Class 8 Exam > Class 8 Notes > General Science Class 8 (Maharashtra Board) > Chapter Notes: Living World and Classification of Microbes
Living World and Classification of Microbes Chapter Notes | General Science Class 8 (Maharashtra Board) PDF Download
Types of Microorganism
Microorganisms Introduction
- Microorganisms, or microbes, are tiny living organisms that include bacteria, viruses, fungi, and the microbes found in yoghurt. These organisms are usually too small to be seen without a microscope.
- They are termed 'micro' due to their very small size.
- Microorganisms are unicellular, meaning they consist of a single cell. They carry out essential life processes and are a fundamental part of ecosystems.
- Microbes are vital in nutrient cycling, decomposition, and as part of the human microbiome.
 Microorganisms
Microorganisms
Fungi
- Fungi are not plants; they do not photosynthesize but instead absorb nutrients from organic materials.
- Fungi can be multicellular (like mushrooms) or unicellular (like yeasts). Moulds, a type of fungi, grow by reproducing through spores, which are capable of traveling through air and growing on new sources.
- Some fungi are beneficial and used in cooking, while others, like certain moulds, can produce toxins and are hazardous.
Bacteria

- Bacteria are unicellular organisms that can reproduce quickly. They can be found in every environment on Earth.
- Bacterial structure is simple, yet they are involved in both beneficial processes (like digestion and fermentation) and pathogenic activities.
Viruses
- Viruses are not cells but are tiny particles that infect living cells.
- Viruses must enter into a living cell to replicate (copy) themselves.
- Viruses can infect all types of life forms, from plants and animals to bacteria.
Microorganisms and Decay
History and Discovery of Microorganisms
- Antonie van Leeuwenhoek first observed microorganisms in 1674.
- Initial scientific belief was that microorganisms spontaneously generated from the materials they were found in, such as bread creating mold.
Louis Pasteur's Experiments
- Louis Pasteur, a French scientist in the 19th century, questioned why clear soup would turn cloudy and start to smell when left open.
- He hypothesized that microorganisms in the air were responsible for spoiling food.
- Pasteur's experiments involved boiling soup in glass containers to kill any existing microorganisms and then allowing air to contact some of the soup while keeping other samples isolated. Only the soup exposed to air spoiled, supporting his hypothesis.
Scientific Method
- Involves asking questions, formulating hypotheses, and conducting experiments to test these hypotheses.
- A hypothesis must be testable, meaning experiments can be conducted to prove it right or wrong.
- The results from these experiments provide evidence to support or reject the hypothesis.
Decay
- Decomposers like bacteria and fungi cause decay/breakdown of materials.
- They also play a role in recycling nutrients from dead matter back into the soil.
Food Chain
- A food chain is a diagram showing feeding relationships in a habitat

- It consists of producers (organisms that make their own food, like plants using sunlight) and consumers (animals that eat producers).
- Consumers can be classified as:
- Herbivores: Animals that eat only plants (primary consumers)
- Carnivores: Animals that eat other animals (secondary/tertiary consumers)
- Omnivores: Animals that can eat plants or animals
- Predators: Animals that hunt and eat other animals
- Prey: Animals that are hunted and eaten by other animals
Food Web
A food web is a diagram that shows how different food chains all interact in a habitat.
For example :
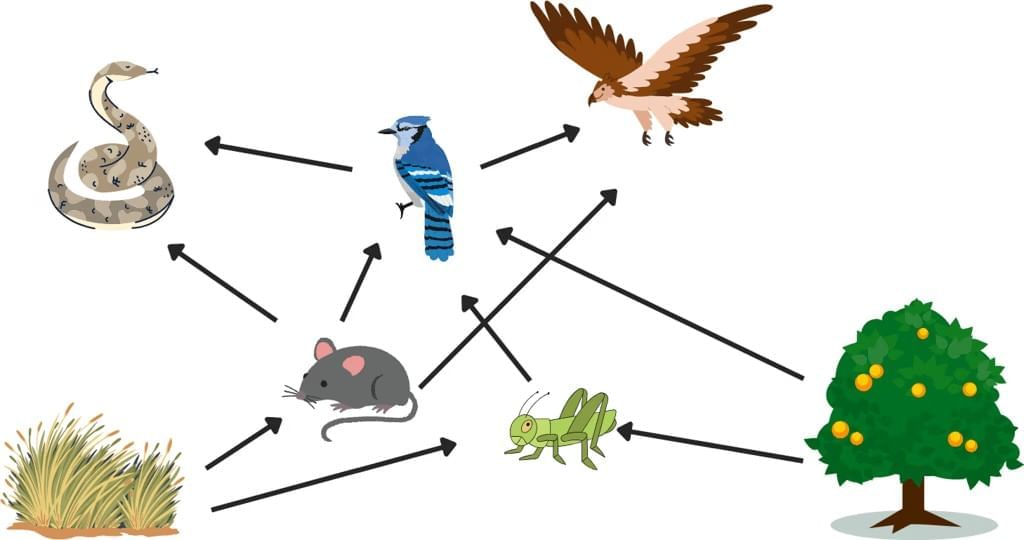 Food Web
Food Web
Energy Flow in Ecosystems
- Energy flows from producers to various levels of consumers. Not all energy consumed by one level is transferred to the next; some is lost a through respiration, waste, and organism death.
- Decomposers ensure that no energy is wasted by breaking down dead matter and recycling it into the ecosystem.
The document Living World and Classification of Microbes Chapter Notes | General Science Class 8 (Maharashtra Board) is a part of the Class 8 Course General Science Class 8 (Maharashtra Board).
All you need of Class 8 at this link: Class 8
|
52 videos|175 docs|32 tests
|
FAQs on Living World and Classification of Microbes Chapter Notes - General Science Class 8 (Maharashtra Board)
| 1. What are the main types of microorganisms? |  |
Ans. The main types of microorganisms include bacteria, viruses, fungi, protozoa, and algae. Each type has distinct characteristics and roles in the environment. Bacteria are single-celled organisms that can be beneficial or harmful. Viruses are much smaller and require a host to reproduce. Fungi, such as molds and yeast, play a crucial role in decomposition. Protozoa are single-celled organisms that can be found in water or soil, and algae are plant-like organisms that can perform photosynthesis.
| 2. How do microorganisms contribute to decay? |  |
Ans. Microorganisms play a vital role in the process of decay by breaking down dead organic matter. Bacteria and fungi decompose plant and animal remains, converting them into simpler substances. This process not only recycles nutrients back into the soil but also helps maintain ecosystem balance. Without microorganisms, organic waste would accumulate, and essential nutrients would remain locked in dead material, unavailable to living organisms.
| 3. What are the beneficial roles of microorganisms? |  |
Ans. Microorganisms have several beneficial roles, including aiding in digestion, producing antibiotics, and contributing to nutrient cycling in ecosystems. For instance, certain bacteria in the human gut help digest food and synthesize vitamins. Additionally, fungi are used in the production of antibiotics like penicillin, which combat bacterial infections. Microorganisms also help decompose organic matter, enriching the soil and supporting plant growth.
| 4. Can microorganisms be harmful, and if so, how? |  |
Ans. Yes, microorganisms can be harmful and are responsible for various diseases in humans, animals, and plants. Pathogenic bacteria and viruses can cause illnesses such as influenza, tuberculosis, and food poisoning. Fungi can lead to infections like athlete's foot or allergies. Understanding the harmful effects of certain microorganisms is crucial in public health and agriculture to prevent outbreaks and ensure food safety.
| 5. What is the significance of microorganisms in the food industry? |  |
Ans. Microorganisms play a significant role in the food industry by aiding in food preservation, fermentation, and flavor enhancement. For example, yeast is used in baking and brewing, while bacteria are essential in the production of yogurt and cheese. Fermentation processes not only improve the taste and texture of foods but also extend their shelf life by inhibiting the growth of spoilage organisms.
Related Searches















