Immunity Chapter Notes | Microbiology - NEET PG PDF Download
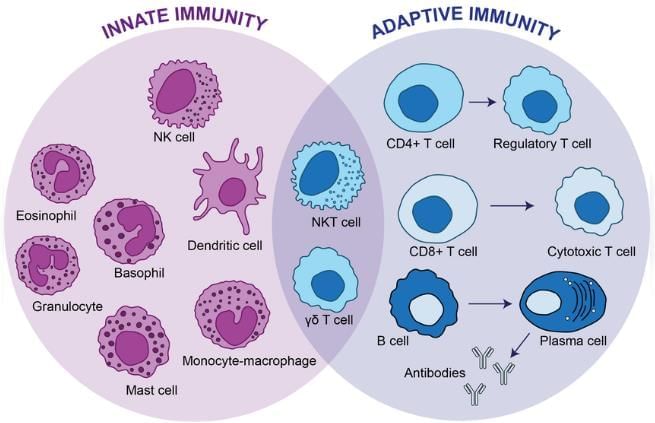
Innate Immunity
Immunity is the body's ability to defend against microorganisms or foreign substances. It can be broadly categorized into:
- Innate Immunity: This type of immunity is present from birth.
- Acquired/Adaptive Immunity: This immunity develops during an individual's life.
Differences between Innate and Acquired Immunity
Innate Immunity:
- Resistance to infection present from birth.
- Immune response occurs within minutes.
- Prior exposure to the antigen is not required.
- Limited diversity, acting through a restricted set of reactions.
- Responds to microbe-associated molecular patterns (MAMPs) shared by many microbes.
- Host cell receptors, such as pattern recognition receptors (e.g., Toll-like receptors), are nonspecific.
Acquired Immunity:
- Resistance to infection acquired during an individual's lifetime.
- Immune response takes days to develop.
- Develops following antigenic exposure.
- More varied and specialized responses.
- Immunological memory responses are present.
- Responds to specific microbial antigens.
- Host cell receptors, such as T cell receptors and B cell immunoglobulin receptors, are specific.
Components of Innate Immunity
- Anatomical Barriers: Skin and mucosa act as physical barriers to prevent infection.
- Physiological Barriers: Factors like body temperature that create an inhospitable environment for pathogens.
- Phagocytes: Cells such as neutrophils, macrophages, and monocytes that engulf and destroy pathogens.
- Natural Killer (NK) Cells: Lymphocytes that target and destroy infected or cancerous cells.
- Other Classes of Lymphocytes: Includes γδ T cells, NK-T cells, B-1 cells, and marginal-zone B cells with various immune functions.
- Mast Cells: Cells involved in allergic responses and the release of inflammatory mediators.
- Dendritic Cells: Antigen-presenting cells that activate the adaptive immune response.
- Complement Pathways: Alternate and mannose-binding pathways that enhance the immune response.
- Fever and Inflammatory Responses: Systemic reactions to infection that help contain and eliminate pathogens.
- Normal Resident Flora: Beneficial microorganisms that occupy niches and prevent pathogen colonization.
- Cytokines: Signaling proteins such as TNF, interleukins, and interferons that regulate immune responses.
- Acute Phase Reactant Proteins (APRs): Proteins that increase in response to inflammation and infection.
Components of Acquired Immunity
- Classical Complement Pathway: part of the immune system that enhances the ability to clear pathogens.
- Antigen Presenting Cells: Cells that process and present antigens to T cells, initiating an immune response.
- Cytokines: Signaling molecules like IL-2, IL-4, IL-5, and IFN-γ that regulate immune responses.
Types of Acquired Immunity
Acquired immunity can be classified in two ways:
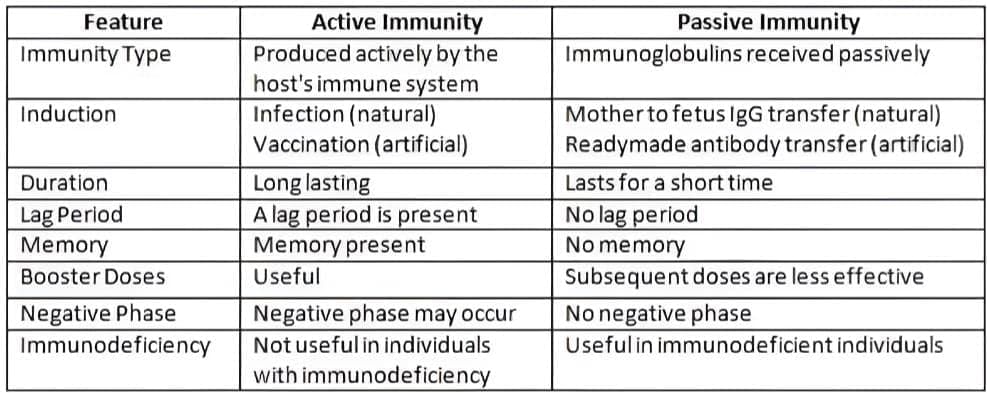
- Active and Passive Immunity: Active immunity involves the development of antibodies in response to an antigen, while passive immunity involves the transfer of antibodies from one individual to another.
- Artificial and Natural Immunity: Artificial immunity is induced through medical interventions, such as vaccinations, while natural immunity occurs through natural exposure to pathogens.
Factors Affecting Innate Immunity
- Innate immunity is influenced by various factors, including species, race, and individual genetic makeup.
- Other important factors include age, hormonal influences, and nutrition.
Toll-Like Receptors (TLRs)
TLRs are named after the Toll receptors found in the fruit fly Drosophila , which play a crucial role in initiating innate immunity by recognizing specific Microbial Associated Molecular Patterns (MAMPs) on microbes.
There are 13 types of TLRs, each with a specific function:
- TLR-2: Recognizes bacterial peptidoglycan.
- TLR-3: Recognizes double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) from viruses.
- TLR-4: Recognizes lipopolysaccharides (LPS) from Gram-negative bacteria.
- TLR-5: Recognizes bacterial flagella.
- TLR-7 and TLR-8: Recognize single-stranded RNA (ssRNA) from viruses.
- TLR-9: Recognizes bacterial DNA.
Acute Phase Reactant Proteins (APRs)
- APRs are proteins produced by the liver, typically at stable levels, but their production can significantly increase during acute inflammation.
- While the liver is the primary source of APRs, they can also be produced by other cells such as:
- Endothelial cells
- Fibroblasts
- Monocytes
- Adipocytes
- Positive APRs increase during inflammation and include:
- Serum Amyloid A
- C-Reactive protein
- Complement proteins (e.g., C1–C9, factor B, D, properdin)
- Coagulation proteins (e.g., fibrinogen, von Willebrand factor)
- Proteinase inhibitors (e.g., α1 antitrypsin)
- α1 acid glycoprotein
- Mannose binding protein
- Haptoglobin
- Metal binding proteins (e.g., ceruloplasmin)
- Negative APRs decrease during inflammation, signaling the liver to produce more positive APRs. Examples include:
- Albumin
- Transferrin
- Antithrombin
- APRs play various roles in defending the body, such as:
- Exhibiting antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory properties (e.g., complement)
- Metal binding proteins sequester metals like iron and copper, limiting their availability to bacteria
C-Reactive Protein (CRP)
CRP is a type of acute phase reactant that increases during sudden inflammatory conditions, especially when caused by bacterial infections. It is part of the beta globulin family.
- CRP gets its name because it reacts with the C-carbohydrate (a type of polysaccharide) found in Pneumococcus. However, it is important to note that it is not an antibody specific to this C-carbohydrate. Instead, it is a general marker that can increase in any inflammatory condition.
- It is one of the most common markers for acute inflammation and is widely used in diagnostic laboratories.
CRP Level
The normal level of CRP is less than 0.2 mg/dl. However, this level can rise significantly during acute inflammatory situations.
- Insignificant increase of CRP (< 1 mg/dl): Occurs in conditions such as heavy exercise, common cold, and pregnancy.
- Moderate increase (1–10 mg/dl): This level can be seen in conditions such as bronchitis, cystitis, certain cancers, pancreatitis, and myocardial infarction.
- Marked increase (> 10 mg/dl): This level often occurs in serious situations like acute bacterial infections, major trauma, and systemic vasculitis.
Methods for Detecting CRP
- Precipitation method using C-carbohydrate antigen (this method is now outdated and not commonly used).
- Latex agglutination test: This test uses latex particles that are coated with anti-CRP antibodies.
- It is the most widely used method around the world.
- The detection limit for CRP using the latex agglutination test is 0.6 mg/dl.
- Highly sensitive CRP (hs-CRP) test: This method can detect very small amounts of CRP using various techniques such as nephelometry and enzyme immunoassays. It is helpful in evaluating the risk of cardiovascular diseases.
Acquired or Adaptive Immunity
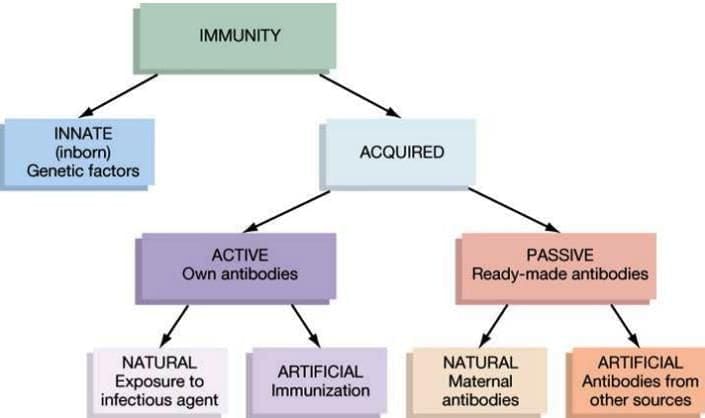
Acquired immunity is the body’s ability to resist foreign substances that it develops or adjusts to throughout life.
There are two main types of immunity: active and passive.
- Active immunity can be further divided into:
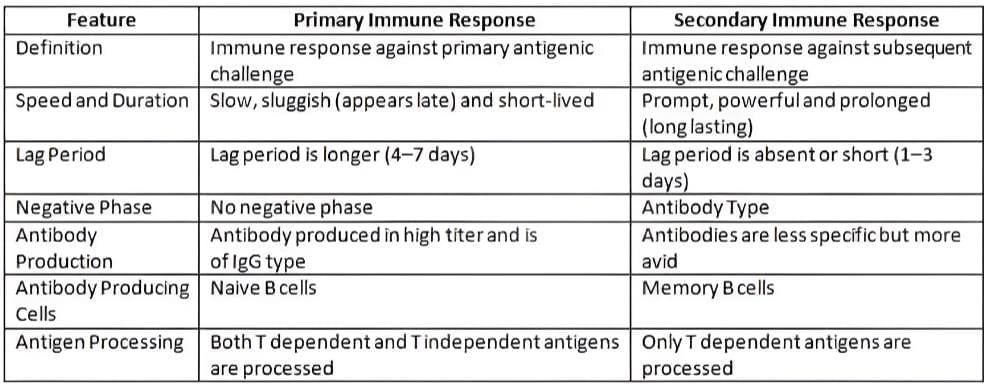
- Primary immune response (develops after the first exposure to a microbe)
- Secondary immune response (develops after later exposures to the same microbe)
Differences between Active and Passive Immunity
Differences between Primary and Secondary Immune Response
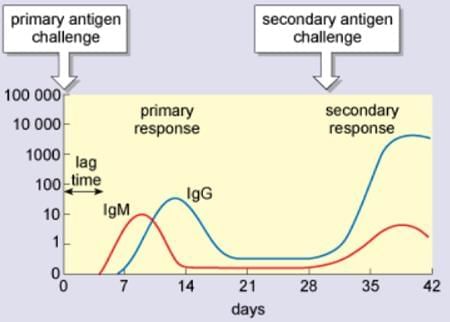
Different Types of Immunity
1. Local (or Mucosal) Immunity
- Local or mucosal immunity refers to the immune response that operates at mucosal surfaces in the body.
- This type of immunity is primarily driven by a specific antibody called secretory IgA.
- Mucosal immunity can be triggered by natural infections or through live vaccinations.
- It is active in areas such as the intestines, respiratory system, and genitourinary tract, where it plays a crucial role in protecting against pathogens.
- Local immunity is typically mediated by secretory IgA antibodies, which are specialized for mucosal surfaces.
- Importantly, this type of immunity can only be induced by natural infections or live vaccinations, such as the oral polio vaccine (OPV). It cannot be triggered by killed vaccines.
2. Herd Immunity
Herd immunity refers to the overall level of immunity within a community, often called a herd, against a specific pathogen.
Importance of Herd Immunity
- Herd immunity is crucial for stopping the spread of epidemic diseases. When a large portion of the community is immune to a pathogen, the chances of an outbreak are significantly reduced, which may even lead to the complete elimination of the disease.
Factors that Strengthen Herd Immunity
- The presence of both clinical and subclinical cases within the herd contributes to immunity.
- An active immunization program helps build and maintain herd immunity.
- The structure of the herd, which refers to the type of population involved, plays a role in overall immunity.
- The specific type of pathogen is important, as herd immunity might vary against different pathogens.
Vaccines that Promote Herd Immunity
- Diphtheria and Pertussis vaccines
- Measles, Mumps, and Rubella (MMR) vaccine
- Polio (Oral polio vaccine)
- Smallpox vaccine
3. Adoptive Immunity
- Adoptive immunity involves the transfer of cellular immunity (CMI) from one individual to another.
- This process is carried out by injecting immunologically competent T-lymphocytes known as Transfer factor.
- Adoptive immunity is beneficial in situations where CMI levels are low, such as in certain cases of lepromatous leprosy.
|
75 docs|5 tests
|
FAQs on Immunity Chapter Notes - Microbiology - NEET PG
| 1. What are the main differences between innate immunity and acquired (adaptive) immunity? |  |
| 2. How do vaccines contribute to acquired immunity? |  |
| 3. What are some examples of innate immunity mechanisms? |  |
| 4. What role do T cells and B cells play in acquired immunity? |  |
| 5. Can you explain the concept of herd immunity and its relation to acquired immunity? |  |





















