Human Body: Organ Systems Class 3 Notes Science
| Table of contents |

|
| The Skeletal System |

|
| The Muscular System |

|
| The Digestive System |

|
| The Circulatory System |

|
| The Respiratory System |

|
| The Nervous System |

|
| The Sense Organs |

|
| The Excretory System |

|
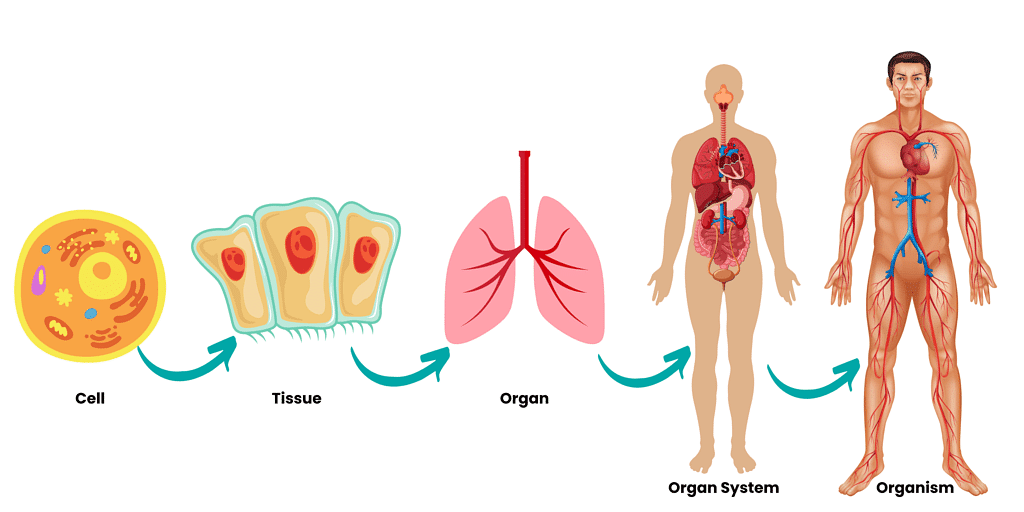
Our body is made up of a large number of small cells. Similar types of cells form a tissue. Different types of tissues join to form organs.
- Our stomach, liver, ears and lungs are organs made up of different types of tissues.
- The human body is a wonderful combination of many systems. A system is made of many organs connected together to perform a special function.
- The different systems work together to carry out different types of jobs to keep us alive and healthy.

The Skeletal System
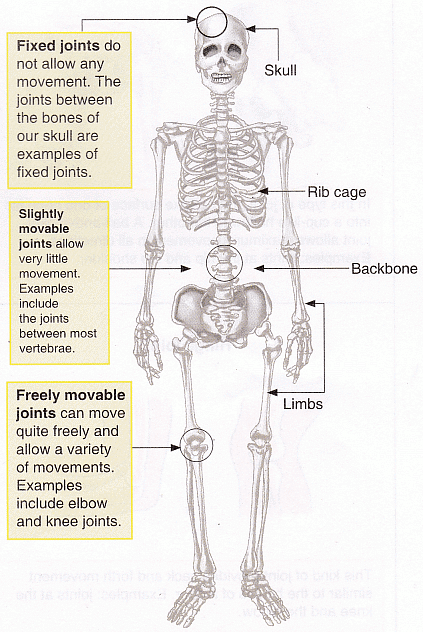
This system is made up of bones that are joined to form a framework known as the skeleton.
- There are 206 bones in an adult. Some of them join together as we grow older.
- Bones are the hard and strong parts of our body.
Functions of the Skeletal System
- It gives shape and support to the body. Without bones our body would be just like a blob of jelly.
- It also protects the very delicate parts inside your body such as the brain, heart and lungs.
- Skull, ribcage, backbone, and limbs are main parts of the skeleton.
 Skeletal System
Skeletal System
The Muscular System
 Muscular System
Muscular System
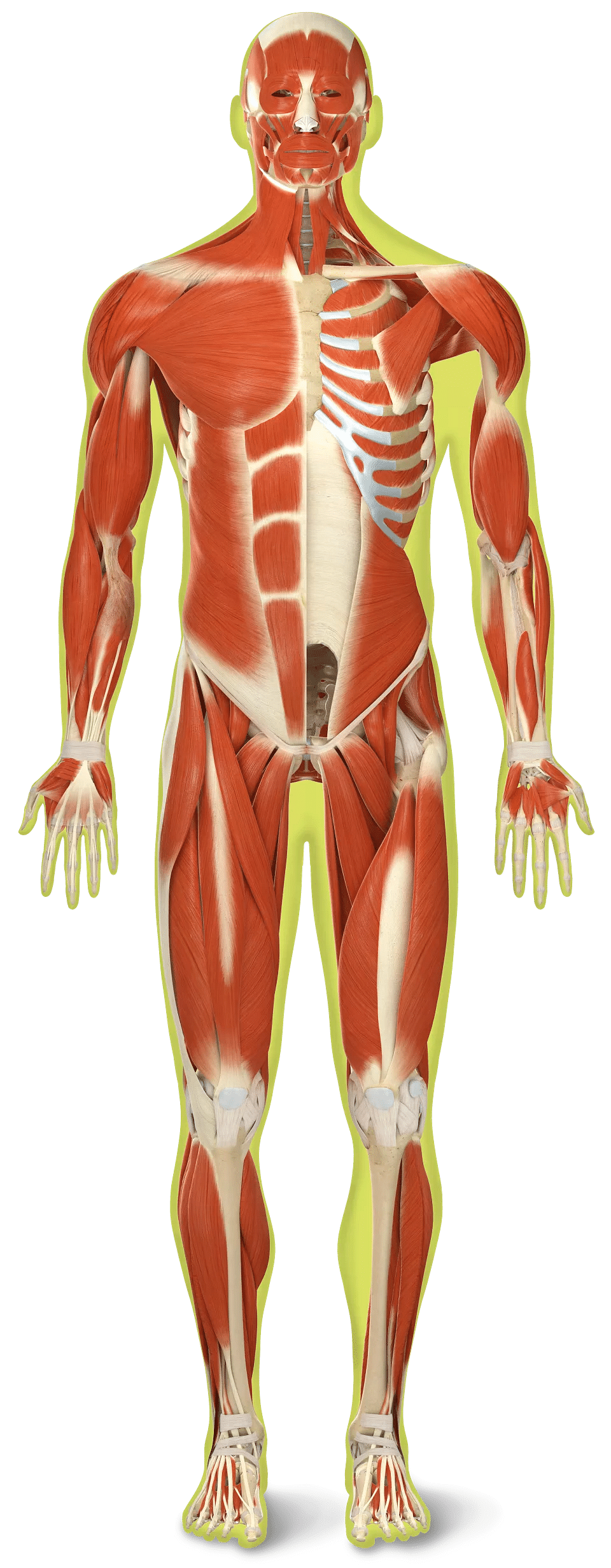
The system that helps us in the movement of our body is known as the muscular system.
- The bones are joined to the muscles. Muscles are stretchy bands of tissues. From the tiny blink of the eye to jumping up and down on your powerful legs, anytime you move, you are using muscles.
- They work together to help us move. Internal organs also move because of muscles. Our heart keeps beating and the food we eat moves through our body because of the muscles.
- Our eyes too can move because there are some very delicate muscles which help them to do so. Our facial expressions are also caused by muscles. There are more than 600 muscles in a human body.
The Digestive System
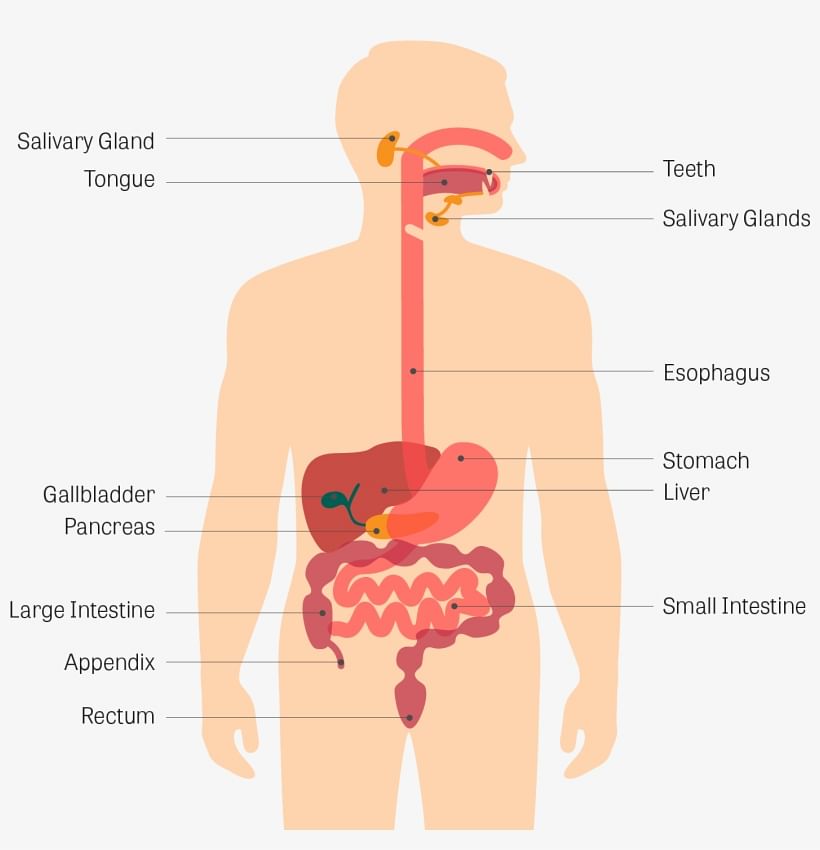 Digestive System
Digestive System
The food that we eat cannot be used by our body as it is. The process by which food is broken down into simple useful substances that can be used by the body to get energy is called digestion.
- The digestive system is made up of different organs such as the mouth, food pipe, stomach, small intestine, large intestine and rectum.
- It helps the body to break down and digest the food we eat, so that we get energy to work and play.
The Circulatory System
The heart, blood and blood vessels make up the circulatory system of the body.
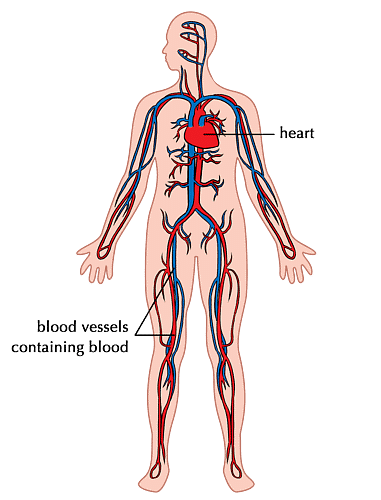 Circulatory System
Circulatory System
- The heart is made up of muscles and helps to pump blood.
- The blood carries nutrients and gases like oxygen and carbon dioxide to different parts of the body through a thin tubes called blood vessels.
Note:-Put your hands on your chest. Can you feel something going ‘lub-dub lub-dub’? This is your heart.
The Respiratory System
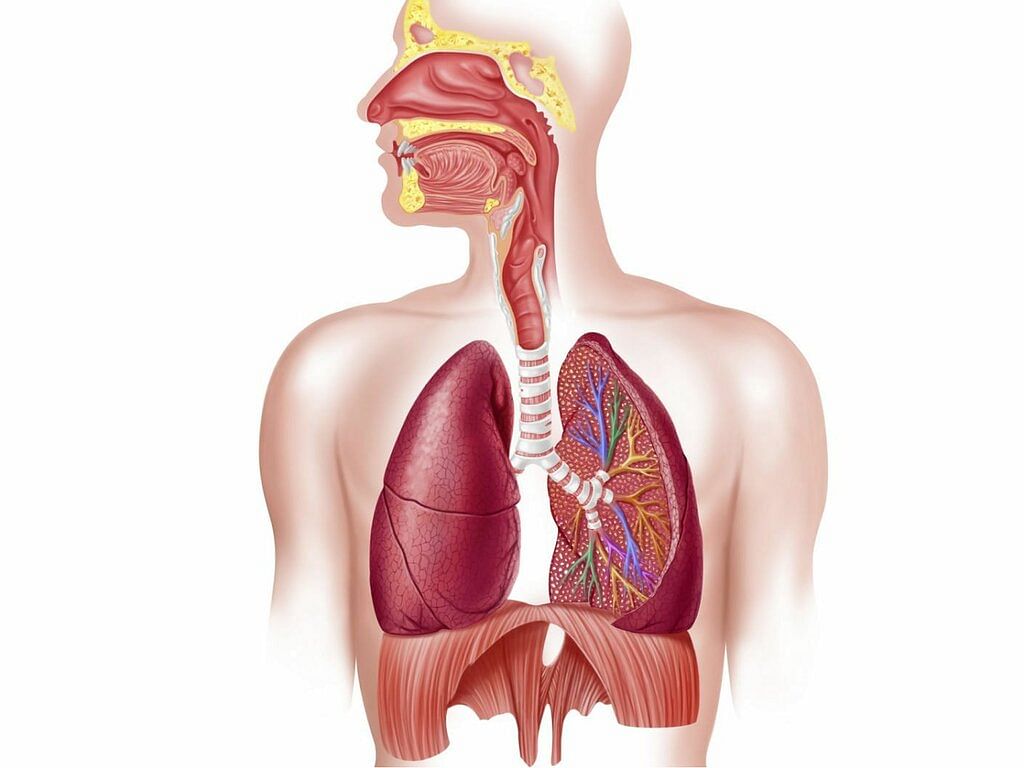 Respiratory System
Respiratory System
The nose, the windpipe and the lungs make up the respiratory system.
- The respiratory system helps us to breathe.
- We breathe in air through our nose or mouth. The air then goes down through the windpipe and reaches the lungs.
- The air we breathe in is called inhaled air and the air we breathe out is called exhaled air.
The Nervous System
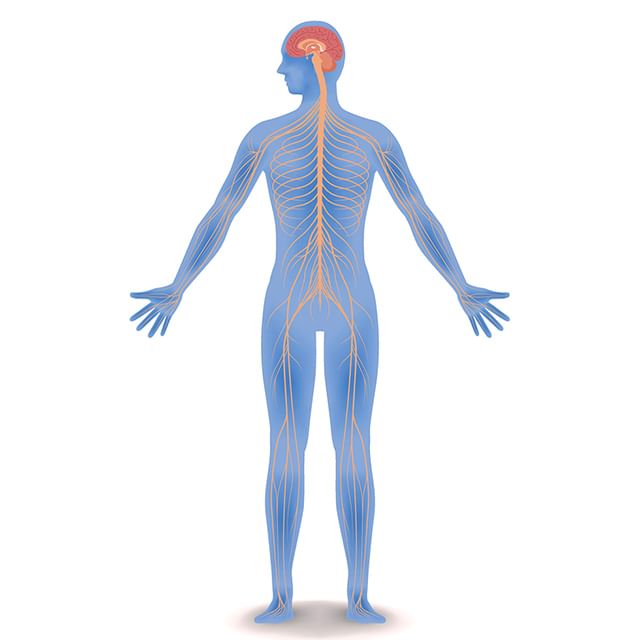 Nervous System
Nervous System
The brain, spinal cord and the nerves together make up our nervous system.
- Brain is the main organ of the nervous system. It controls all the other organs by sending and receiving information from all parts of the body.
- Nervous system helps us to think, act and learn.
The Sense Organs
We know about the world around us through the parts of our body called the sense organs.
These sense organs are as follows:
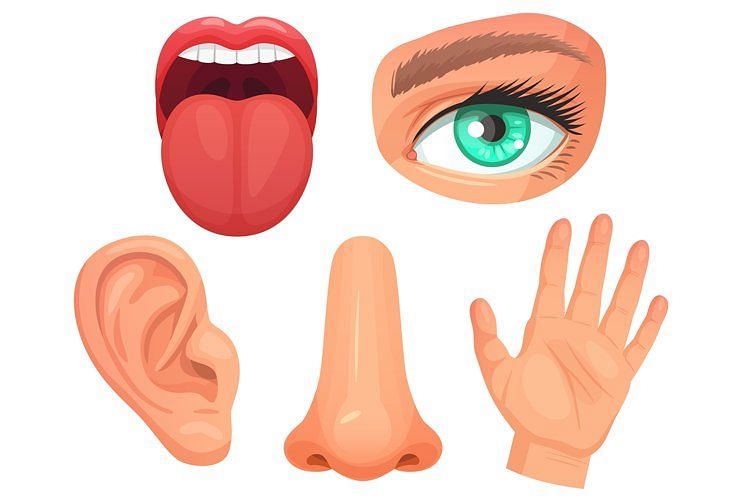 Sense OrgansEyes: They help us to see things. They also help us to see if something is far or near.
Sense OrgansEyes: They help us to see things. They also help us to see if something is far or near.
Ears: We hear sounds which may be loud or soft, sharp or dull, and pleasant or unpleasant to our ears.
Nose: It allows us to smell.
Tongue: We can taste sweet, salty, sour or bitter tastes with it.
Skin: It enables us to feel pain, hot or cold, smooth or rough, hard or soft substances.
The Excretory System
 Excretory System
Excretory System
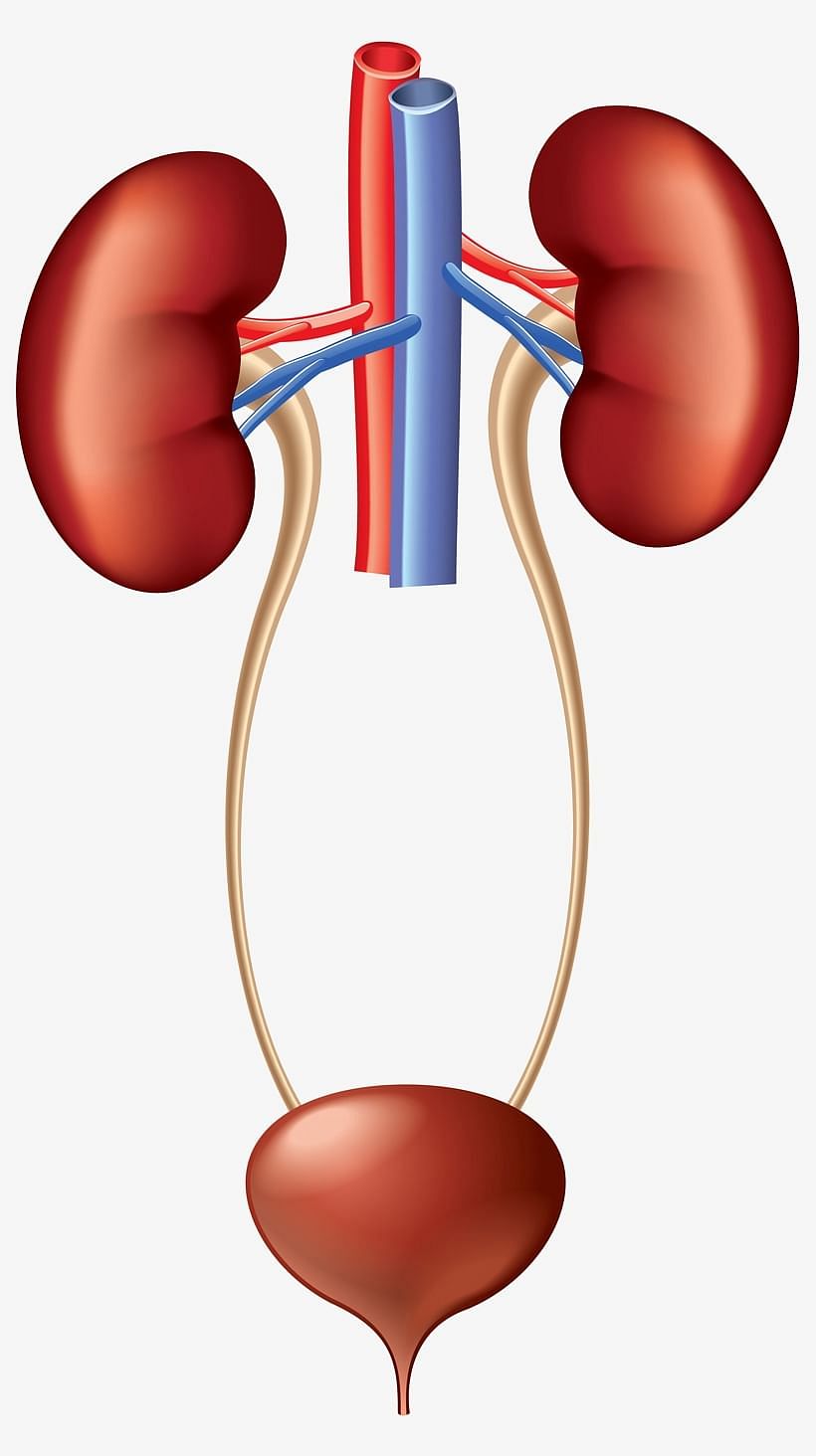
The organs that remove waste like urine, carbon dioxide, sweat etc. produced in the body form the excretory system.
- As the body parts do their work, waste materials are produced. For example, when food is converted into energy, a gas called carbon dioxide is produced.
- The main organ of this system is a pair of kidneys. The lungs and the skin also help in removing wastes from the body.
- The kidneys expel out urine from the body. The lungs get rid of carbon dioxide. The skin gets rid of sweat.
|
19 videos|48 docs|30 tests
|
FAQs on Human Body: Organ Systems Class 3 Notes Science
| 1. What is the function of the skeletal system? |  |
| 2. How does the muscular system work with the skeletal system? |  |
| 3. What is the role of the digestive system in the human body? |  |
| 4. How does the circulatory system function in the body? |  |
| 5. What is the main function of the respiratory system? |  |

|
Explore Courses for Class 3 exam
|

|