago, sending money far away required going to the Post Office for a money order or waiting in line at a bank for a demand draft.
This technological change has led to an increase in online criminals who steal money without leaving their homes. To address these crimes, many governments have introduced new laws specifically targeting cybercrime.
Some cybercriminals, who choose to rob others instead of using their skills for good, have been caught. These criminals are punished in court, facing consequences like fines or imprisonment.
The three branches of government work together to handle cybercrime: The legislature creates laws against cybercrime, the executive enforces these laws through bodies like the cyber police, the judiciary ensures justice is done when the laws are violated.
For a government to function effectively, these three branches must remain separate. They also need to cooperate with each other to ensure proper functioning. Keeping them separate helps maintain a balance of power and ensures that each part does its job properly.
[ Intext Question]
How the Three Branches of Government Work Together
Think of the government as a team with three key players, each with a specific role. Here’s how they collaborate: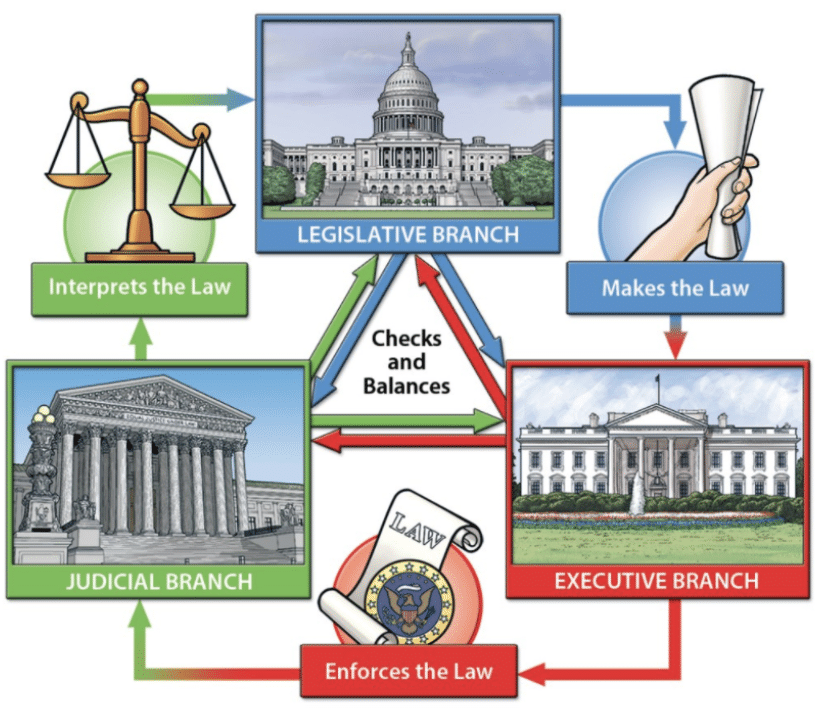
1. The Legislature: Making the Rules
- The legislature makes and changes laws.
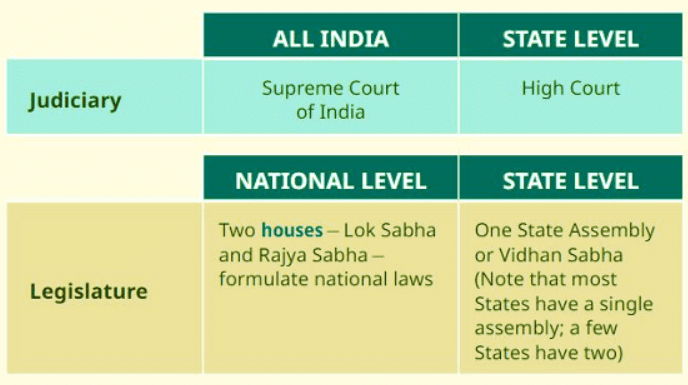
- In India, this role is carried out by Parliament, which includes the Lok Sabha (House of the People) and the Rajya Sabha (Council of States).
- It can also remove outdated laws.
2. The Executive: Putting the Rules into Action
- The executive is responsible for implementing the laws.
- This includes the head of state (who could be a president, prime minister, or chief minister), along with ministers and various agencies that ensure law and order.
- For instance, the cyber police is an agency that enforces laws related to online conduct.
3. The Judiciary: Ensuring Fairness and Justice
- The judiciary acts as a referee, determining if the law is broken and deciding on punishment.
- It also reviews the executive's decisions and checks if laws are fair.
- In India, the judiciary is made up of different court levels, with the Supreme Court at the top.
These three branches work based on the principle of separation of powers, which creates a system of checks and balances. Each branch can monitor the others to maintain balance if one exceeds its role.
Three Levels of Government
In India, there are three levels of government: local, state or regional, and national. Each level has its own duties. This system operates within a democratic framework and relies on elected representatives at both the state and national levels. Here’s a closer look at these levels: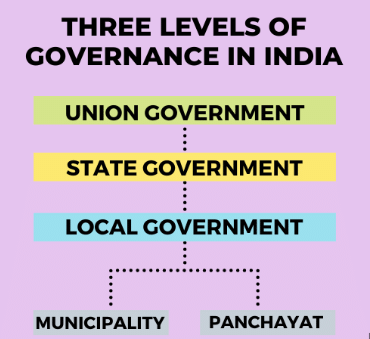
Local State or Regional National
- Local Government: This is the level that is nearest to the public and addresses issues specific to areas like towns or villages. Local authorities manage concerns that affect small communities, such as minor floods in neighbourhoods. They take care of tasks like rubbish collection, street cleaning, and park maintenance. (Local government will be explored in more detail in the following chapters.)
- State Government: When problems affect multiple towns and villages, the State Government intervenes and dispatches rescue teams to assist those in need. They oversee areas such as education, healthcare, and transport within their regions.
- Central or Union Government: In the event of a significant flood impacting large areas, the Central Government may also assist by providing relief supplies and deploying the army. This government is responsible for national defence, foreign relations, and large infrastructure projects.
Inspirations from Ancient Texts in Institutional Mottos
- Many institutions in India have mottos that draw inspiration from ancient texts.
- The motto of the Government of India is "Satyameva Jayate," which means "Truth alone triumphs." This underscores the significance of truth in governance.
- The Supreme Court of India uses the motto "Yato Dharmastato Jayah," translating to "Where there is dharma, there is victory." This highlights the importance of dharma, or righteousness, in attaining success.
Dr. A.P.J. Abdul Kalam

- Dr. A.P.J. Abdul Kalam was born in a humble family in Rameswaram, Tamil Nadu, in 1931.
- He was a famous scientist, known as the 'Missile Man of India' for his vital contributions to India's space and missile programmes, along with its nuclear capabilities.
- Dr. Kalam held the position of 11th President of India from 2002 to 2007.
- Despite his prestigious role, he remained closely connected to the people, especially the youth, through his dedication to quality education and innovation.
- He motivated millions with his humility, devotion to social causes, and commitment to the nation.
- Dr. Kalam encouraged young Indians to dream big and strive to realise their ambitions.
- His role as President, although largely ceremonial, allowed him to significantly influence many lives.
- Here are some of his inspiring thoughts:

Democracy

- A system of governance where representatives of the people make decisions for the citizens is known as democracy. The word 'democracy' comes from Greek words: 'demos' meaning 'people' and 'kratos' meaning 'rule' or 'power', which together mean 'rule of the people.'
- Direct Democracy: This is an instance of direct democracy where every student's opinion was considered to decide the location.
- Grassroots Democracy: This term describes a system that empowers and promotes participation from ordinary citizens, allowing them to influence decisions that impact their lives.
- Structure of Government in India: The Indian government operates at three levels: Centre or national, State, and local. Understanding this structure is vital for grasping how governance functions in the country.
- Importance of Democracy: Democracy provides the framework for this system, operating through elected representatives at both the State and national levels.Question for Chapter Notes: GovernanceTry yourself:What is the term used to describe a system of governance where representatives of the people make decisions on behalf of the citizens?View Solution
Features of Indian Democracy
- India operates as a representative democracy, where citizens choose representatives to make decisions for them.
- It holds the title of the world’s largest democracy, with approximately 970 million voters in 2024.
- Voting rights are granted to all Indian citizens aged 18 and above.
- At the State level, the elected representatives are known as Members of Legislative Assembly (MLAs).
- At the national level, these representatives are referred to as Members of Parliament (MPs).
- Representatives engage in discussions about laws and issues within assemblies, where they aim to persuade each other through dialogue and debate.
- Grassroots democracy allows ordinary citizens to participate in decision-making processes that influence their lives.
- The Indian government operates on three levels: Centre or national, State, and local.
- For instance, if a class is deciding on a picnic spot, they might debate two options, A and B, considering factors like distance and cost. The teacher may then suggest voting, where the option with the most raised hands is chosen. This illustrates a form of direct democracy, valuing each student's opinion.
Key Words
- House: A group where laws are talked about or created. For the Central Government, there are two houses – Lok Sabha and Rajya Sabha - which make national laws.
- Nominal: Only in name. This means that the President of India and the Governor of a State are not the real leaders. They have some powers in special situations, but generally, they do not get involved in Central or State government matters.
- Government – A group of people who make and enforce rules to keep order in a country.
- Governance – The way rules and decisions are made to organise and manage a society.
- Laws – Important rules that everyone must follow to keep peace and fairness.
- Legislature – The part of the government that makes laws. In India, it includes Parliament.
- Executive – The branch that enforces laws and ensures they are followed.
- Judiciary – The system of courts that explains laws and decides punishments when laws are broken.
- Democracy – A system of government where people choose their leaders by voting.
- Separation of Powers – The idea that the three branches of government should work independently but still keep each other in check.
- Checks and Balances – A system where each branch of government watches the others to prevent misuse of power.
- Constitution – The set of rules that explains how a country should be governed.
- Cybercrime – Crimes that happen using the internet, like hacking or online fraud.
- Parliament – A place where elected representatives discuss and pass laws for the country.
- Rights – The freedoms and protections that every person should have, like the right to vote or speak freely.
FAQs on Governance Chapter Notes - Chapter Notes For Class 6
| 1. What are the three levels of government in India? |  |
| 2. How does Dr. A.P.J. Abdul Kalam contribute to democracy in India? |  |
| 3. What is the significance of democracy in governance? |  |
| 4. How does local government function in a democratic setup? |  |
| 5. What role does citizen participation play in a democratic government? |  |
















