Human Body - The Skeletal System Chapter Notes | Science Class 5 ICSE PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| Major Bones and Their Functions |

|
| Importance of Bones |

|
| Joints |

|
| Muscles |

|
| Care of Bones, Muscles and Joints |

|
| Points To Remember |

|
| Glossary |

|
Introduction
The skeletal system is an important part of our body that gives it shape and support. It is made up of bones, joints, and muscles that work together to help us move, stand, and protect our internal organs. In this chapter, we will learn about the different bones in our body, how joints help us move, and the role of muscles. We will also understand how to take care of our skeletal system by eating healthy food, maintaining good posture, and doing regular exercise.
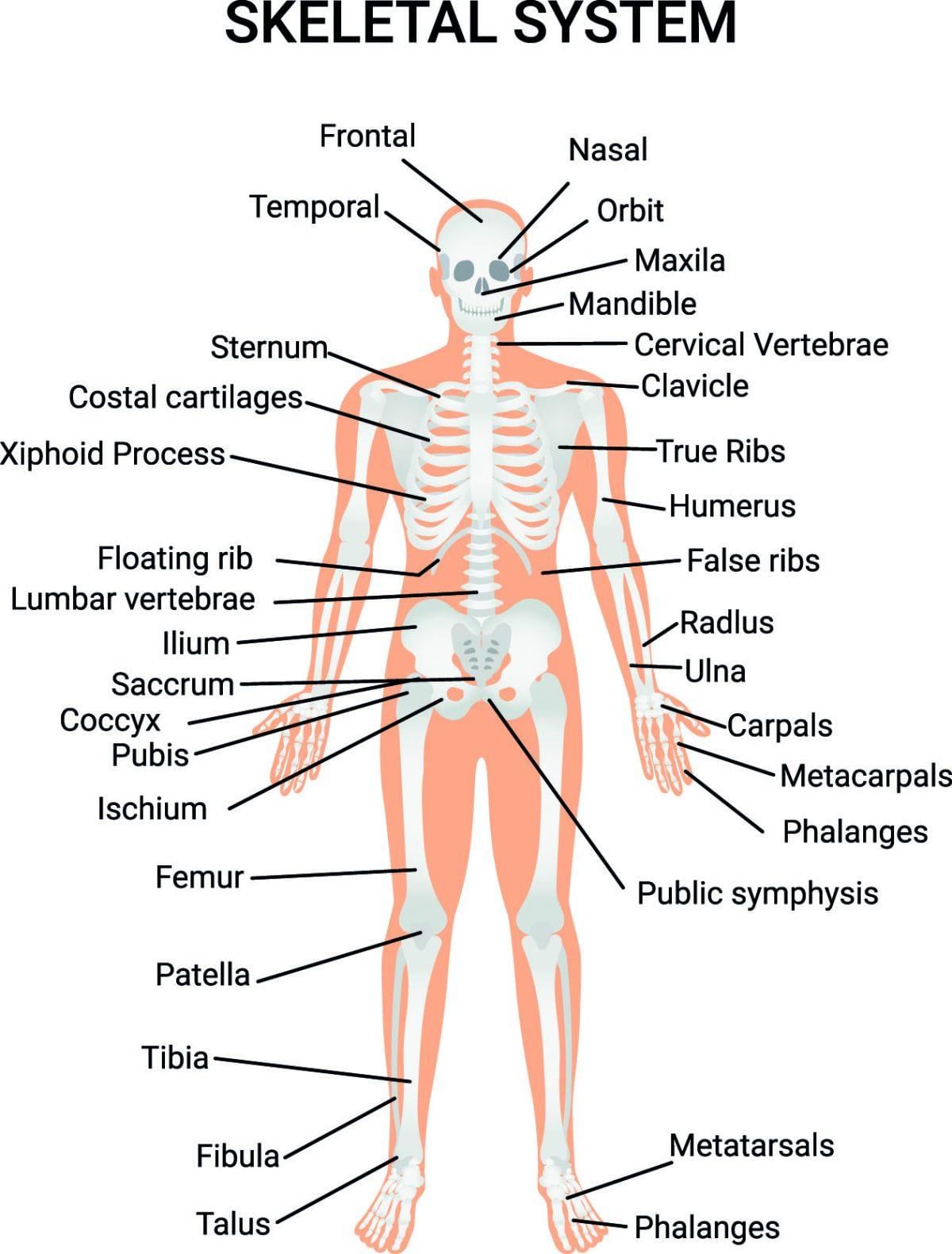
The Skeletal System
- The skeletal system is a strong structure of bones in our body.
- It gives support, shape, and strength to the body.
- It protects the soft internal organs like the brain, heart, and lungs.
- The skeletal system works with the muscular system to help us move.
- There are 206 bones in an adult human body.
- All the bones together form a structure called the skeleton.
Major Bones and Their Functions
The main bones in our body are the skull, limbs, backbone, ribcage, and jawbone.
Skull
- The skull is the bony structure that makes the head.
- It protects the brain, which is a very important organ.
- The skull gives shape to our face.
- It has 22 bones in total.
- Out of these 22 bones, 8 bones form a protective cover around the brain.
- 14 bones form the upper and lower jaws and other facial parts.
- The lower jaw is the only part of the skull that can move.
- We can move the lower jaw to talk, eat, and chew food.
- The other bones in the skull are fixed and cannot move.
Limbs
Humans have two pairs of limbs: forelimbs (arms) and hindlimbs (legs).
Forelimbs
- Forelimbs are the arms of our body.
- Each arm is divided into two parts: the upper arm and the lower arm.
- The upper arm has one long bone called the humerus.
- The lower arm has two long, parallel bones called the ulna and radius.
- The humerus is joined to the ulna and radius at the elbow.
- Many small bones join together to form the wrist.
- The forelimbs work with muscles and joints to help us move our arms.
- They help us do activities like writing, eating, and holding things.
Hindlimbs
- Hindlimbs are the legs of our body.
- Each leg is divided into two parts: the upper leg and the lower leg.
- The upper leg has a long bone called the femur.
- The femur is the longest and strongest bone in the body.
- The lower leg has two long, parallel bones called the tibia and fibula.
- The femur is joined to the tibia and fibula at the knee.
- Many small bones join together to form the ankle and the foot.
- The hindlimbs work with muscles and joints to help us move our legs.
- They help us do activities like walking, running, standing, and jumping.
- The femur supports the body weight during these activities.
Backbone
- The backbone is also called the vertebral column or spine.
- It is made up of 33 small, irregular-shaped bones called vertebrae.
- These vertebrae are placed one above the other to form a strong column.
- The backbone protects the spinal cord, which is a very important part of the body.
- It helps us stand upright and maintain balance.
Ribcage
- The ribcage is the chest bone located in the chest area.
- It is made up of 24 bones called ribs, arranged in 12 pairs.
- The ribs are thin, flat, and curved bones.
- They form a protective cage around the heart and lungs.
- The ribs are joined to the sternum in the front.
- The sternum is a long, flat bone in the chest region.
- The ribs are also joined to the backbone at the back.
- The ribcage helps in breathing by giving support during respiration.
Jawbone
- The jawbone is the bone of the lower jaw.
- It is one of the 14 bones of the facial structure in the skull.
- The jawbone is U-shaped and is the strongest and largest bone in the skull.
- It holds the teeth of the lower jaw.
- It is the only bone in the skull that can move.
- The jawbone helps us eat and speak by moving up and down.
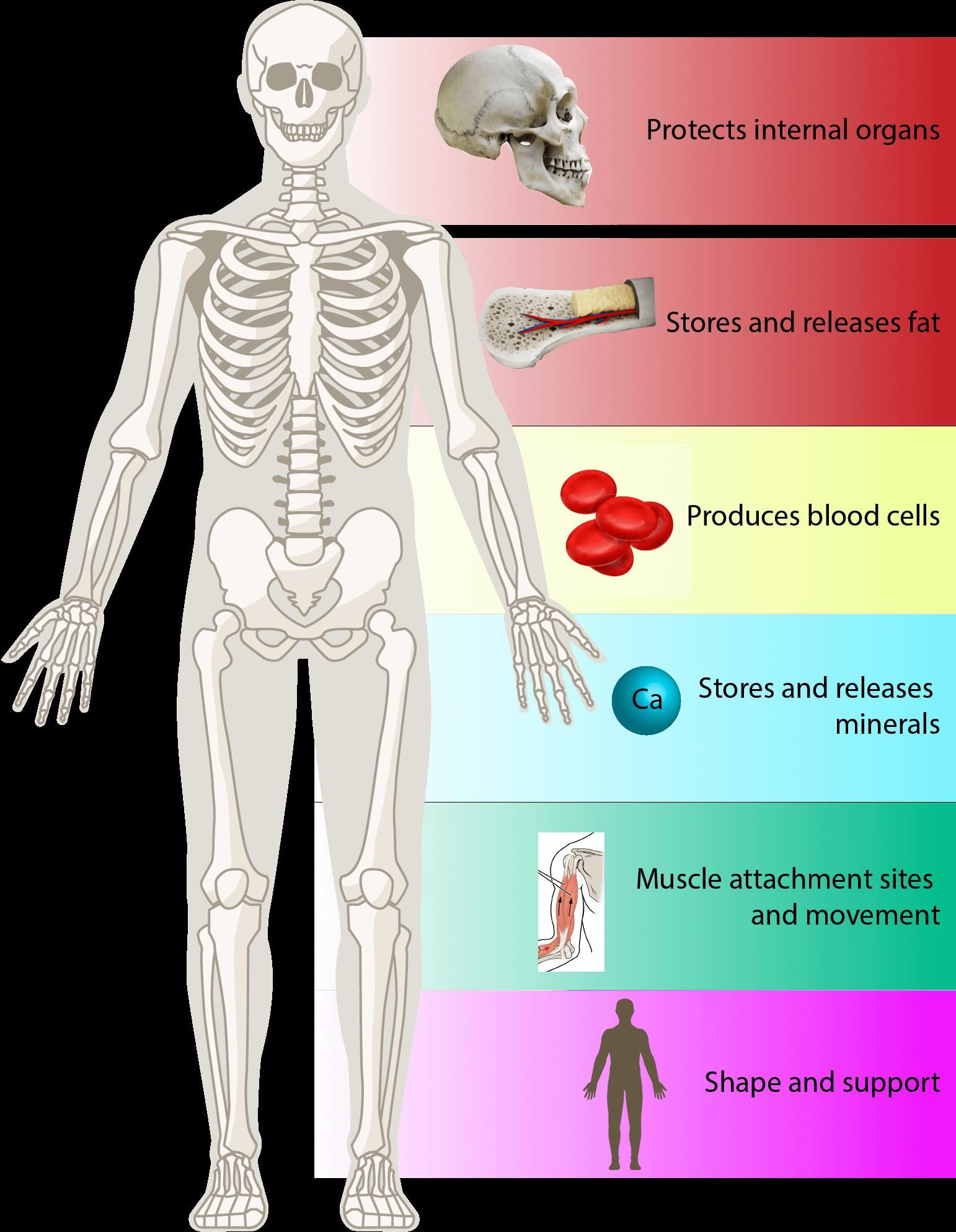
Importance of Bones
- Bones are a very important part of the skeletal system.
- They give shape to the body and act as a framework.
- Bones protect soft internal organs.
- The skull protects the brain.
- The ribcage protects the lungs and heart.
- Bones provide attachment points for muscles and other tissues.
- Bones of the legs and backbone hold up the body.
- Almost all organs are supported by bones in some way.
- Bones help in movement along with muscles and joints.
- They allow us to do activities like walking, running, and writing.
- Bones produce blood cells in a jelly-like substance called bone marrow.
- Red blood cells and white blood cells are made in the bones.
- Bones store minerals like calcium and phosphorus.
- These minerals help keep the body healthy.
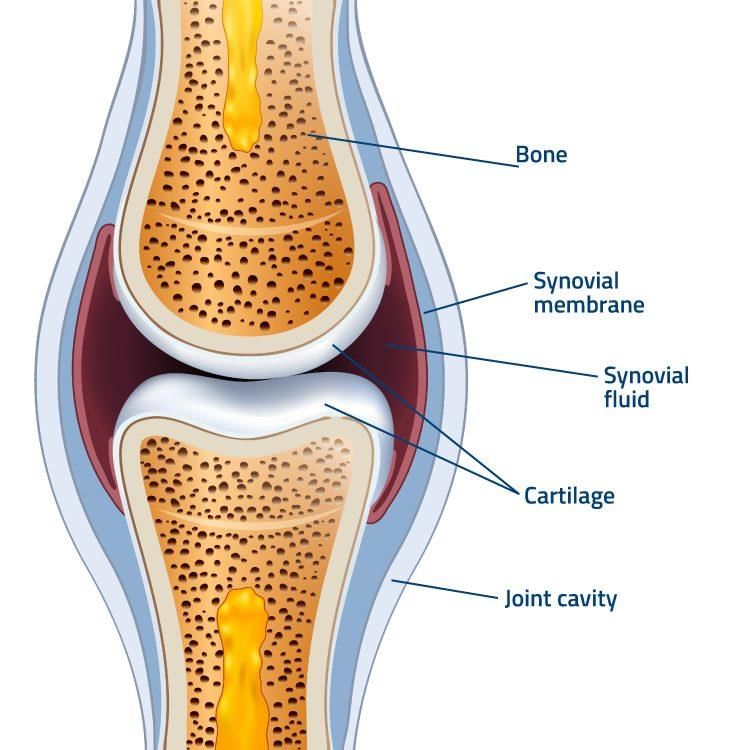
Joints
- Joints are the places where two or more bones meet or join together.
- Bones are held together at the joints by strong tissues called ligaments.
- Joints help us bend and move different parts of our body.
Types of Joints
- Joints are of two types: movable and immovable.
- Most joints in the body are movable, but some are immovable.
- Immovable joints are found in the tooth socket and the skull.
There are four types of movable joints: hinge joint, ball and socket joint, pivot joint, and gliding joint.
Hinge Joint
- Hinge joints allow back-and-forth movement in one direction only.
- They work like the hinges of a door.
- Bones in the elbow, knee, toes, and fingers have hinge joints.
Ball and Socket Joint
- In a ball and socket joint, the ball-like end of one bone fits into a cup-like socket of another bone.
- This joint allows movement in all directions.
- Shoulder and hip joints are examples of ball and socket joints.
Pivot Joint
- Pivot joints allow rotation only.
- In this joint, the rounded surface of one bone fits into a ring formed by another bone.
- The joint between the neck and the head is a pivot joint.
- It helps us rotate our head from side to side.
Gliding Joint
- Gliding joints allow bones to glide or slide over each other.
- Bones of the wrist and ankle have gliding joints.
Importance of Joints
- Bones are hard and cannot bend on their own.
- Joints provide flexibility to our body by allowing bones to move in different directions.
- Different types of joints allow specific movements.
- Fluid present within the joints acts as a lubricant.
- This fluid helps bones move smoothly without friction.
- Joints are important points of movement in the skeletal system.
Muscles
- Muscles are bundles of elastic fibers in our body.
- They are flexible and help bring about movement in body parts.
Types of Muscles
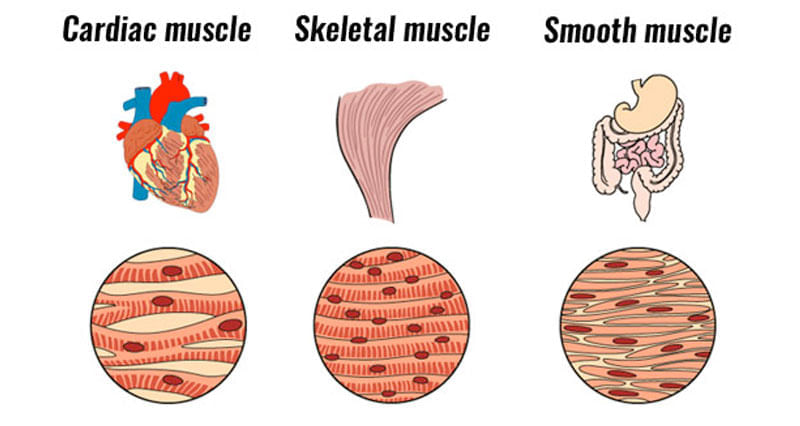
There are three types of muscles in our body: skeletal, smooth, and cardiac muscles.
 Skeletal Muscles
Skeletal Muscles
- Skeletal muscles are the muscles we use to move around.
- We can control their movement, so they are called voluntary muscles.
- They remain attached to the bones by a special tissue called tendon.
- Muscles of the arms, legs, feet, and neck are examples of skeletal muscles.
Smooth Muscles
- Smooth muscles are found in the internal organs of our body.
- We cannot control their movement, so they are called involuntary muscles.
- They move on their own without our control.
- Muscles of the stomach, intestine, and urinary bladder are examples of smooth muscles.
Cardiac Muscles
- Cardiac muscles are found in the heart.
- They are also called heart muscles.
- They are involuntary muscles and work continuously to pump blood to all body parts.
- They are specialized for the continuous movement of the heart.
Importance of Muscles
- Muscles are very important for the body in many ways.
- They control the movement of bones.
- They help in the movement of internal organs.
- Cardiac muscles in the heart keep it beating to pump blood.
- Smooth muscles help food move from the mouth to the stomach through the esophagus.
- Muscles also help maintain body heat.
Care of Bones, Muscles and Joints
- Bones, muscles, and joints are important parts of our body.
- We must take care of them to keep them healthy.
- We can keep them healthy by eating a balanced diet.
- We should take proper rest to allow the body to recover.
- Maintaining a good posture helps reduce stress on bones and muscles.
- Doing regular exercise keeps bones, muscles, and joints strong.
Food for Skeletal System
Our body needs calcium, vitamin D, and proteins for healthy bones and muscles.
Vitamin D and Calcium
- Vitamin D helps the body absorb calcium from food.
- Calcium makes our bones strong.
- Vitamin D also keeps our muscles active by helping in muscle contraction.
- Growing children need more calcium and vitamin D for their growing bones.
- Leafy vegetables like spinach and cabbage are rich in calcium.
- Milk, cheese, and curd are also good sources of calcium.
- Eggs, milk, cheese, and mushrooms are rich sources of vitamin D.
- Sunlight helps the body produce vitamin D naturally.
Proteins
- Proteins are the building blocks of muscles.
- They help in the growth and repair of muscles.
- Good sources of protein include milk, cheese, eggs, soy, beans, pulses, fish, and meat.
Role of Good Posture and Regular Exercise
- Posture is the way we hold our body while standing, sitting, or lying down.
- Good posture means keeping our back straight while sitting and standing.
- This reduces pressure on the backbone and prevents back pain.
- Sitting with a bent back puts extra pressure on the backbone and can cause pain.
- Physical activity is important for all age groups.
- Children who exercise regularly develop strong bones, joints, and muscles.
- Activities like walking, running, dancing, playing outdoor games, and yoga help keep the skeletal system healthy.
Points To Remember
- The skeletal system is a rigid framework of bones that provides support, shape, and strength to the body, and protects the internal organs.
- The major bones of the skeleton include skull, limbs (bones of arms and legs), backbone, ribcage (chest bone), and jawbone.
- Besides providing shape to the body, bones perform various other functions—protection, support, movement, production of blood cells, and mineral storage.
- The places where two or more bones meet or join together are called joints.
- Joints provide flexibility to our body by allowing bones to move in different directions.
- Muscles are bundles of elastic fibers. They are flexible, and thus, bring about movement of all body parts.
- There are three types of muscles present in our body—skeletal, smooth, and cardiac muscles.
- Muscles control the movement of bones.
- We can keep our bones and joints healthy by eating a balanced diet, taking proper rest, maintaining a good posture, and doing regular exercise.
Glossary
- Skeletal system: A rigid framework of bones that provides support, shape, and strength to the body, and protects the internal organs.
- Skeleton: The framework of all the bones together.
- Skull: The bony framework of the head.
- Joints: The places where two or more bones meet or join together.
- Ligaments: The strong tissues that hold bones together at the joints.
- Skeletal muscles: The muscles that we use to move around.
- Tendon: The special tissue by which skeletal muscles remain attached to the bones.
- Smooth muscles: The muscles which are present in the internal organs of our body.
- Cardiac muscles: The muscles which make up the heart.
|
48 docs|11 tests
|
FAQs on Human Body - The Skeletal System Chapter Notes - Science Class 5 ICSE
| 1. What are the major bones in the human body? |  |
| 2. What are the functions of bones in the skeletal system? |  |
| 3. Why is it important to maintain a healthy skeletal system? |  |
| 4. What foods are beneficial for the skeletal system? |  |
| 5. How do bones grow and develop in children? |  |















